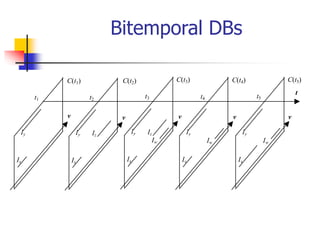
This document discusses temporal databases, which allow querying and maintaining historical data over time. It outlines key aspects of temporal databases including temporal data models that extend relational models with time attributes, temporal query languages, and indexing methods for efficient querying of past database states. The document distinguishes between transaction time databases, which track data changes, and valid time databases that represent time periods for which facts are true, and bitemporal databases that support both notions of time.



![Transaction Time DBs
Queries:
Timestamp (timeslice) queries: ex. “Give me all
employees at 05/94”
Range-timeslice: “Find all employees with id
between 100 and 200 that worked in the
company on 05/94”
Interval (period) queries: “Find all employees
with id in [100,200] from 05/94 to 06/96”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tempdb-230714061432-2c39de31/85/tempDB-ppt-12-320.jpg)