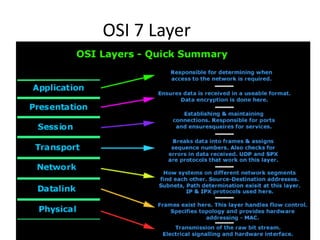
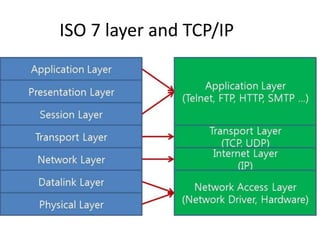
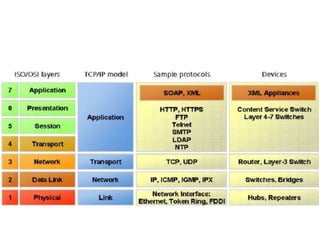
This document discusses the convergence of the Internet and wireless technologies towards an exciting future. It focuses on infrastructure-backed wireless networks and the networking aspects needed to realize this convergence, including high-level service integration, advanced software technologies, high-rate wireless communications, mobility support, and network infrastructure providing service differentiation and secure communications. The document covers topics like the Internet, wireless networking, multimedia over IP, session initiation protocol, mobility management, quality of service, network security, IPv6, and services/applications.