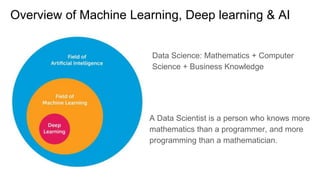
This document provides an overview of machine learning, deep learning, and data science. It discusses the key components of machine learning including supervised and unsupervised learning, as well as reinforcement learning. Deep learning is also introduced. Applications of machine learning discussed include classification algorithms for numbers, generating art using neural style transfer, natural language processing using recurrent neural networks, and detecting objects in images for driverless cars. Generative adversarial networks are also introduced. The document provides resources for learning more about these topics through courses, practice on platforms like Kaggle, and following data scientists on Twitter and blogs.