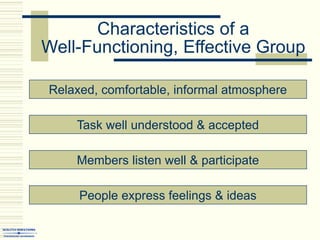
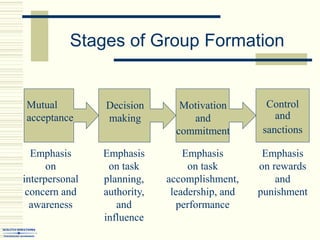
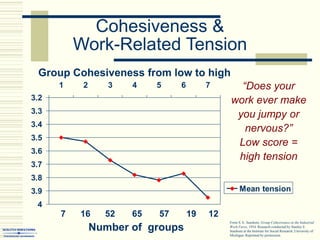
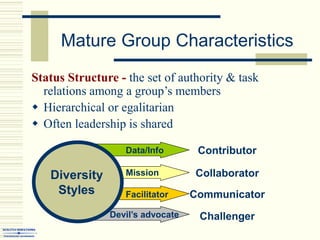
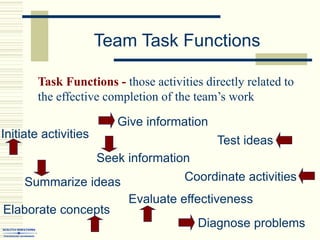
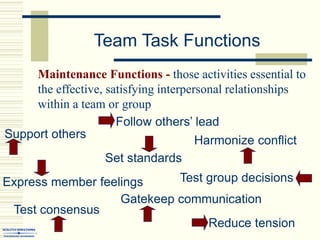
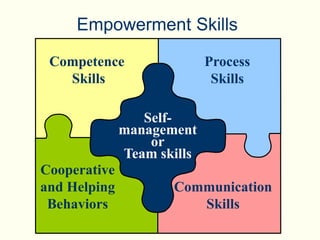
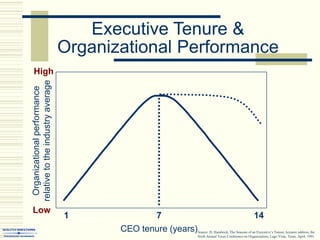
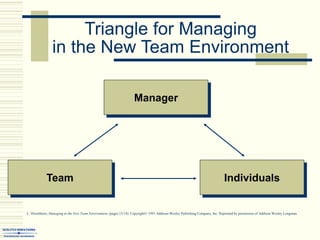
The document summarizes key concepts about work teams and groups. It discusses the characteristics of effective groups, including having a relaxed atmosphere and consensus decision making. It also outlines the stages of group formation from initial mutual acceptance to an emphasis on task accomplishment. Additionally, it describes the functions and benefits of using teams in organizations, such as empowering employees and allowing collaboration. Teams are shown to progress from new to mature forms as they establish norms, cohesion, and status structures.