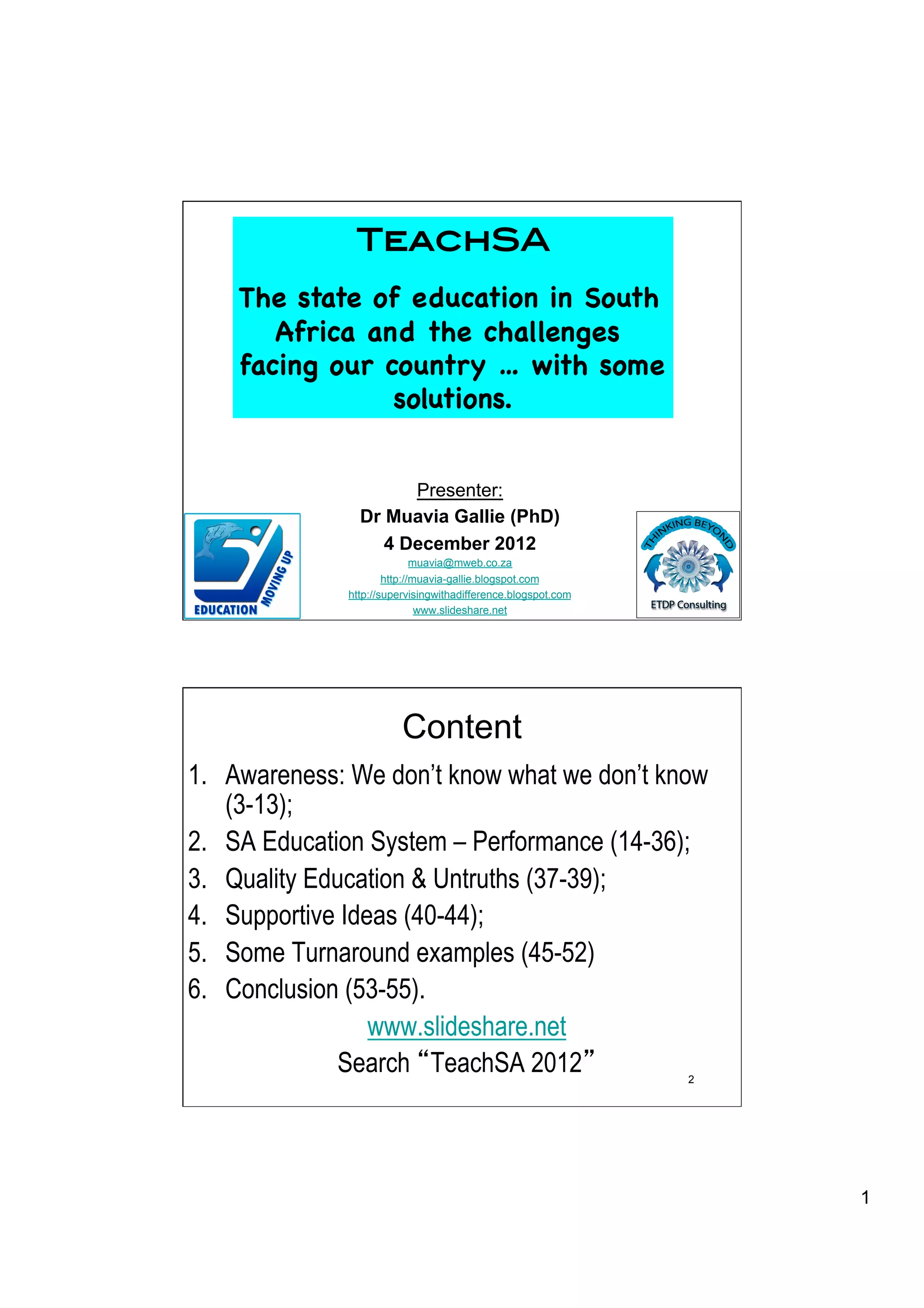
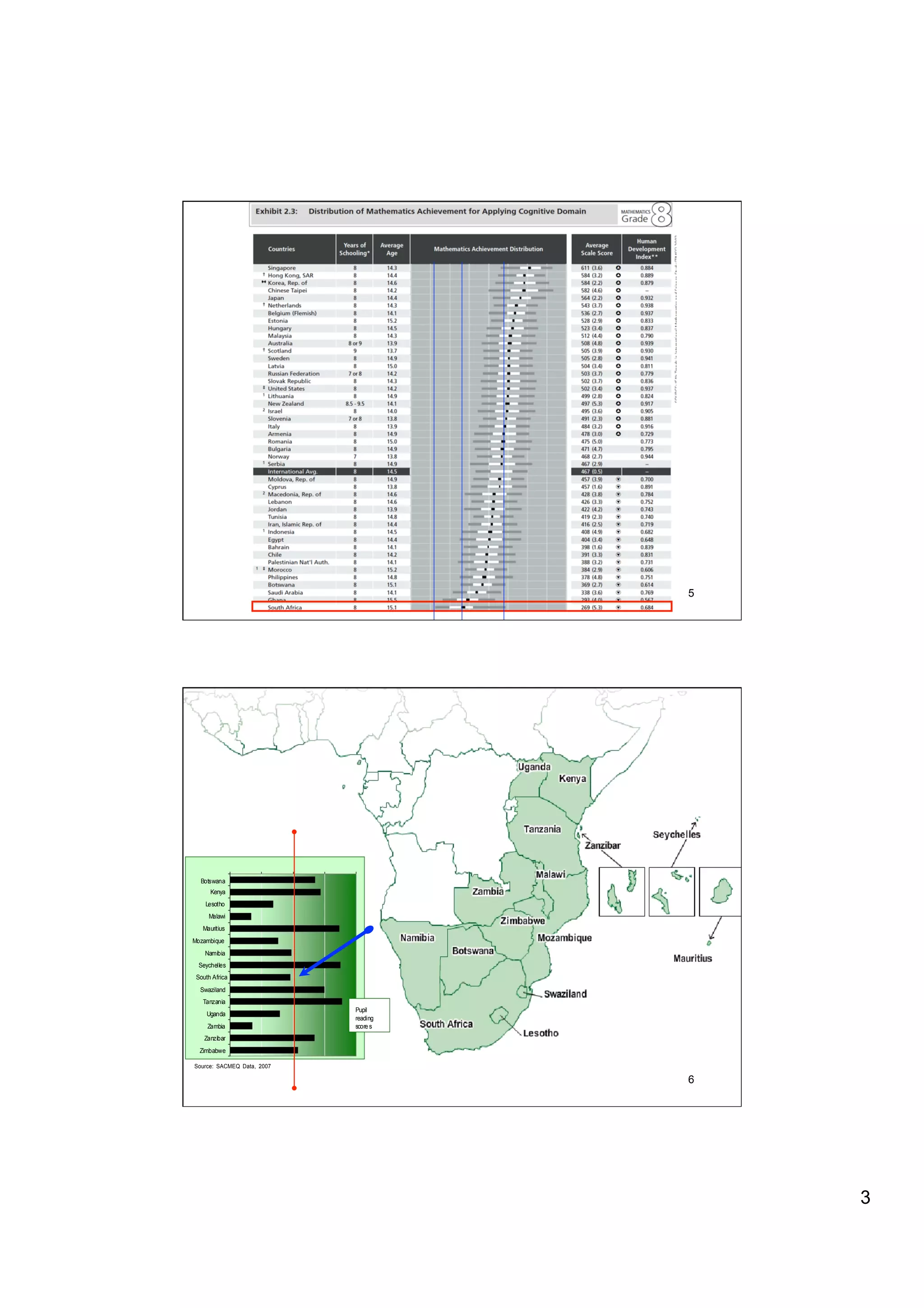
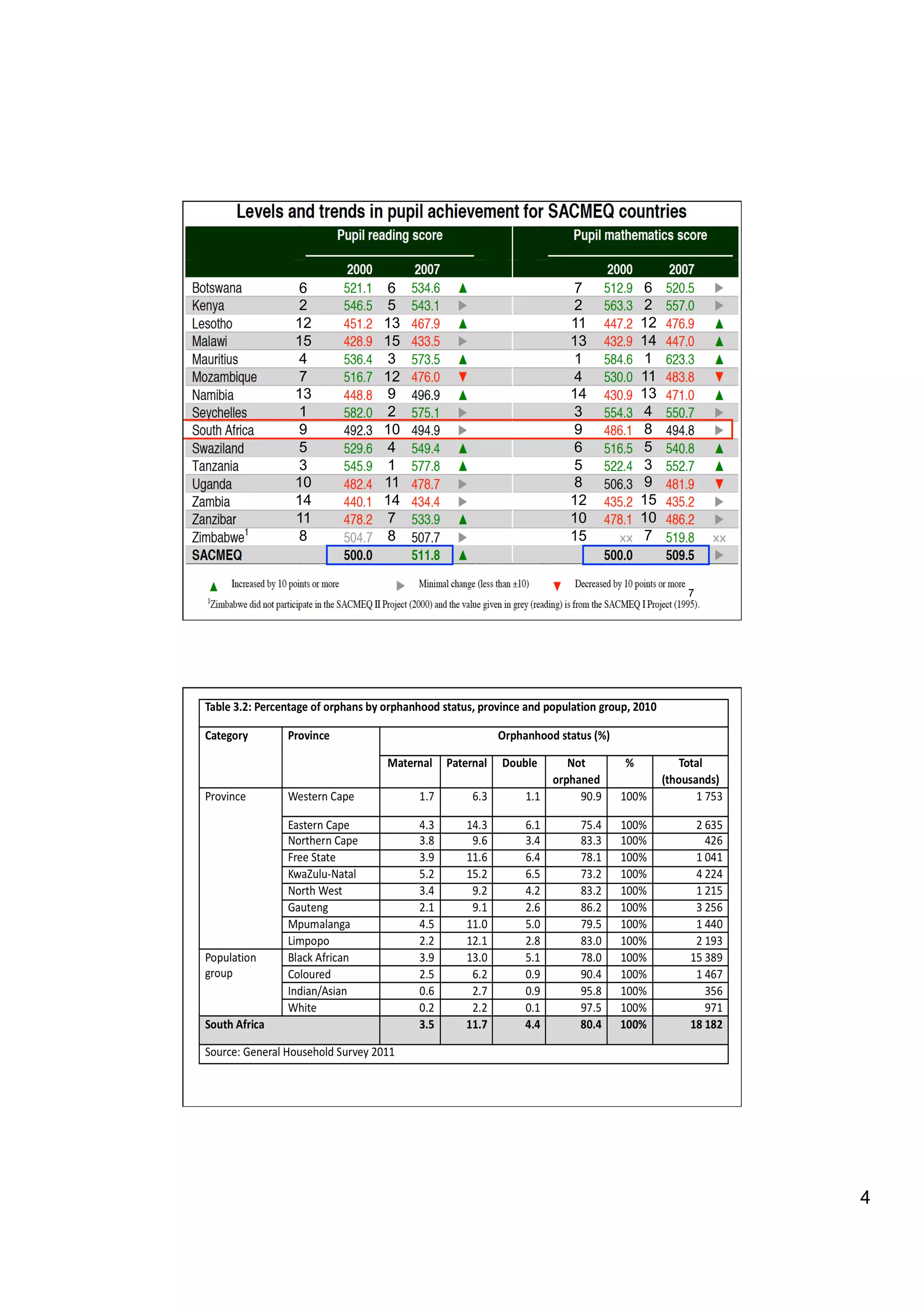
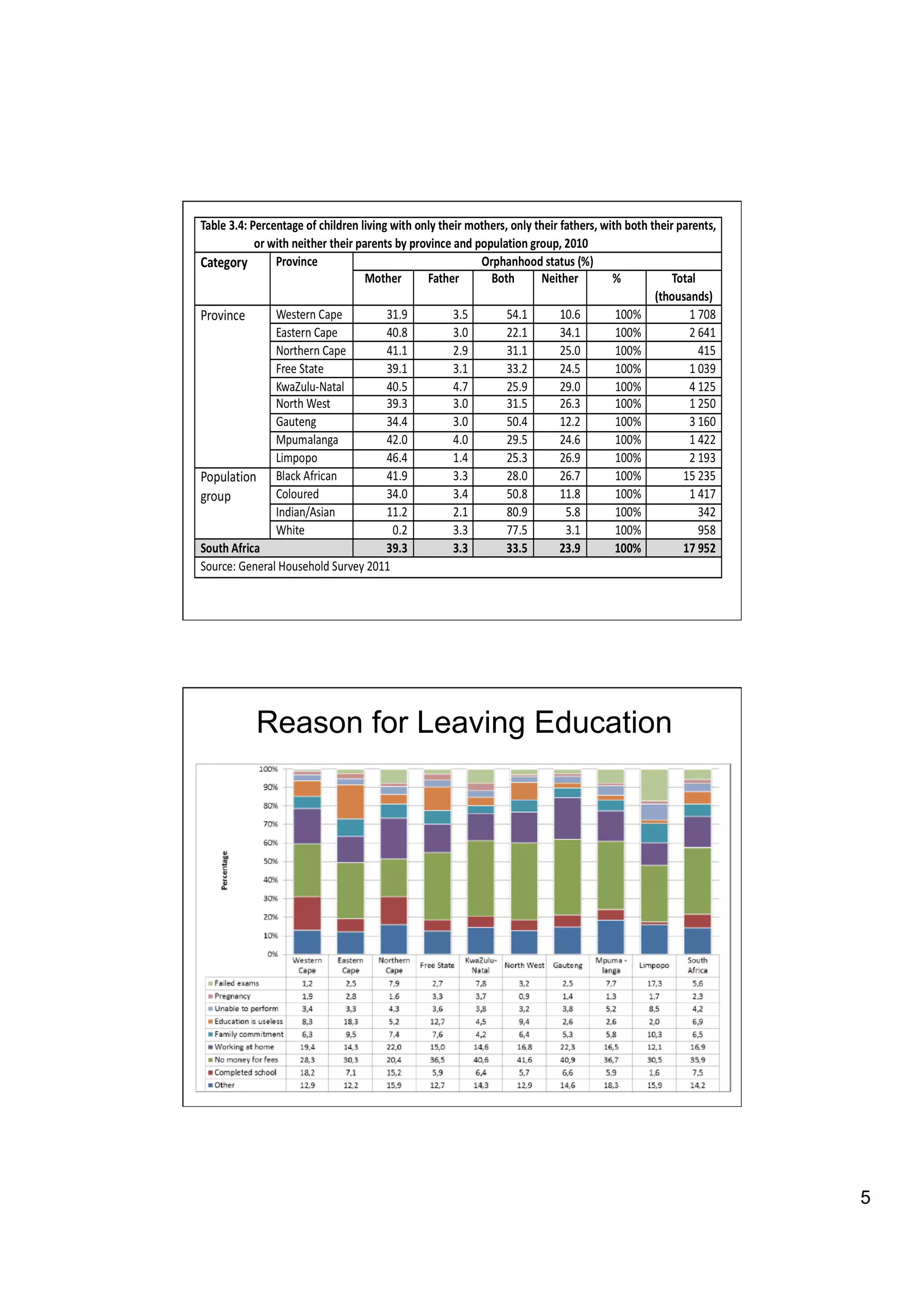
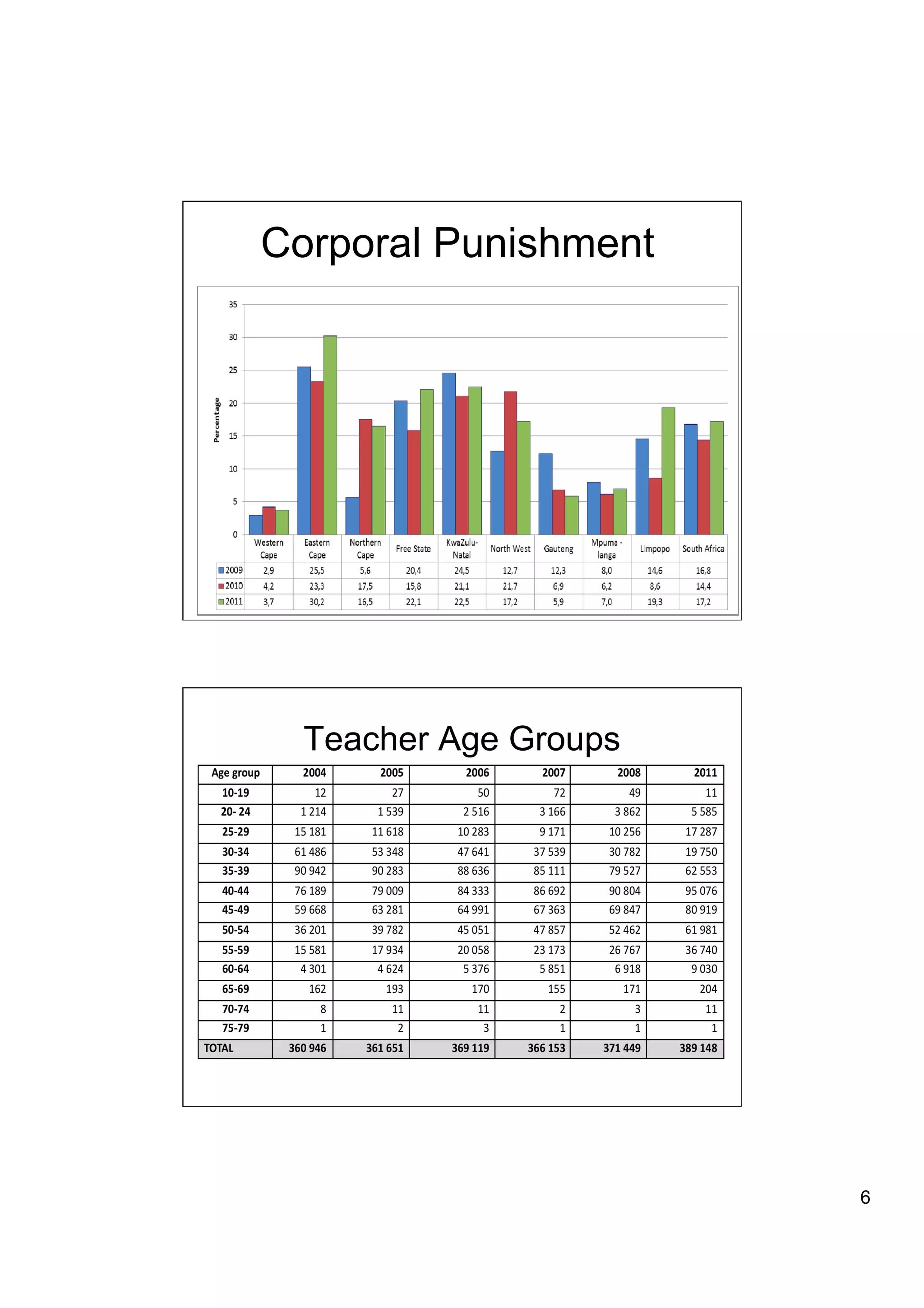
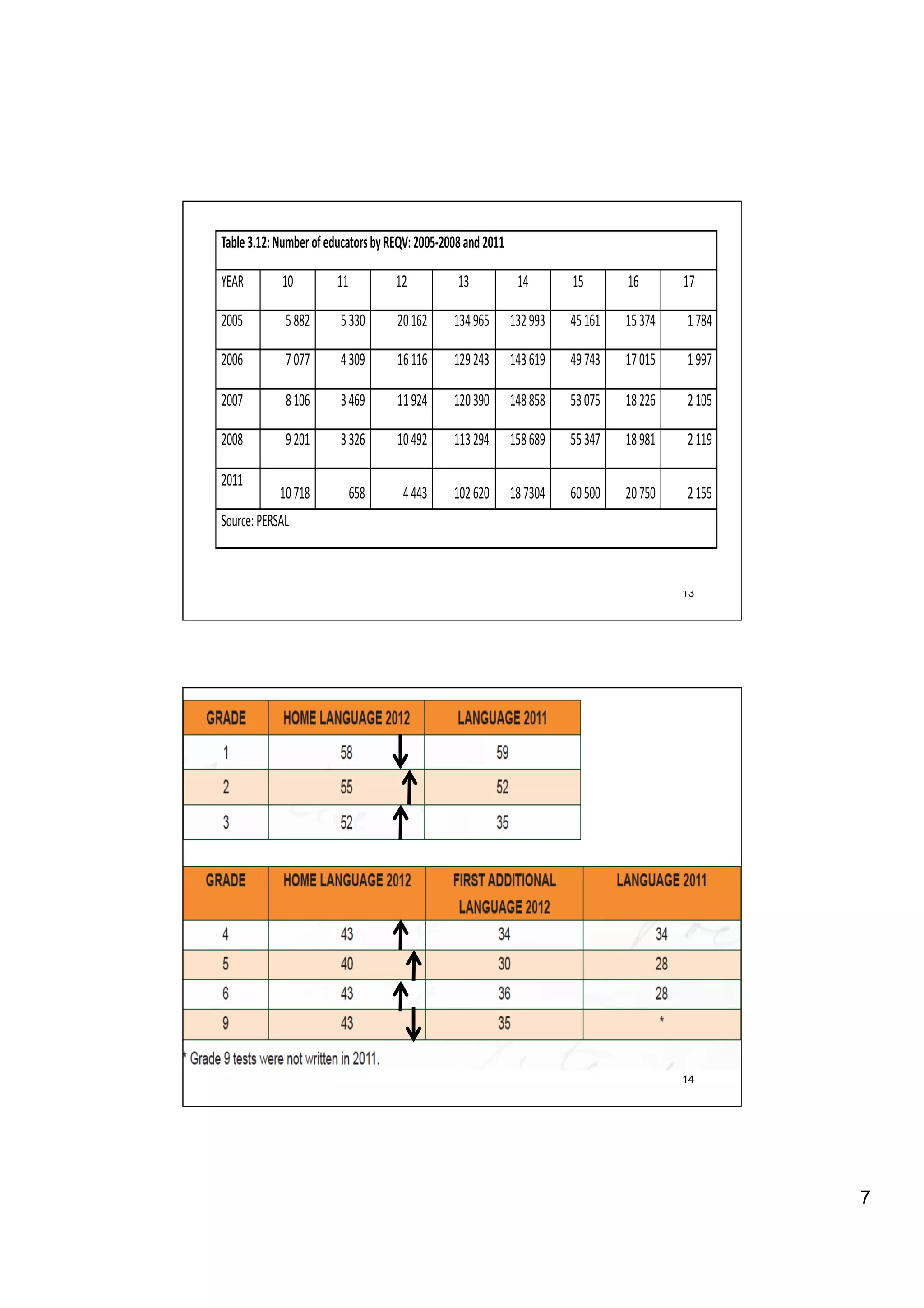
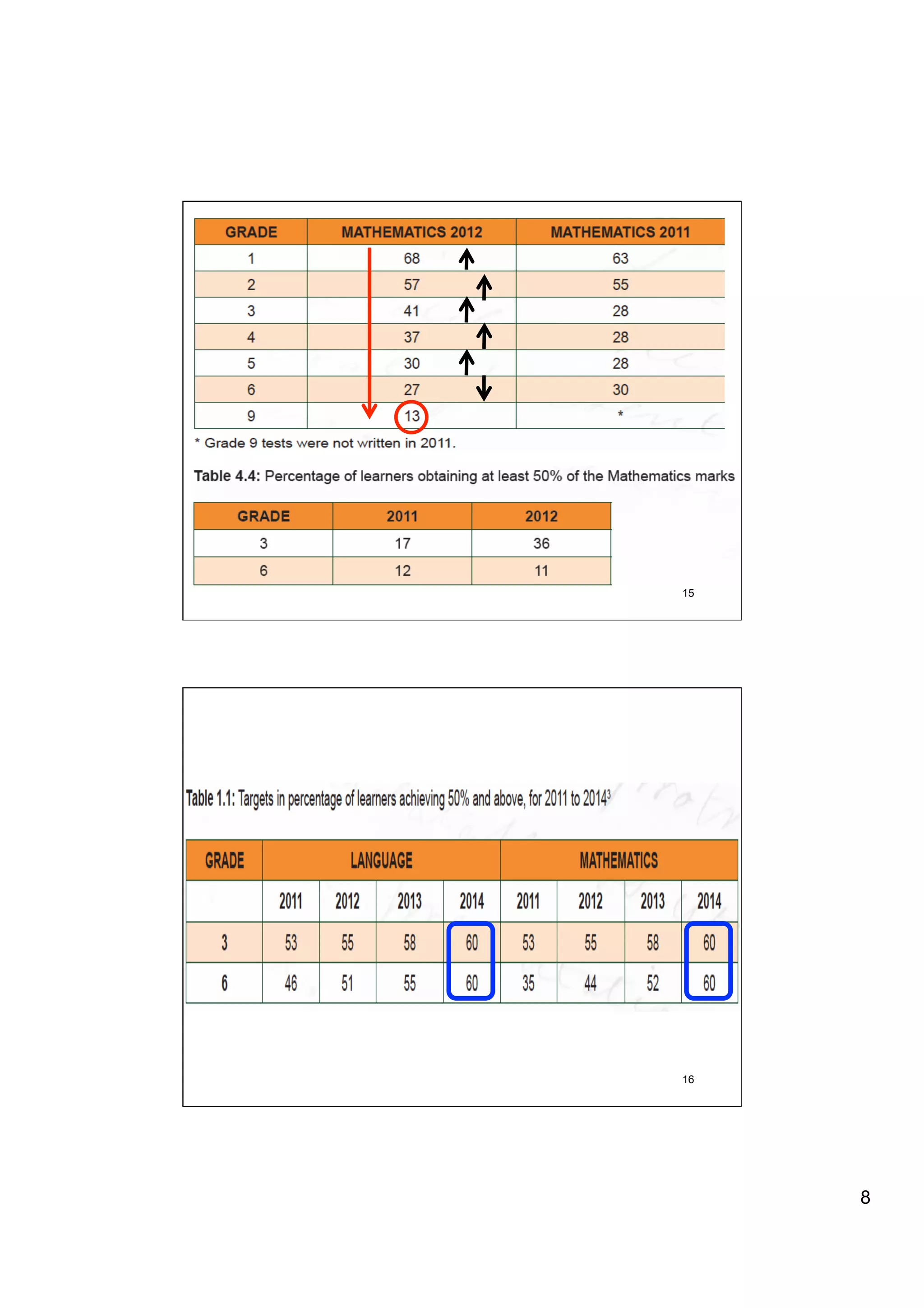
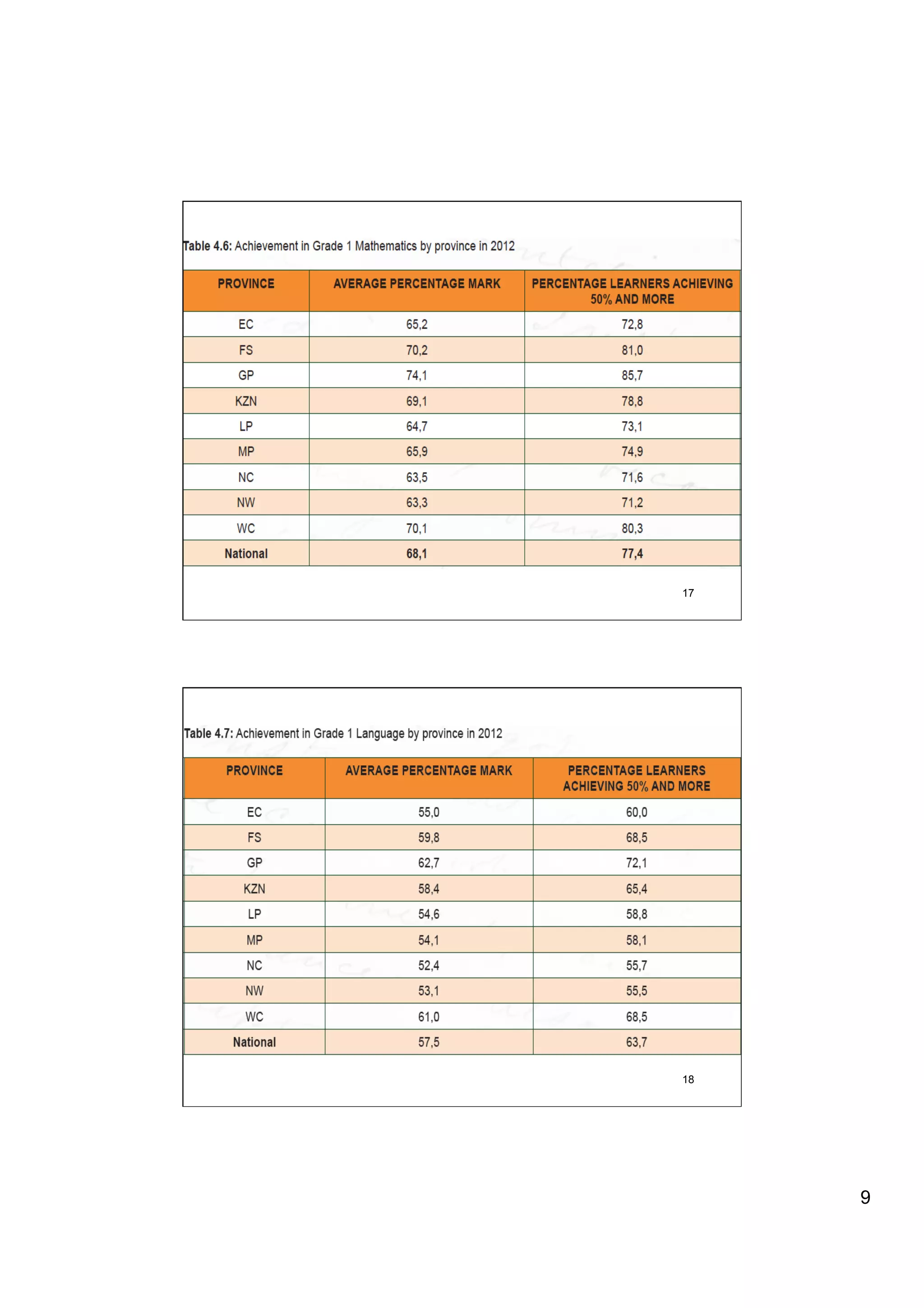
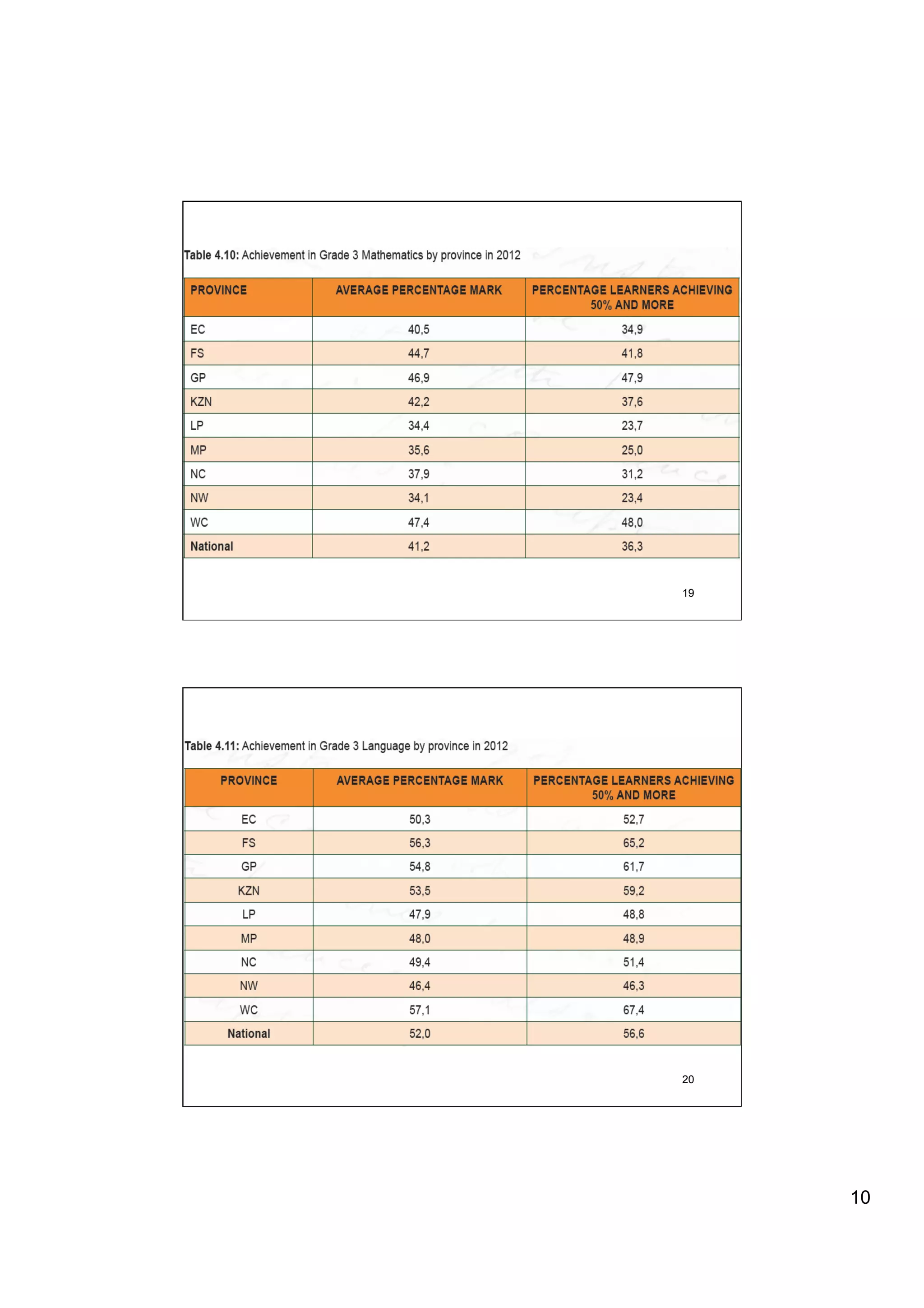
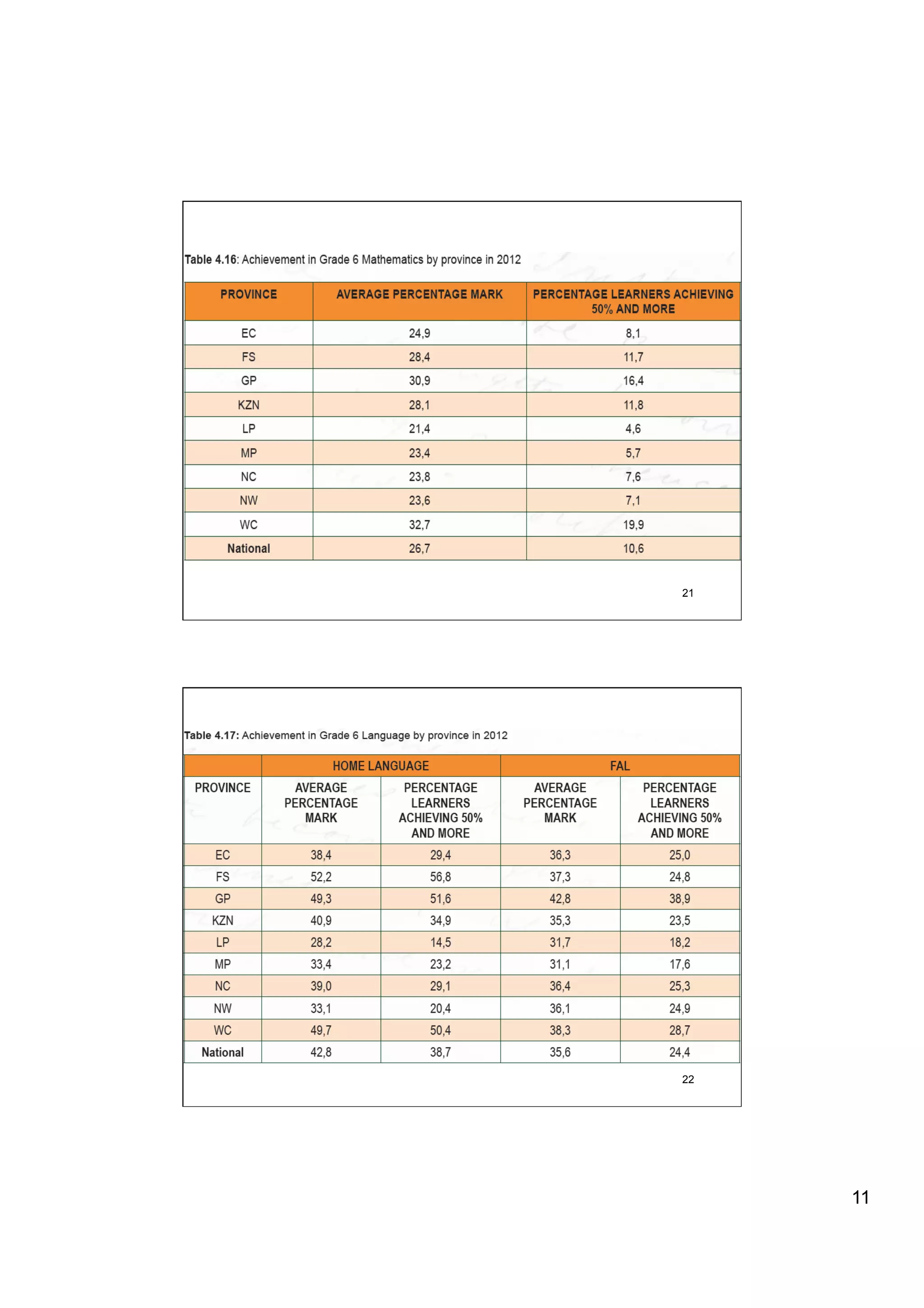
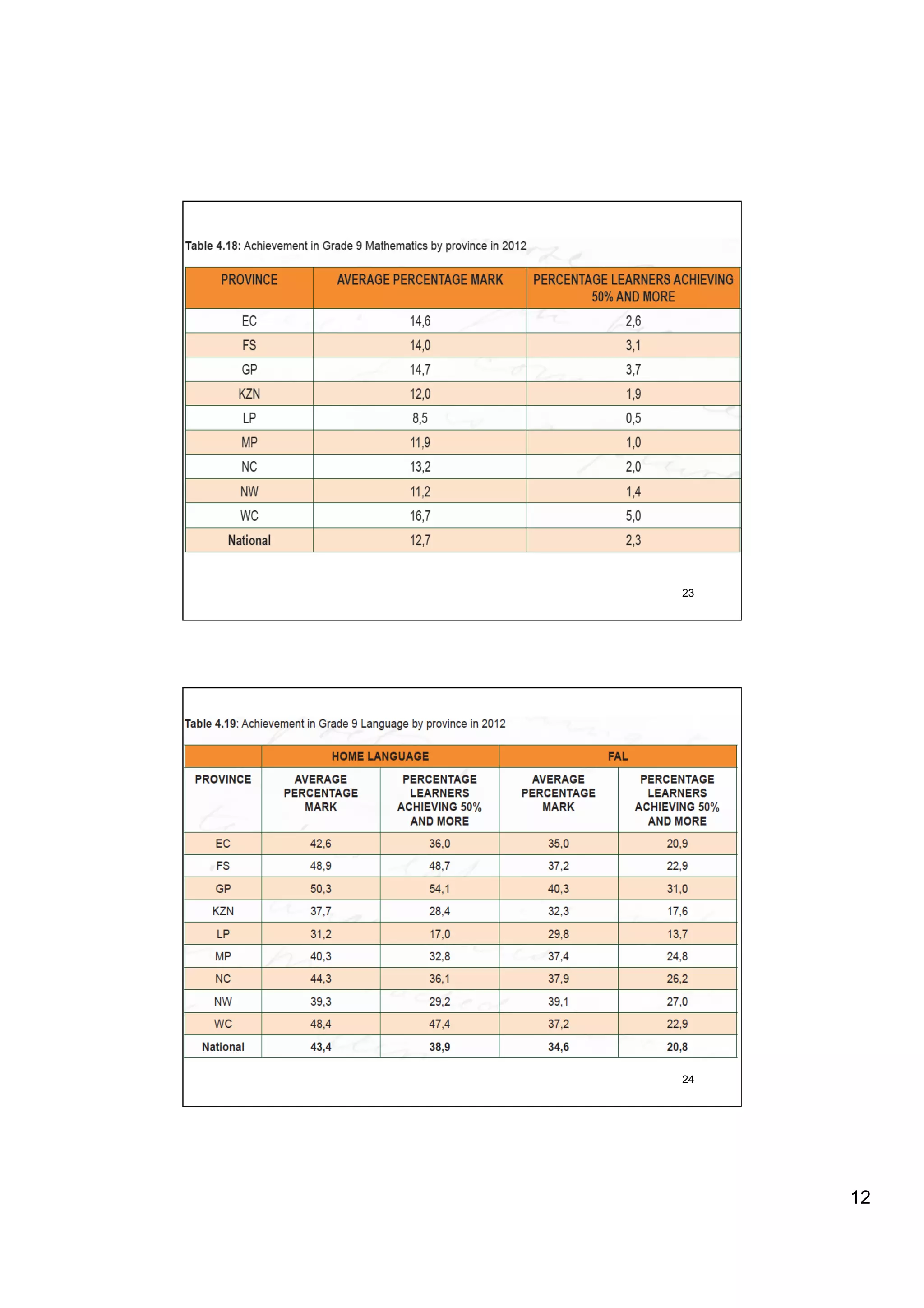
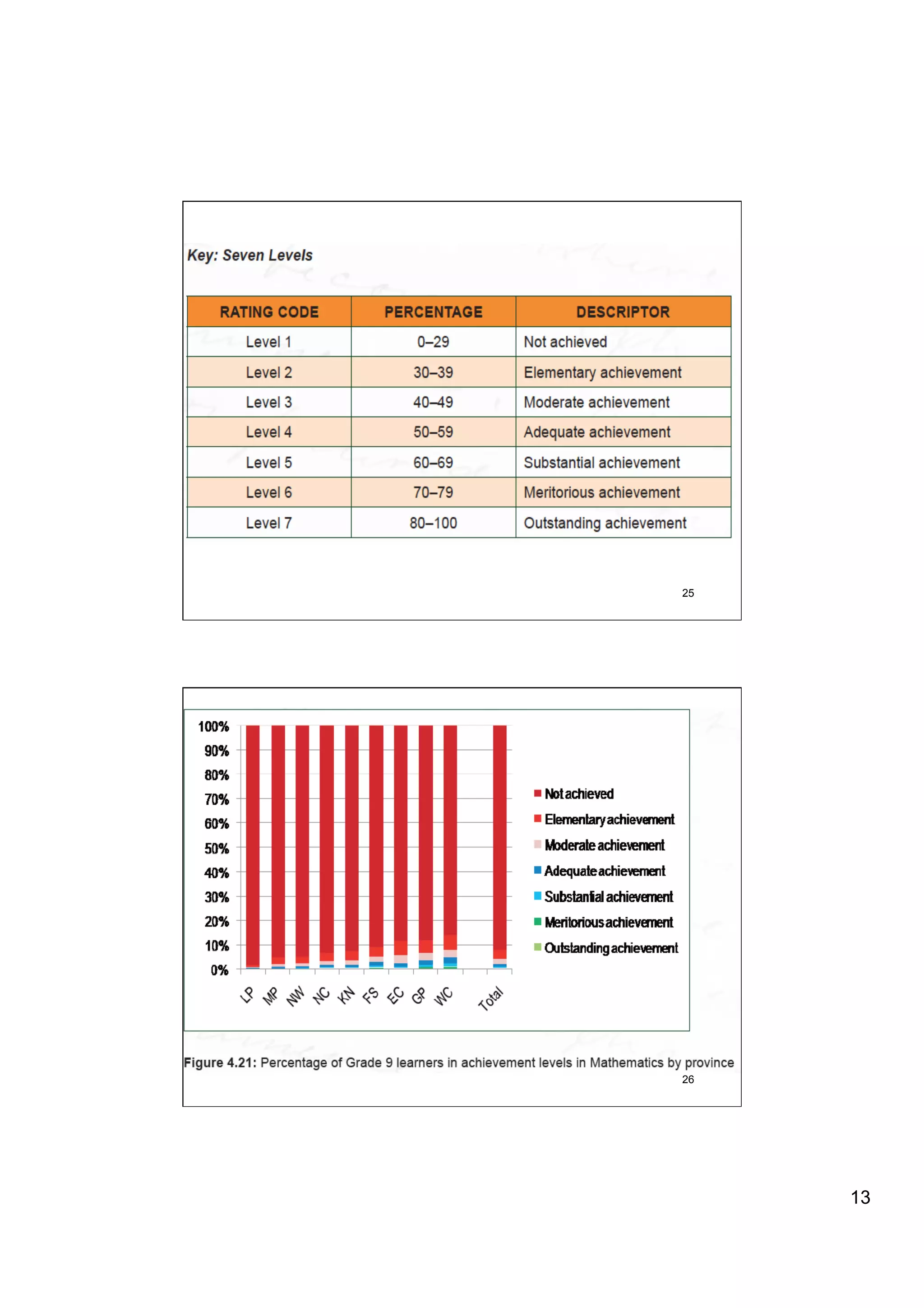
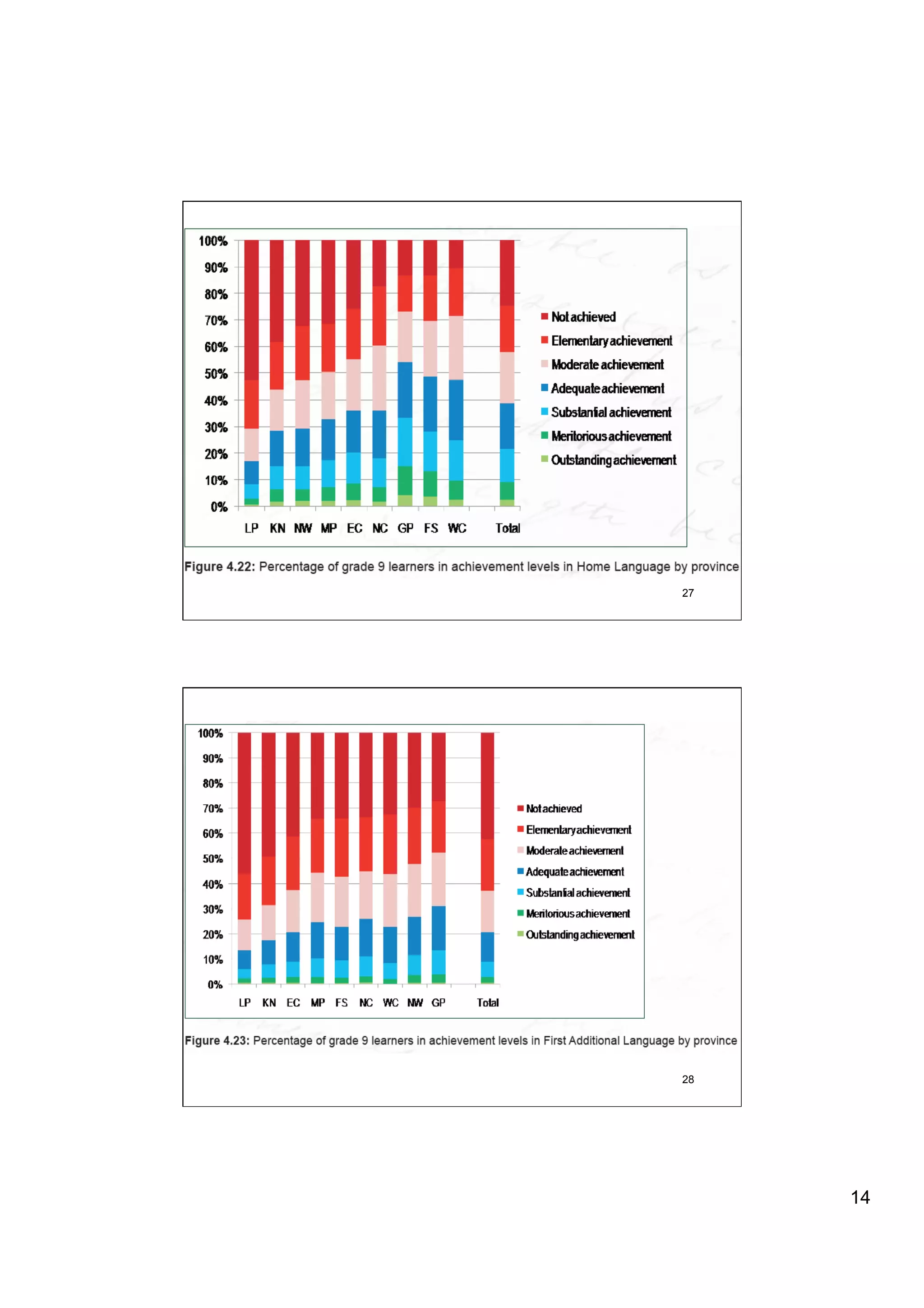
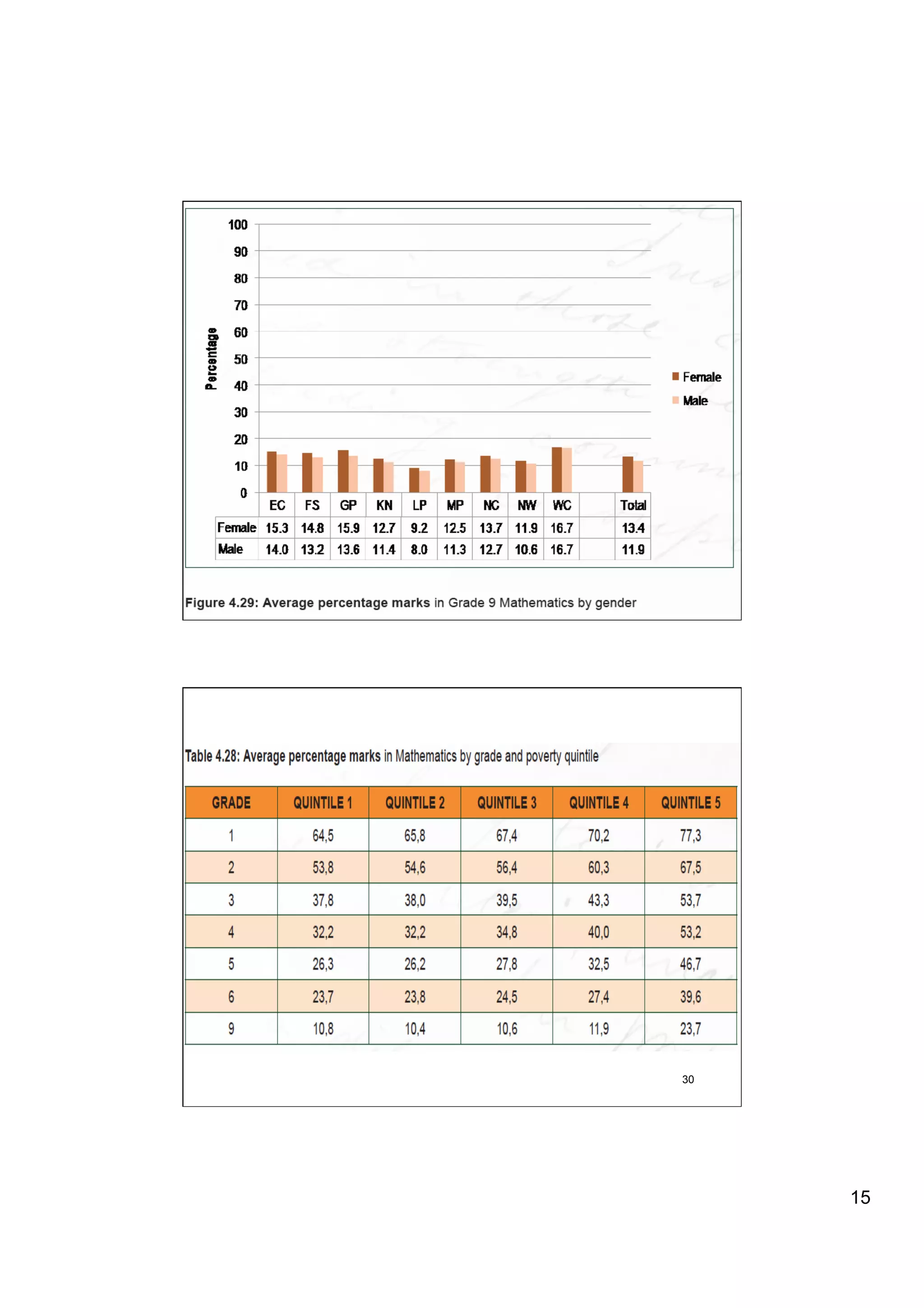
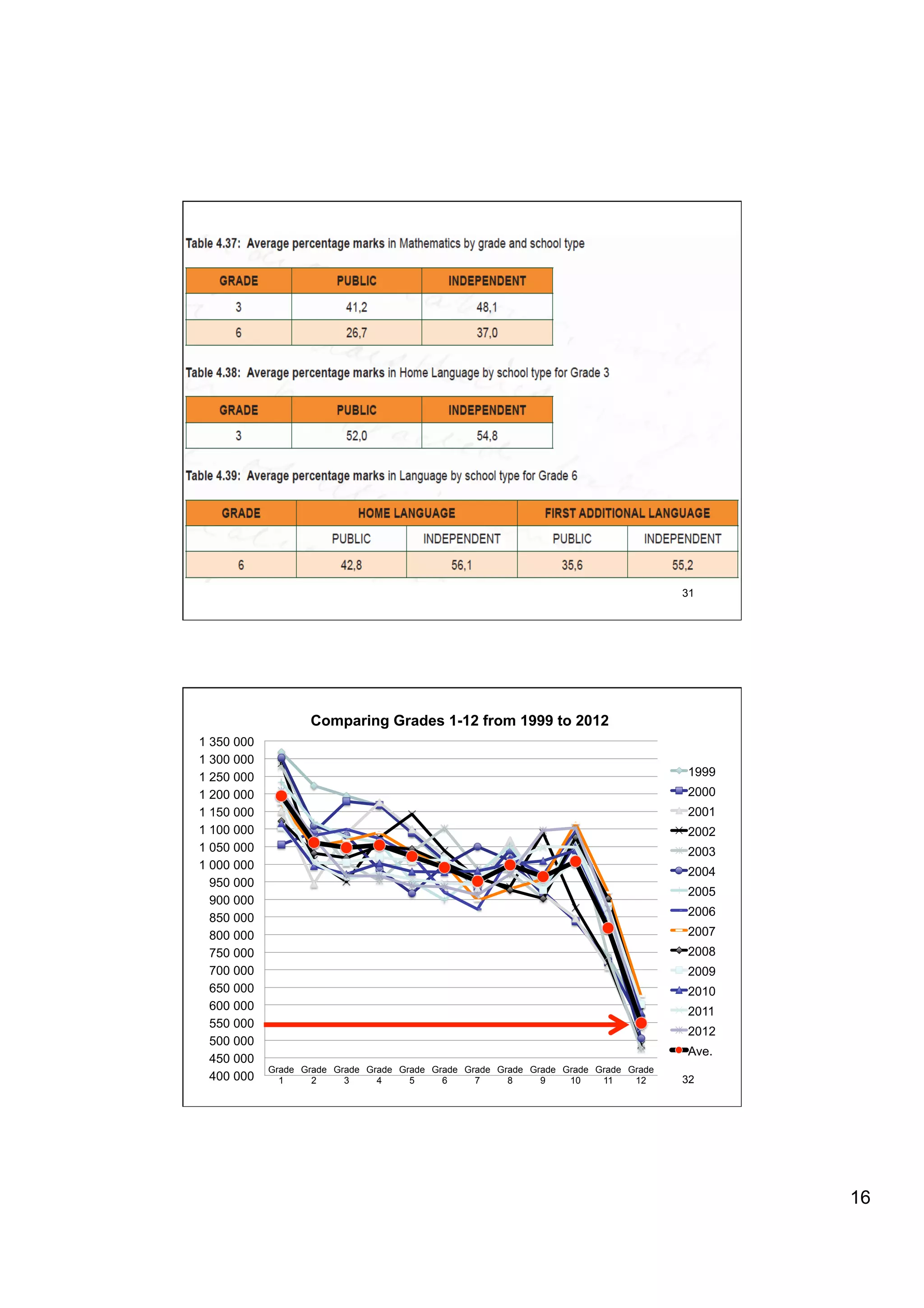
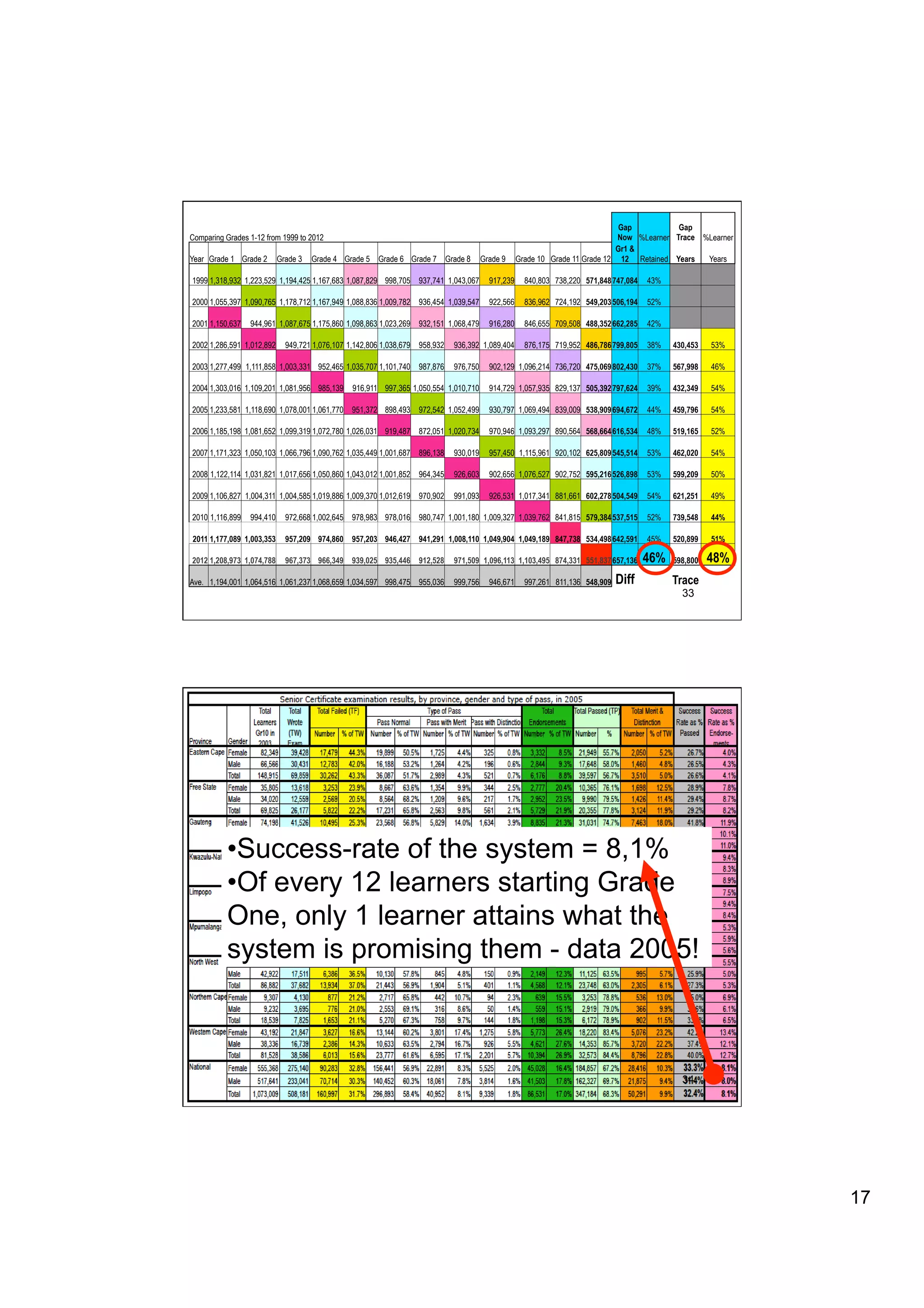
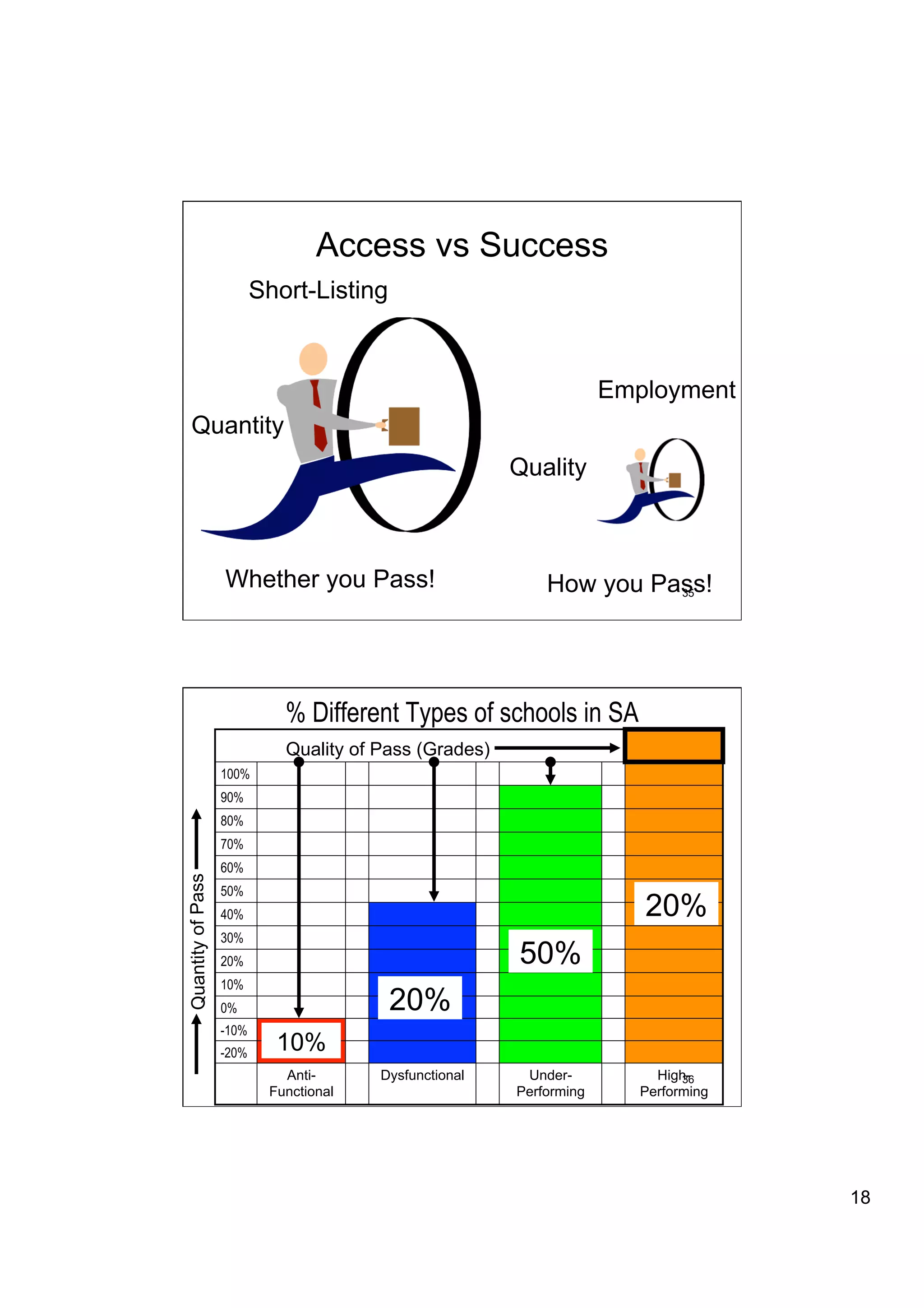
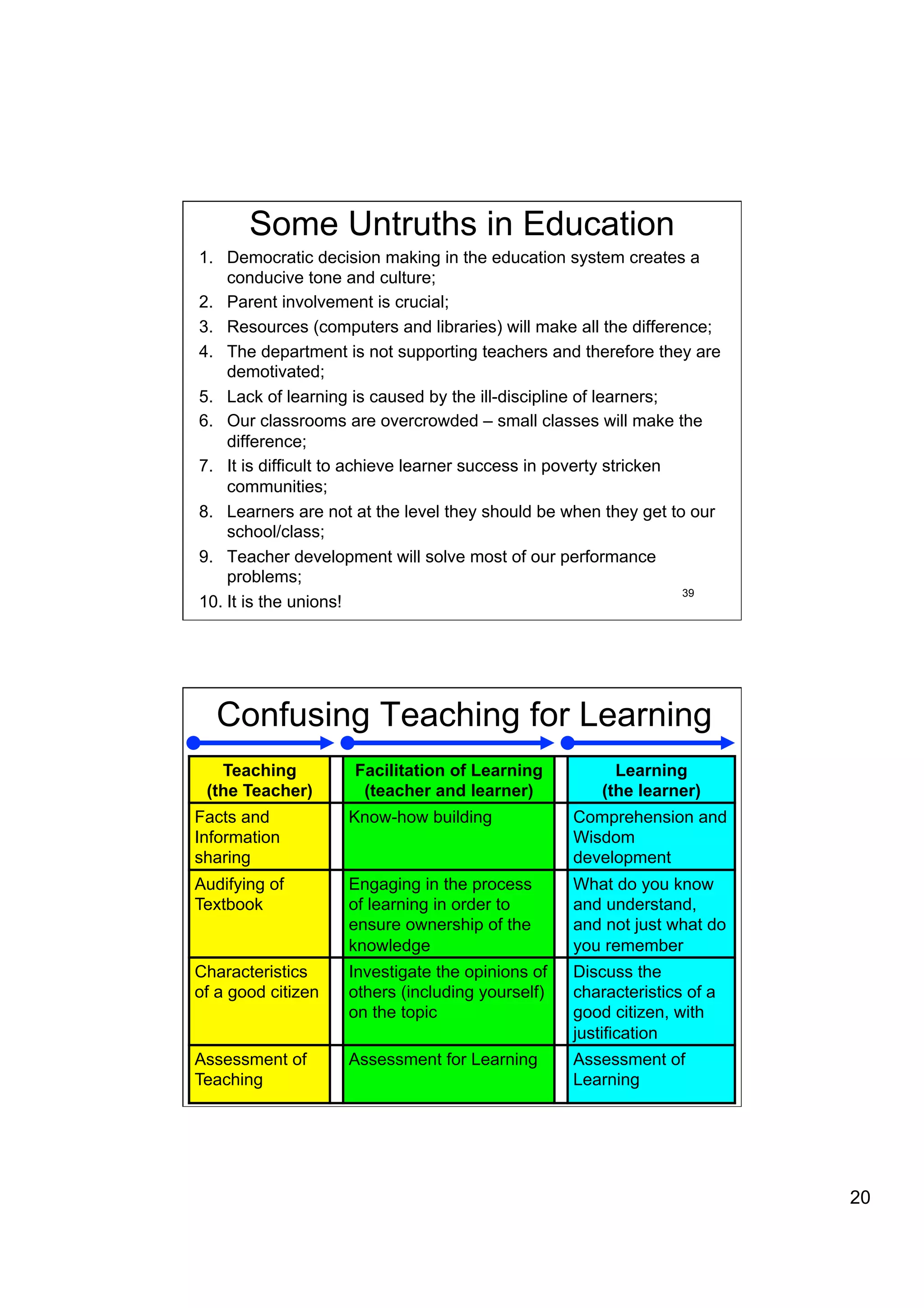
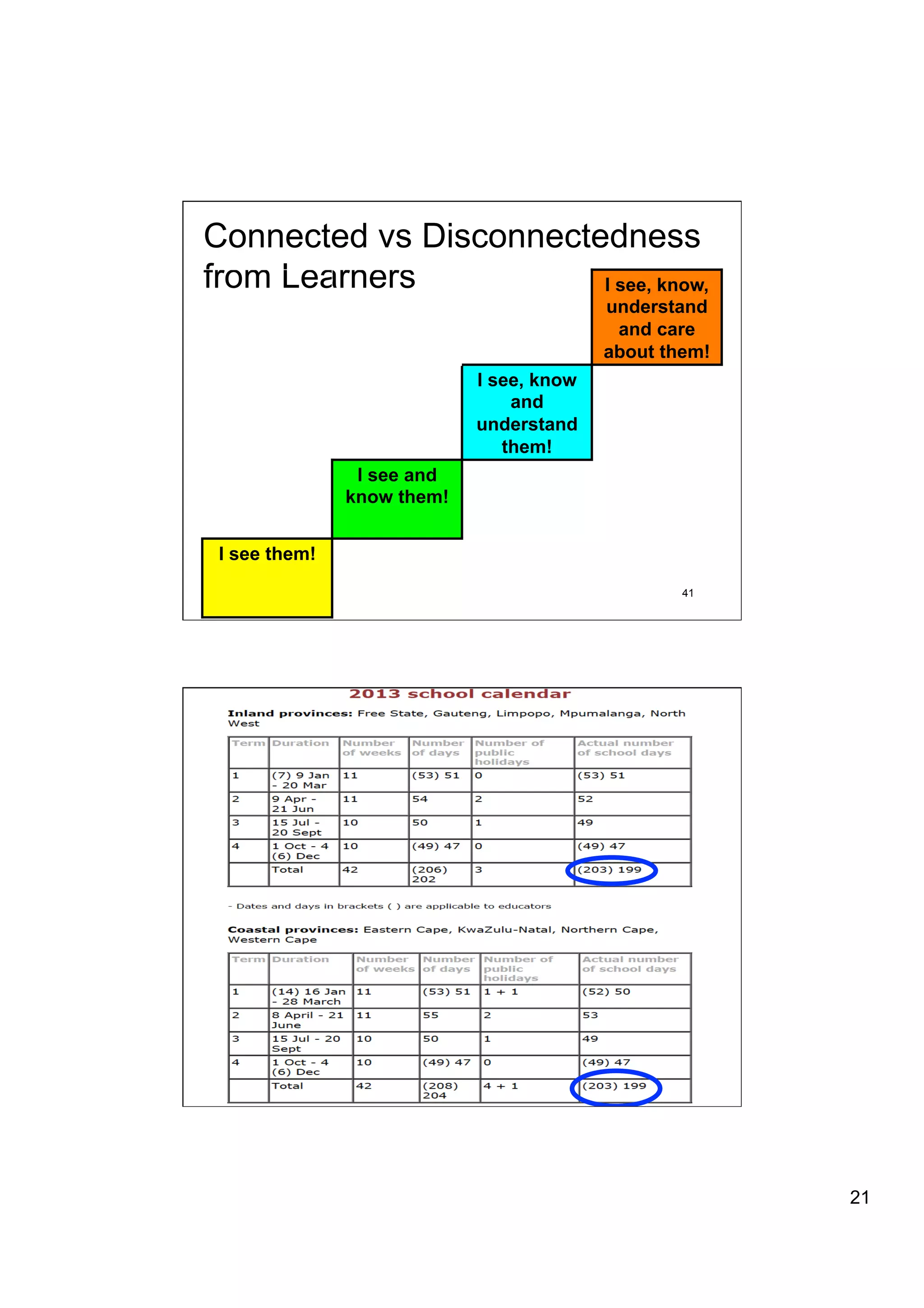
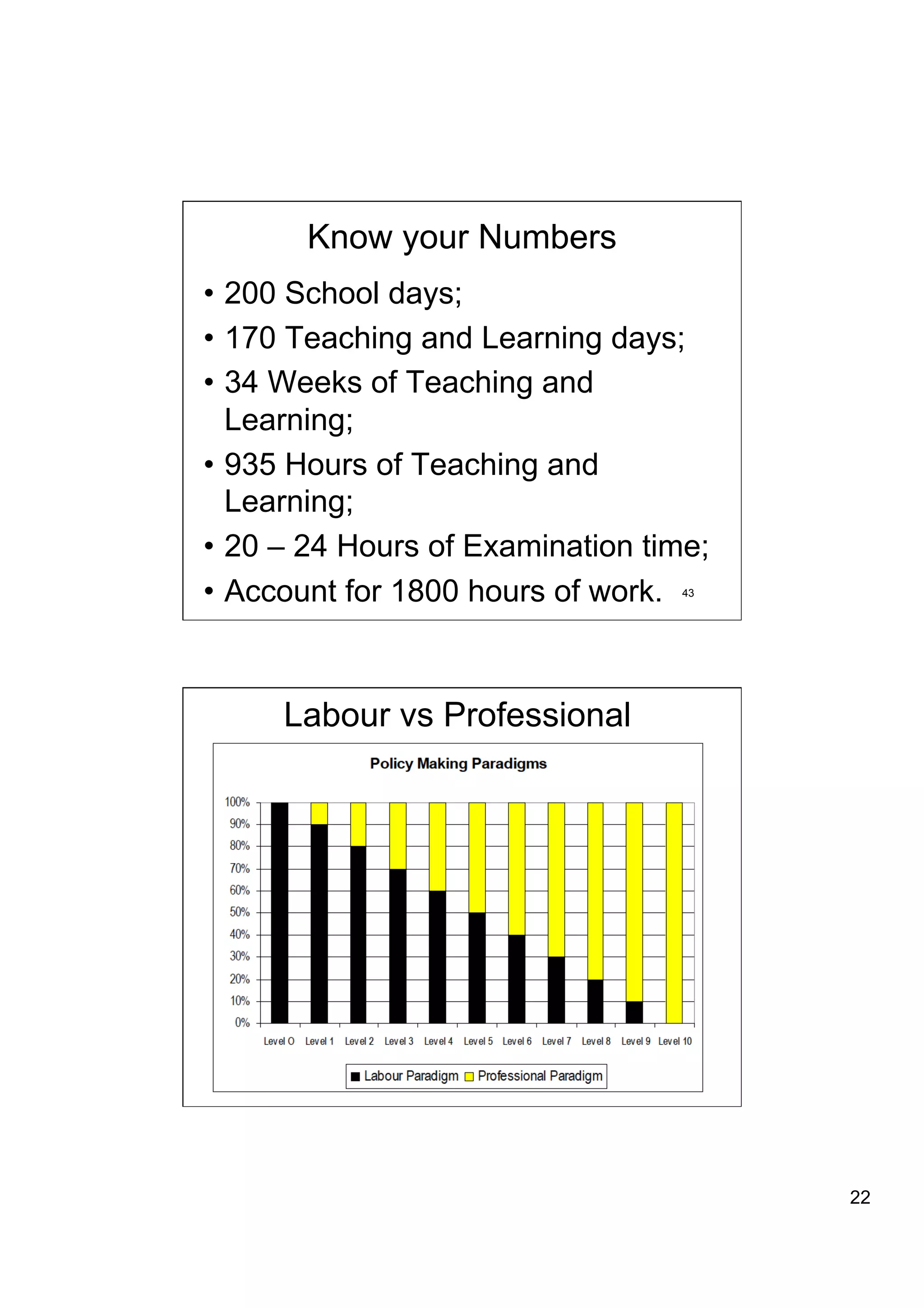
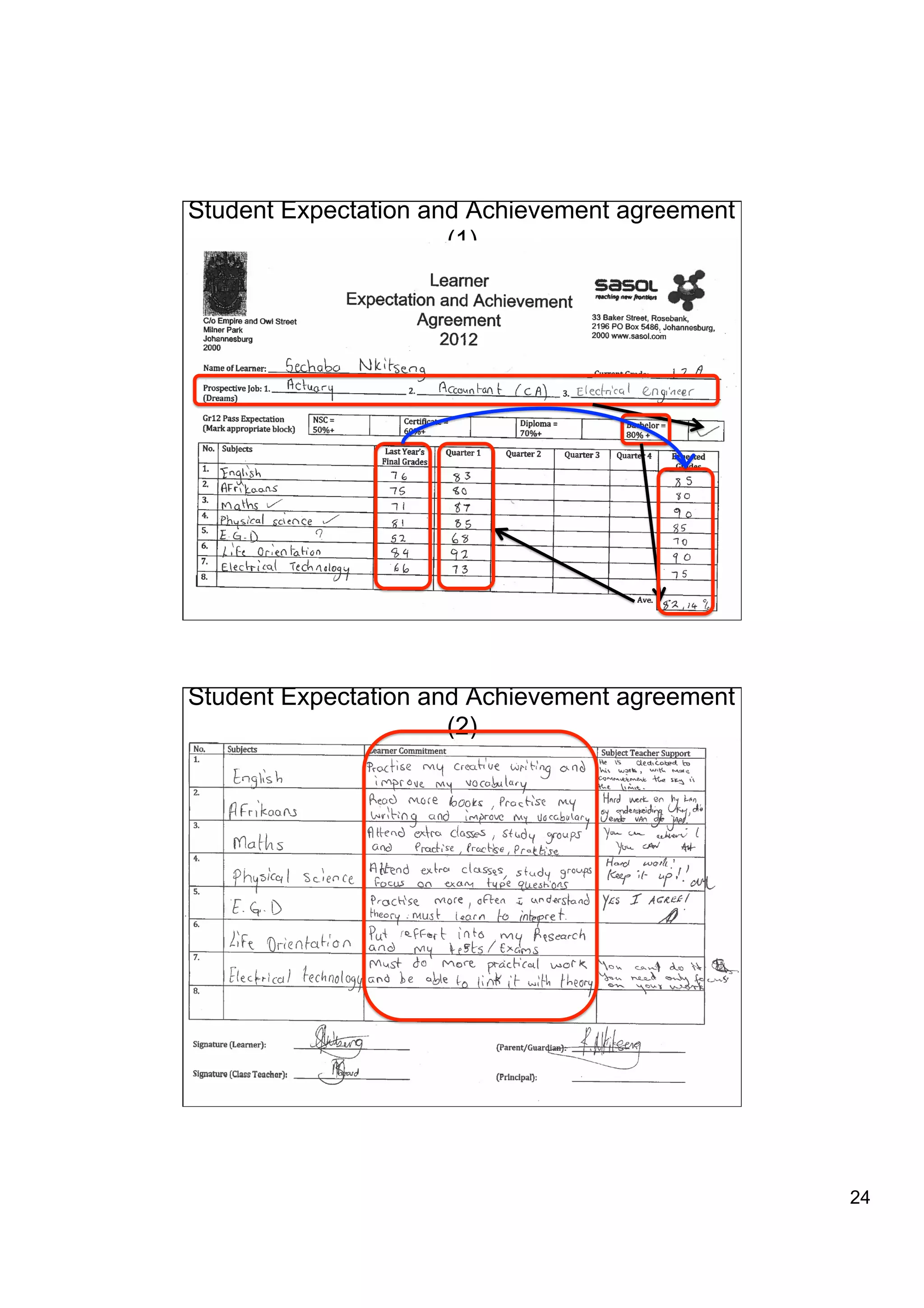
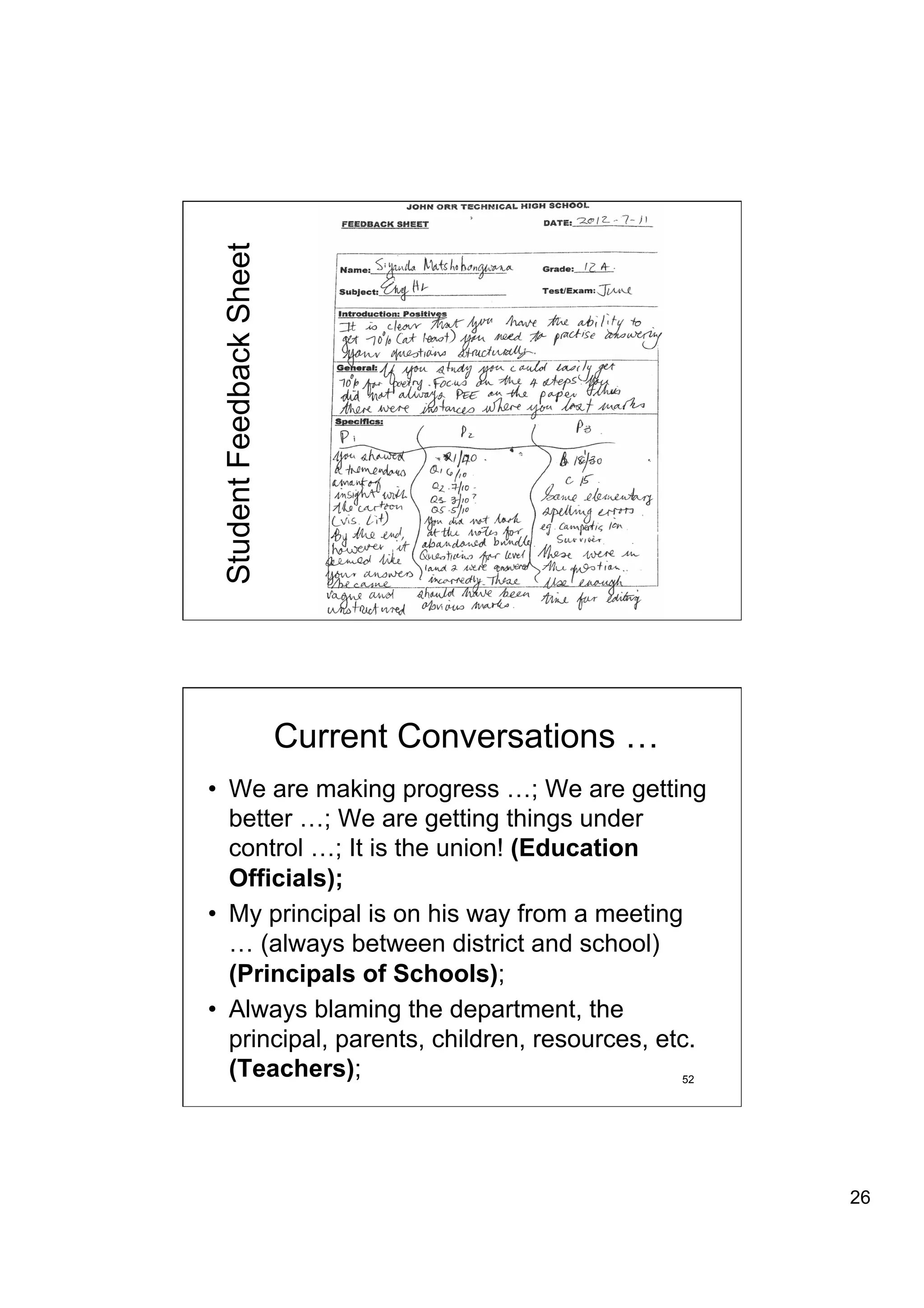
The document provides an overview of the state of education in South Africa and challenges facing the country, with some proposed solutions. It discusses low performance on international tests, high dropout rates, and disparities between school types. Potential causes mentioned include lack of teacher development, dysfunctional school management, and untruths such as overemphasis on resources over quality. The presentation proposes steps to improve education quality, including increasing teacher professionalism, establishing student-teacher connections, and implementing student accountability measures. It aims to raise awareness of educational issues and provide examples of school turnarounds.