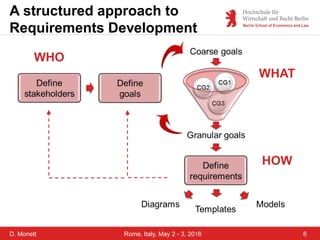
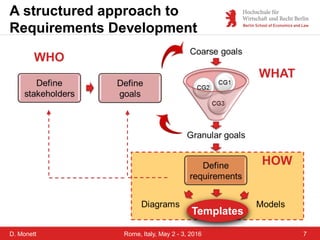
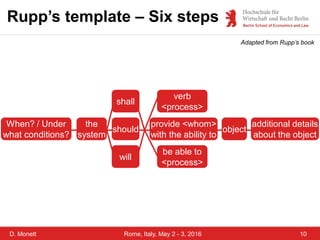
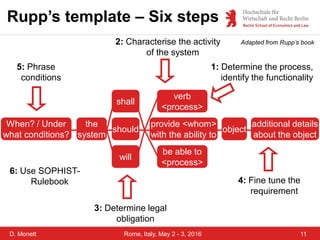
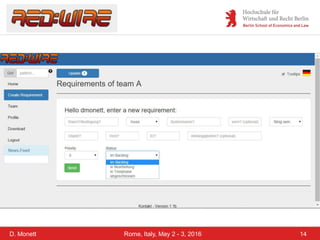
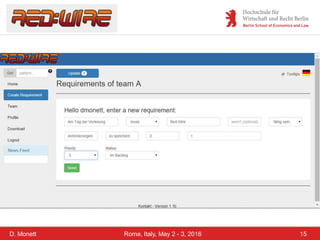
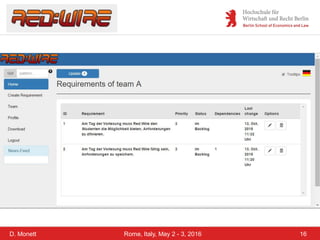
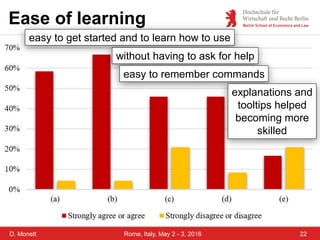
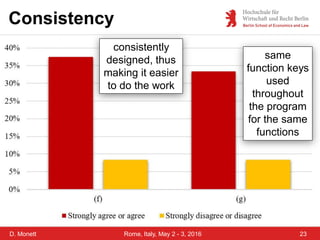
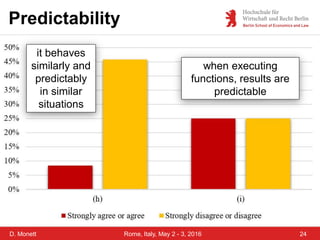
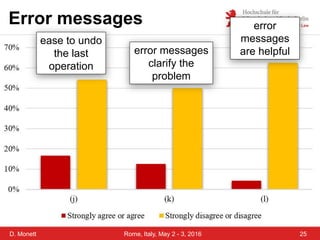
The document discusses a case study on a collaborative requirements engineering tool, red:wire, presented by Prof. Dr. Dagmar Monett at the 18th International Conference on Parallel, Distributed Systems and Software Engineering. It outlines a structured approach to requirements development, teaches students to effectively manage and document software requirements, and evaluates the learnability and effectiveness of red:wire through pre- and post-surveys. The findings indicate that students felt they improved their requirements engineering skills, but further development and testing of the tool are necessary.



![D. Monett 4Rome, Italy, May 2 - 3, 2016
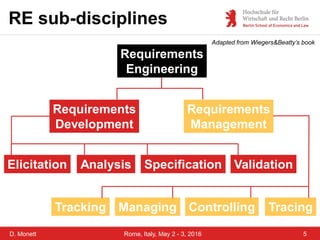
Requirements Engineering
“[It] encompasses all project
activities associated with
understanding a product's
necessary capabilities and
attributes.”
Karl Wiegers and Joy Beatty (2013).
Software Requirements. 3rd Edition, 672 pp. Microsoft Press.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/monett-kujat-hartmannicpdsse2016talk-160425071230/85/Teaching-Students-Collaborative-Requirements-Engineering-Case-Study-Red-Wire-4-320.jpg)