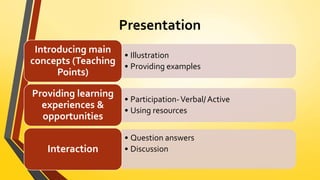
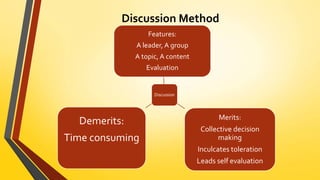
The document discusses various teaching processes and methods, emphasizing the importance of a structured teaching approach that includes steps such as introduction, presentation, recapitulation, application, and assignments. It details several teaching methods including lecture, discussion, and problem-solving, as well as linguistic methods such as the grammar-translation and direct methods. It concludes with a focus on selecting appropriate methods based on factors like learner needs and subject matter.