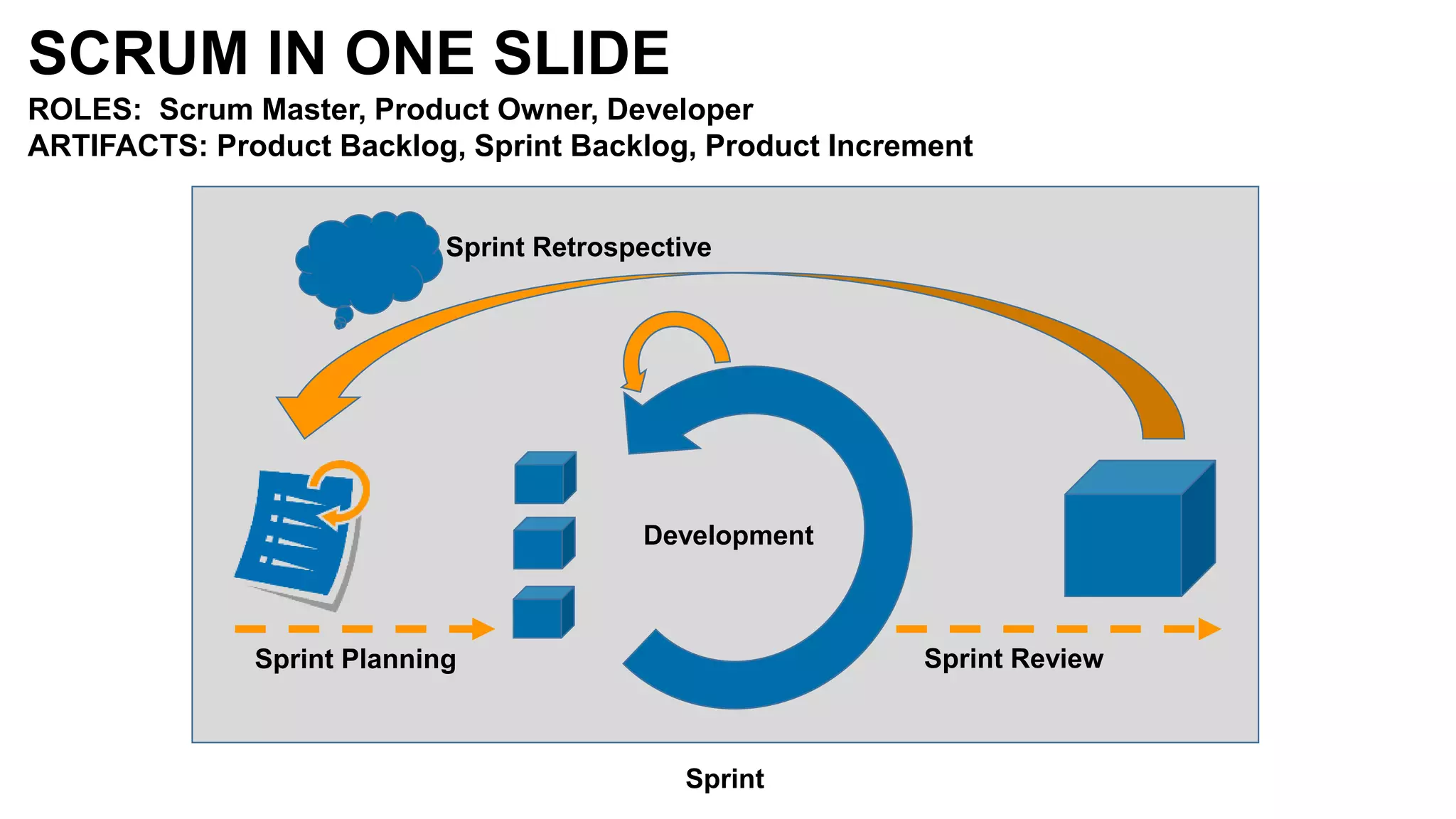
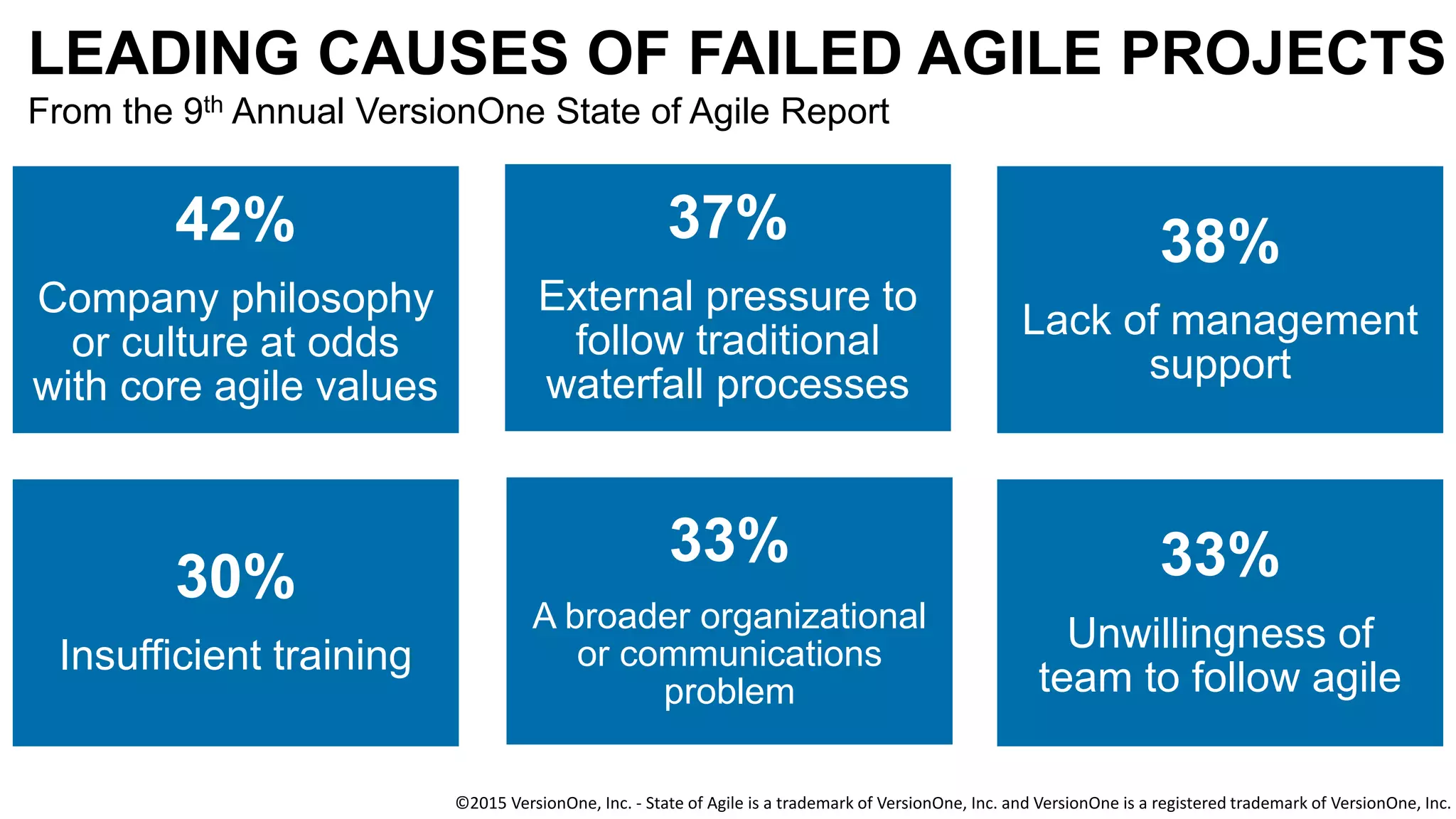
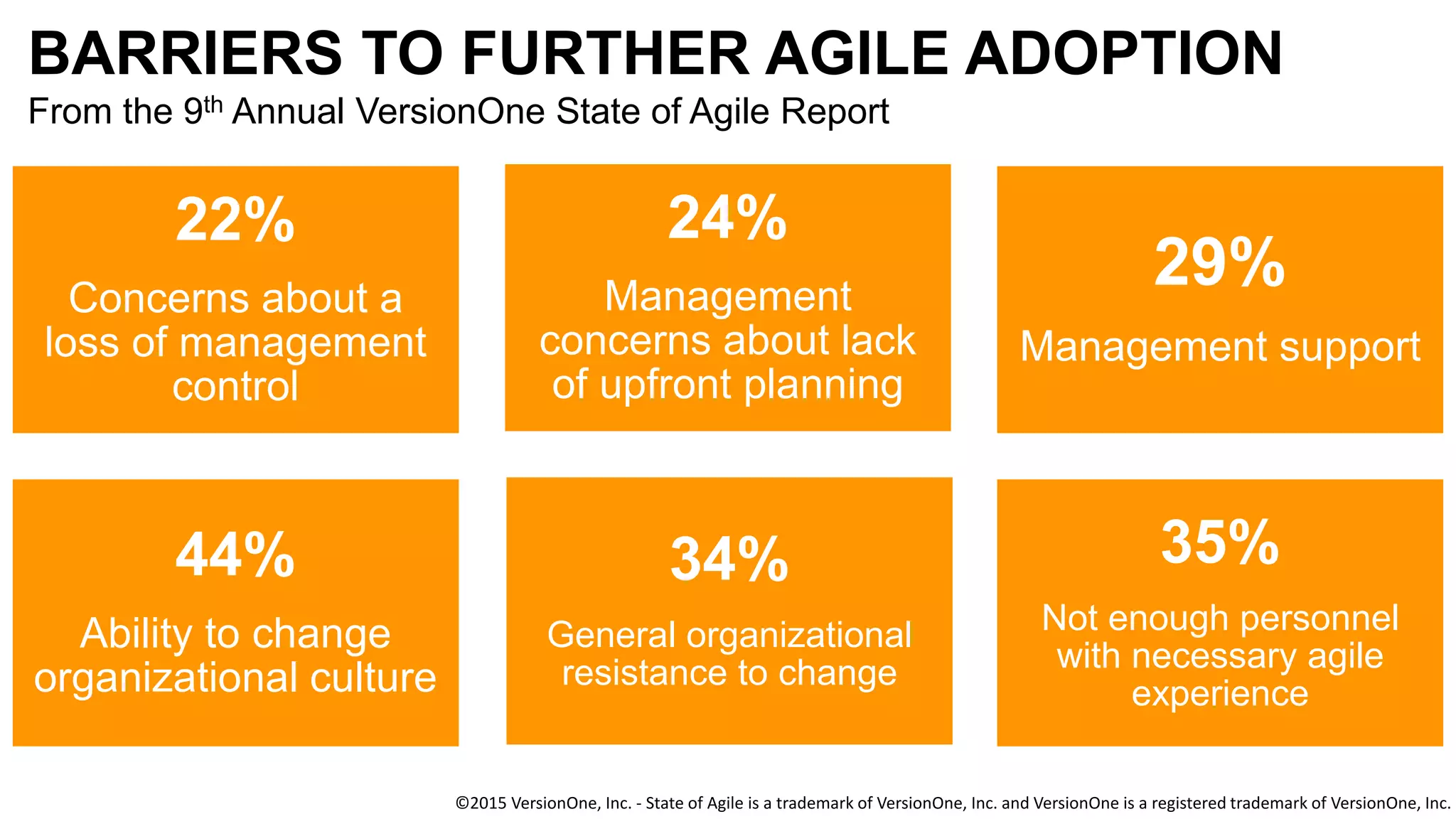
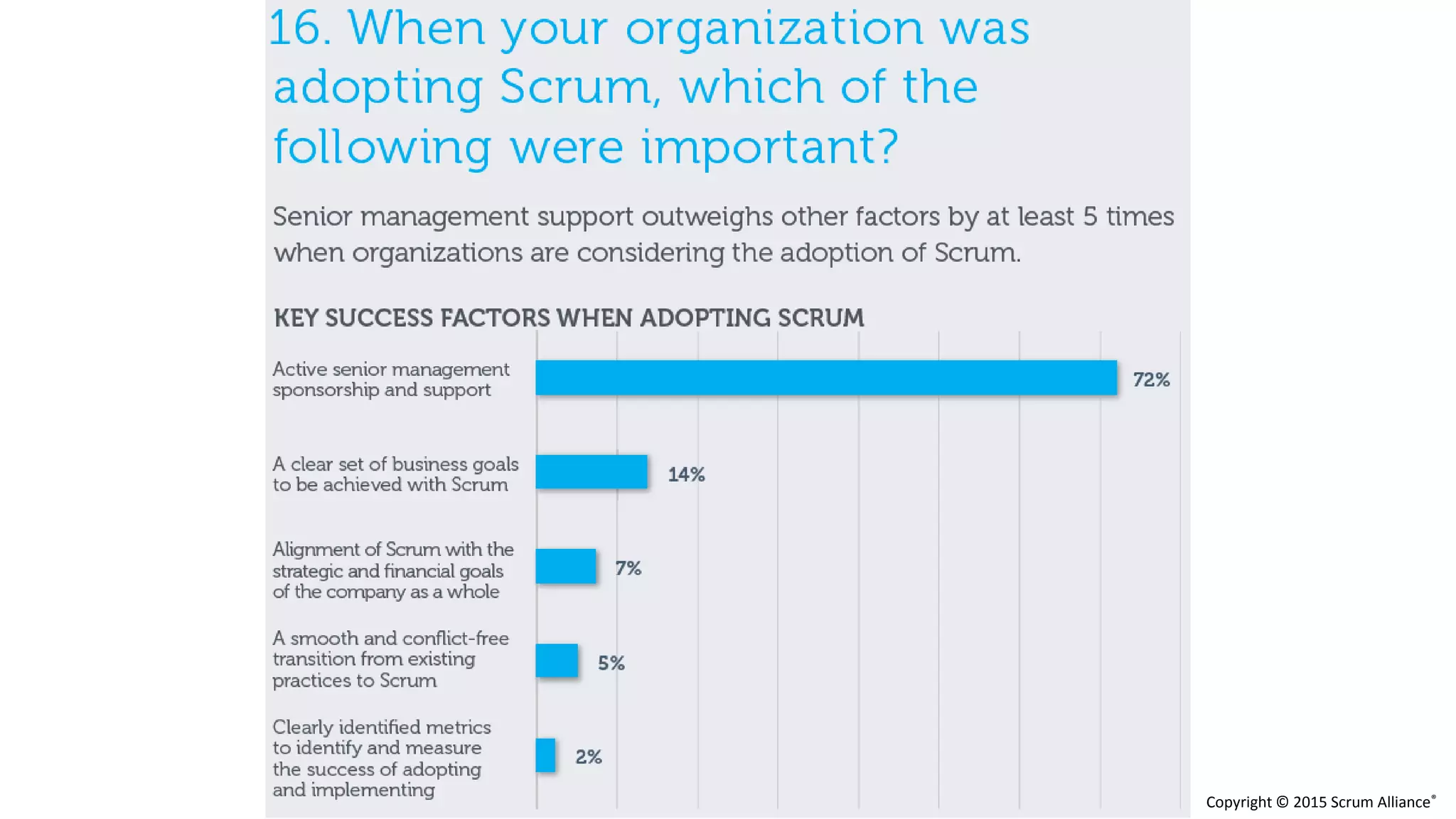
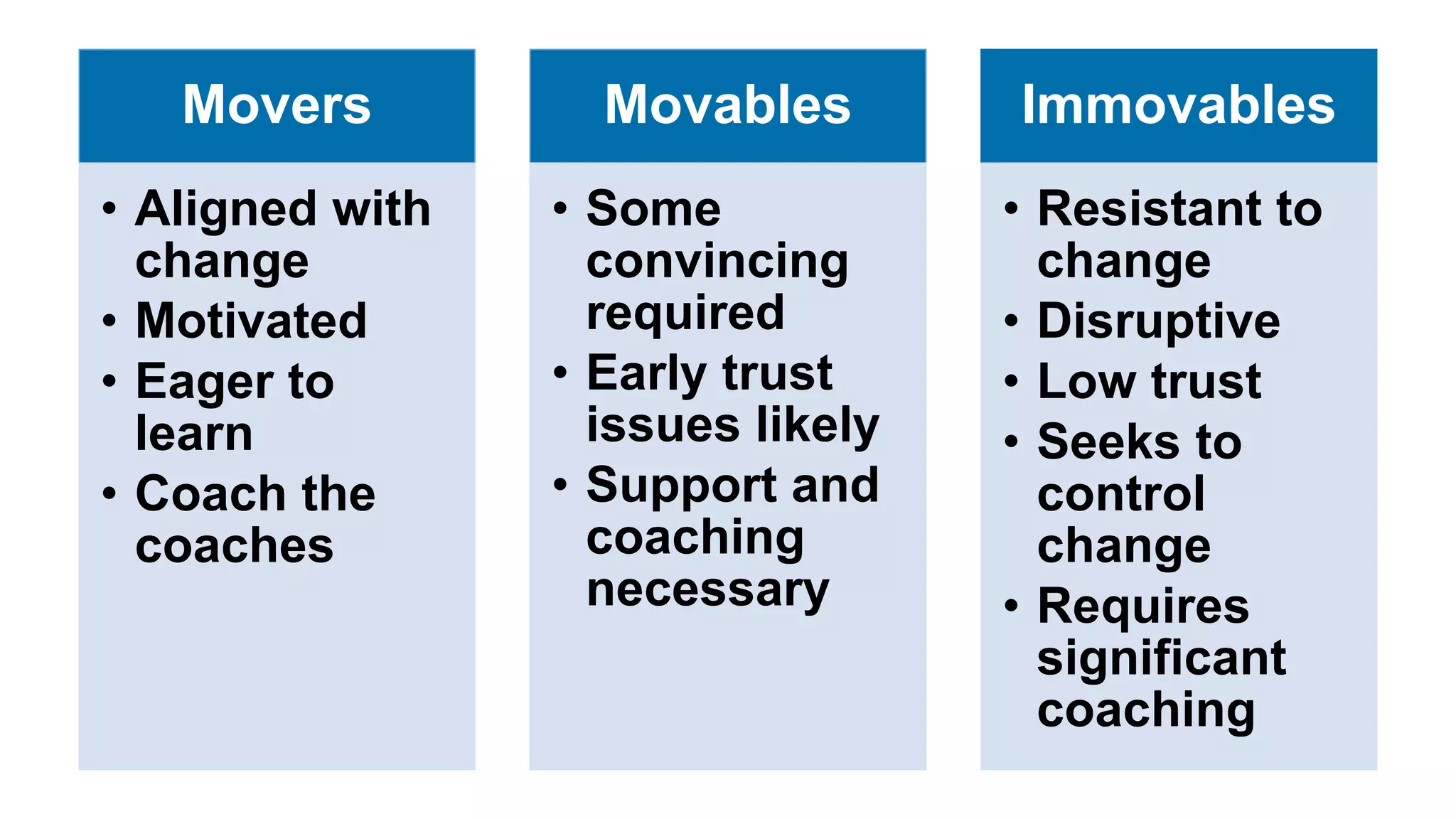
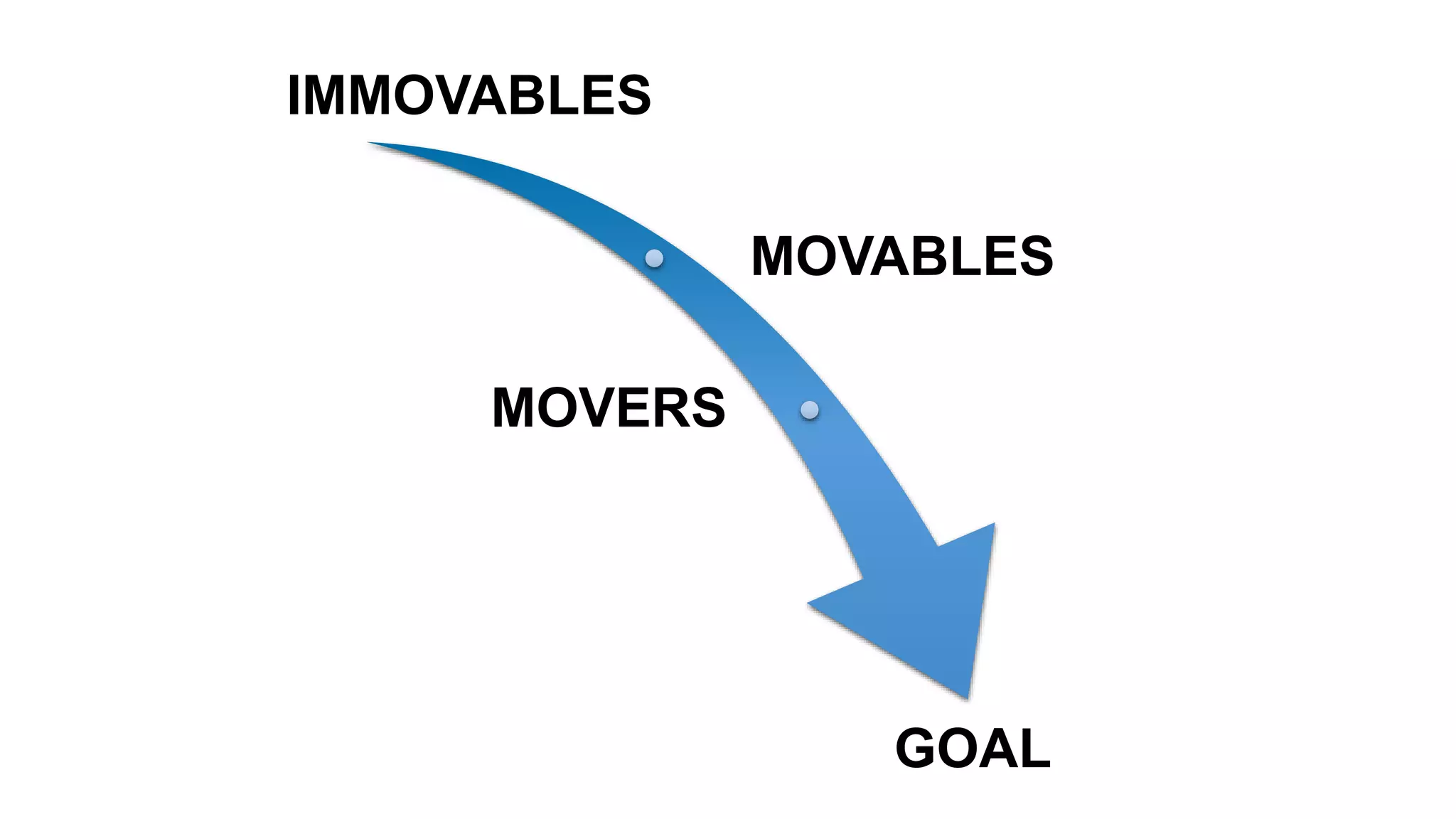
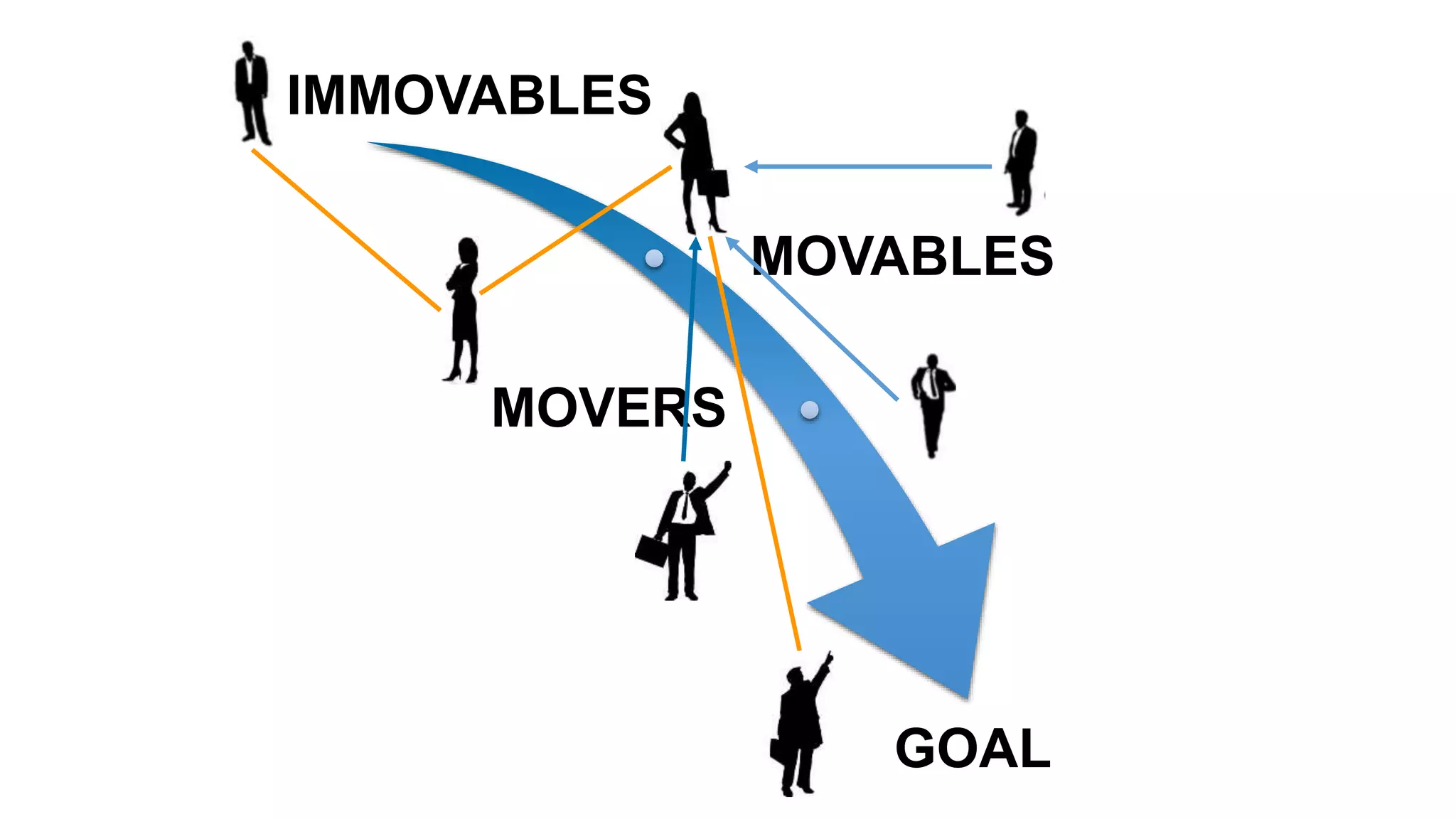
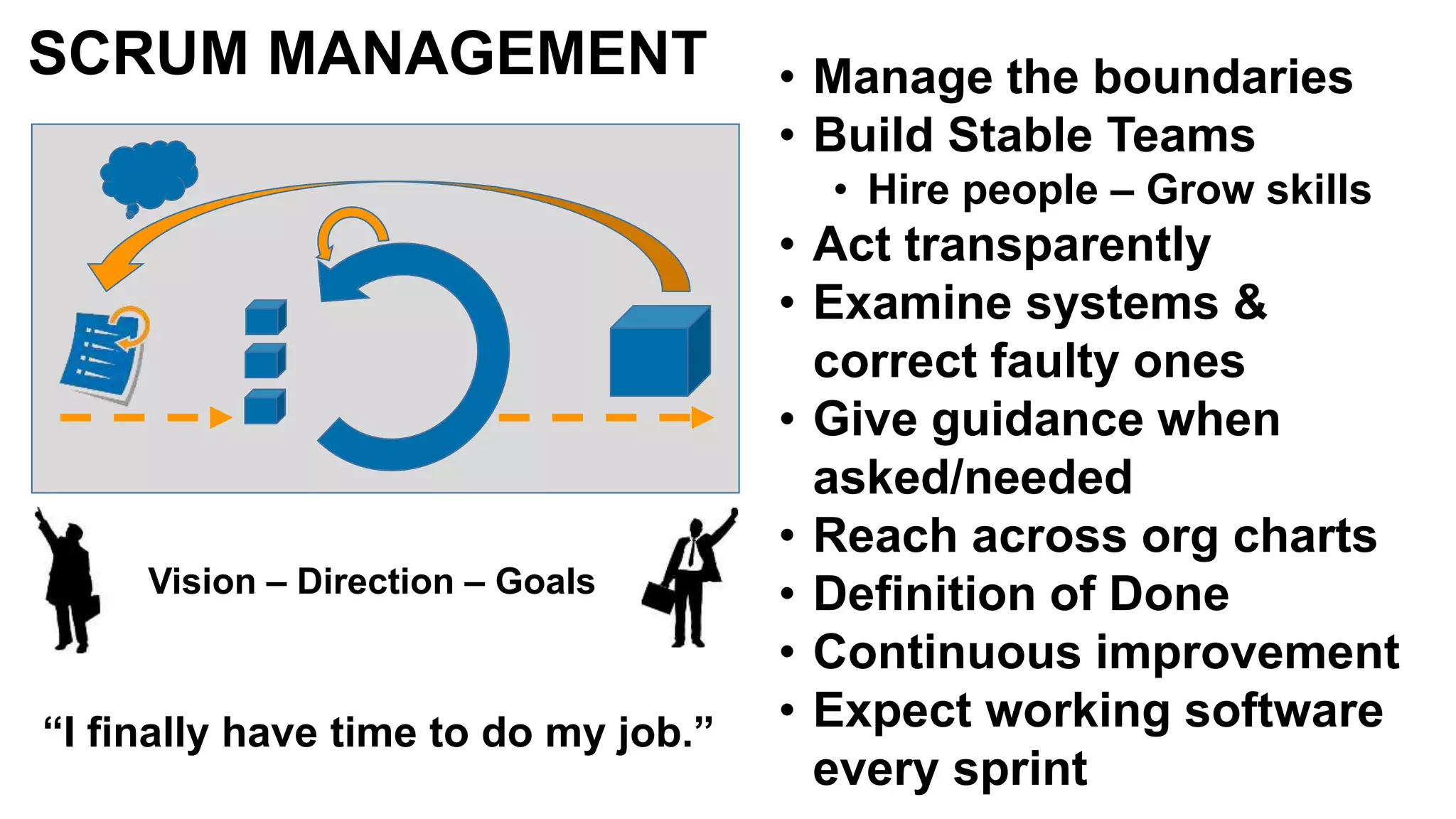
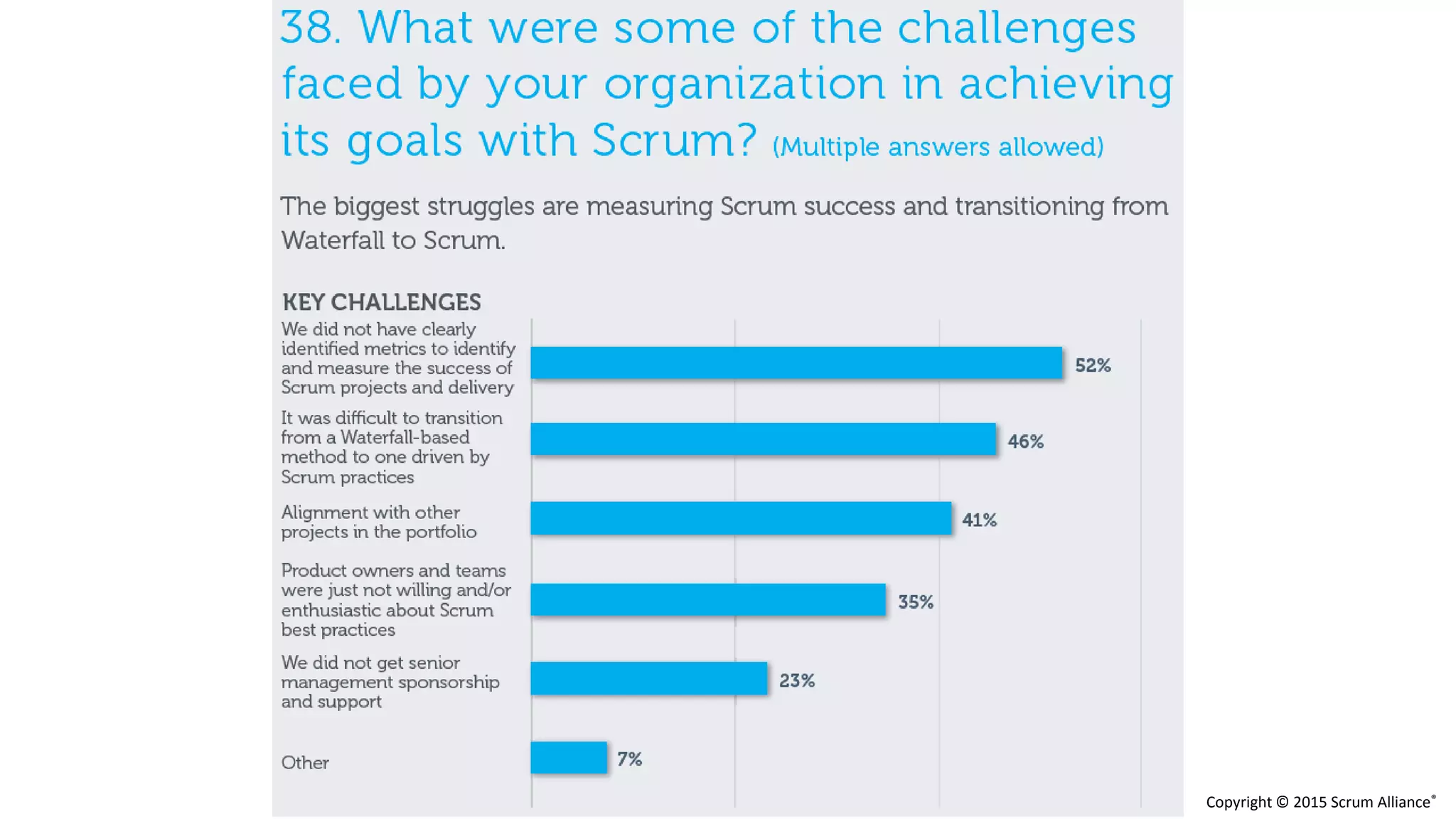
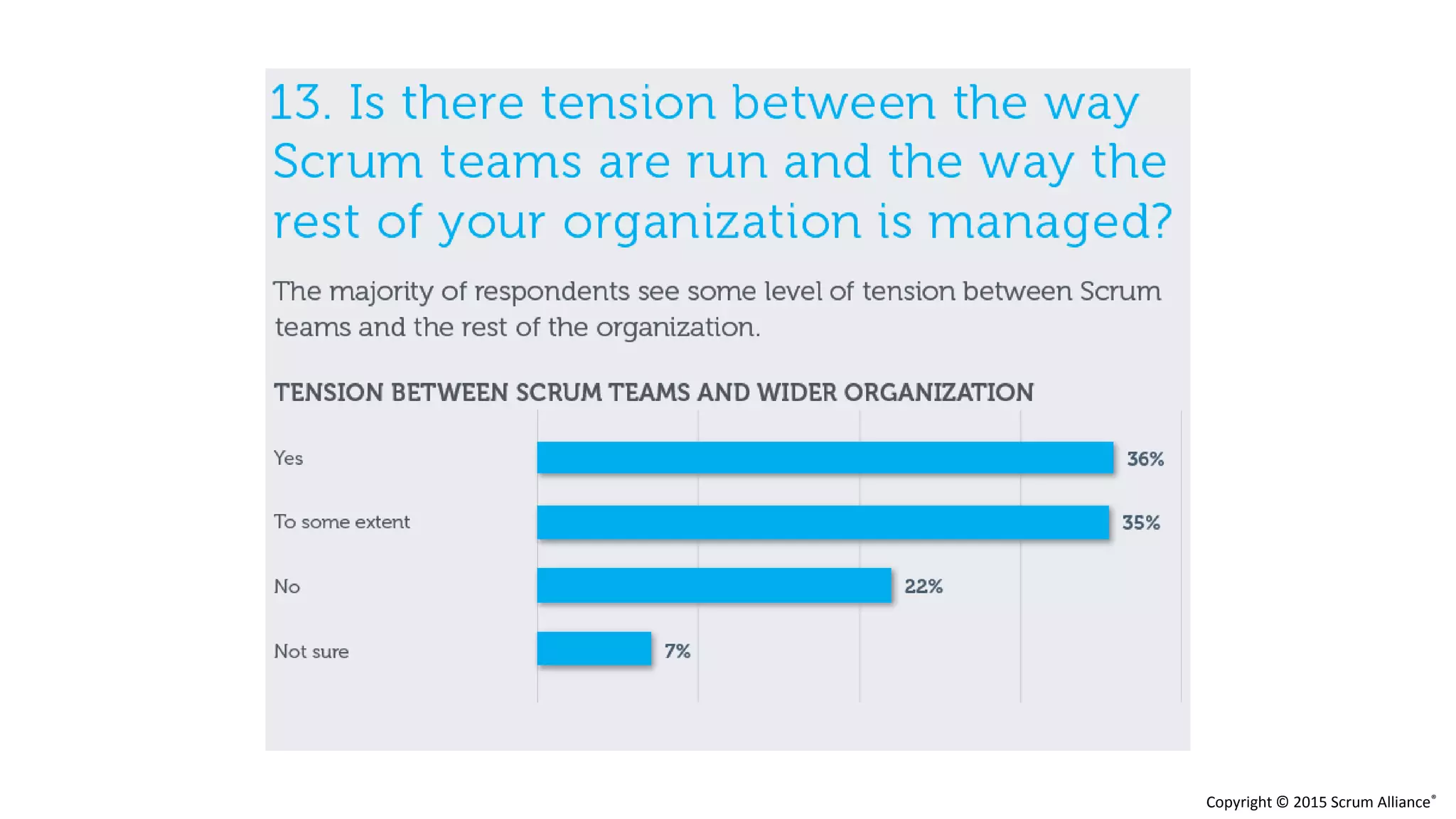
The document discusses the crucial role of management in agile transformations, emphasizing that while self-organizing teams are essential, effective leadership remains necessary. It identifies common barriers to successful agile adoption, including cultural misalignment and lack of management support, and outlines manager personas to facilitate buy-in. The text advocates for understanding managers' needs and concerns to foster a positive environment for change and emphasizes the importance of management in guiding teams within the agile framework.