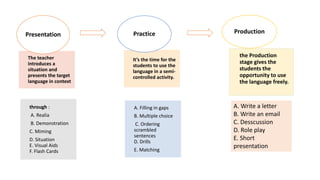
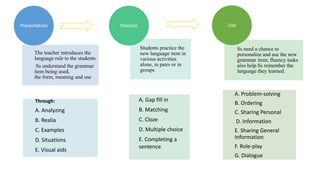
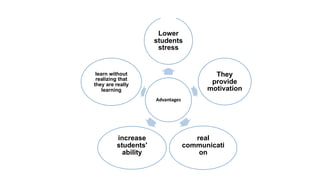
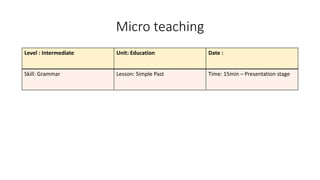
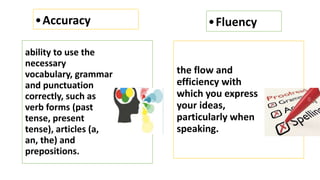
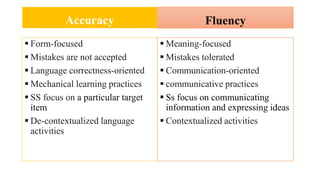
The document provides an overview of teaching language skills, with a focus on teaching grammar. It defines grammar and discusses considerations for teaching grammar, including the differences between fluency and accuracy. It also presents various approaches to teaching grammar, such as deductive versus inductive, and frameworks like PPP and PPU that incorporate presentation, practice and production stages. Controlled and free activities are also addressed.








![Concrete illustration
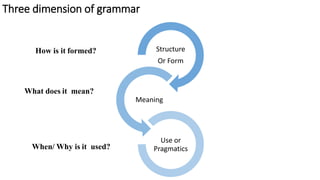
Teacher explains the form and use of “Past Continuous”
Form : Subject +was/were + verb [ing] + obj
Use: to indicate that a longer action in the past was interrupted
Teacher asks Ss to practice the past continuous through completing certain tasks like](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/teachinggrammar-210325160231/85/Teaching-Grammar-CRMEF_SM-2021-13-320.jpg)