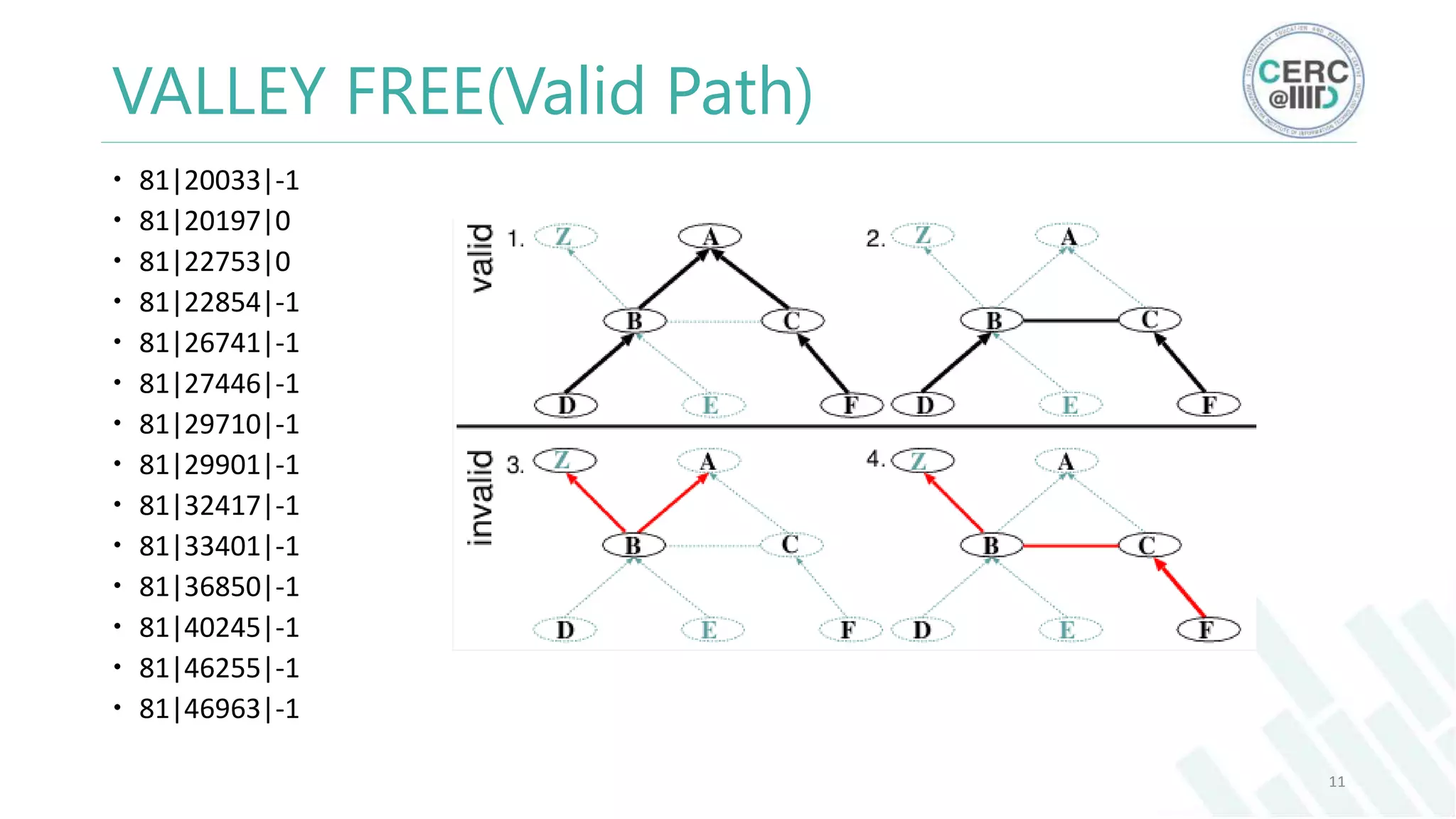
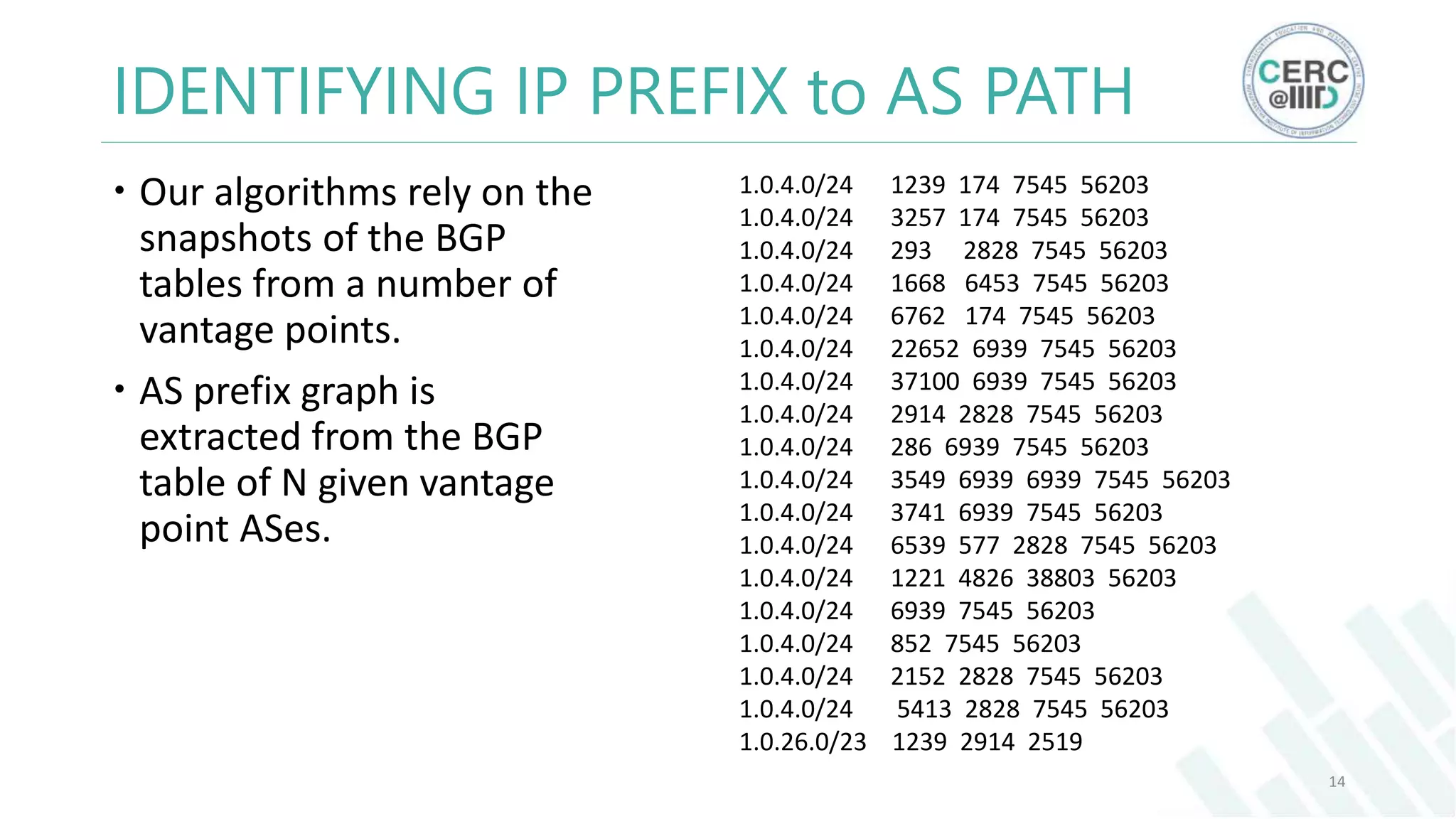
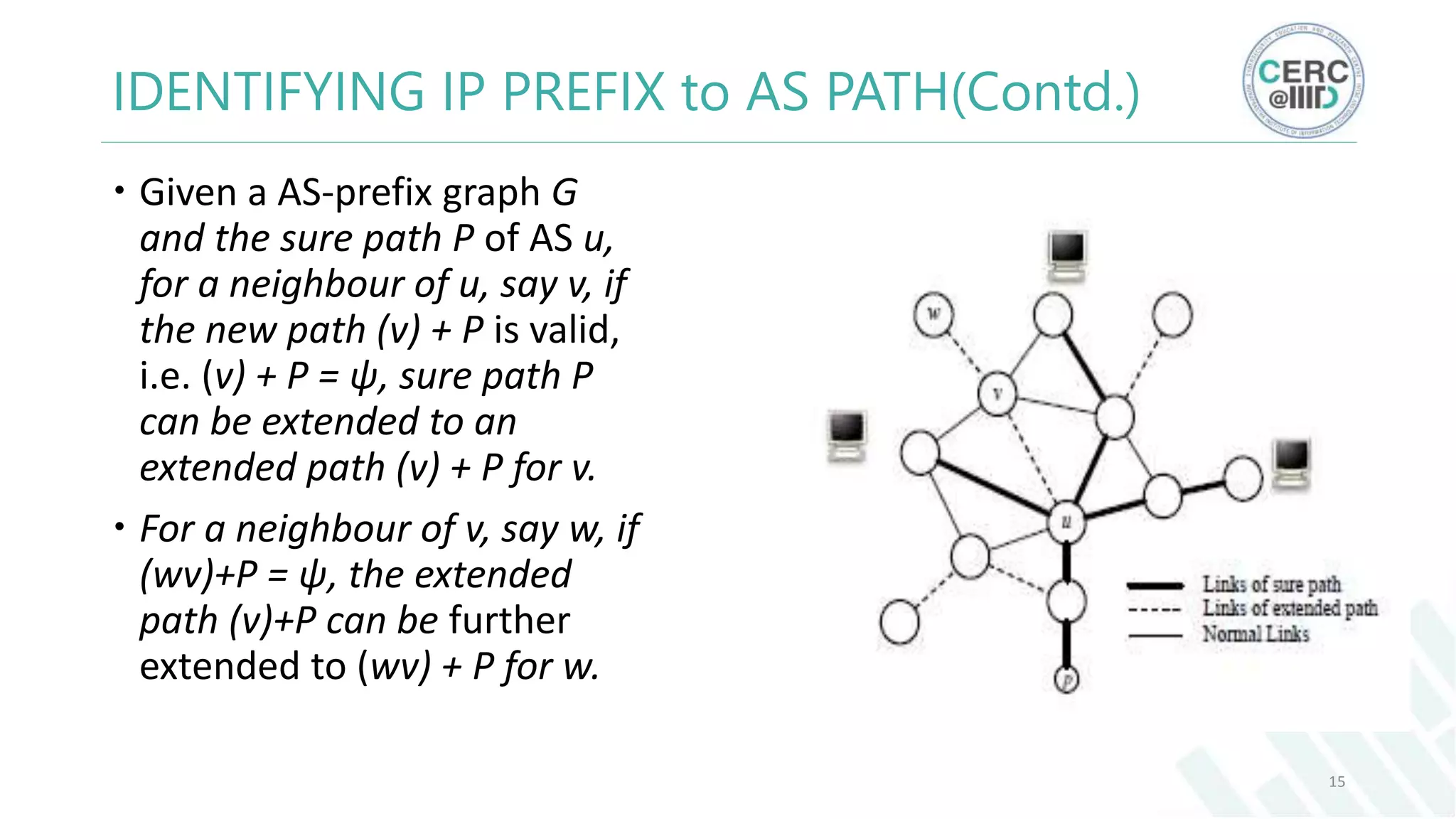
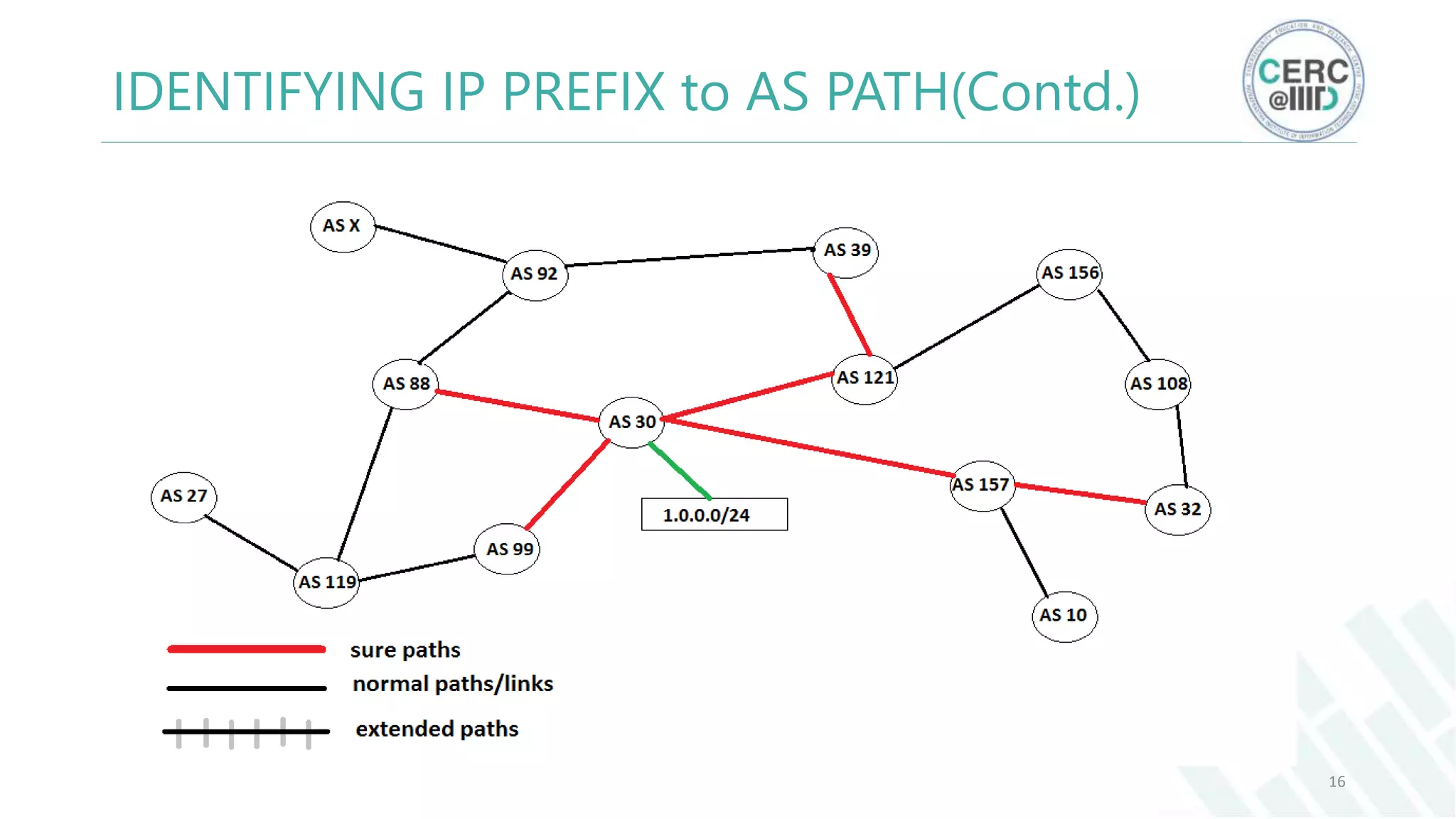
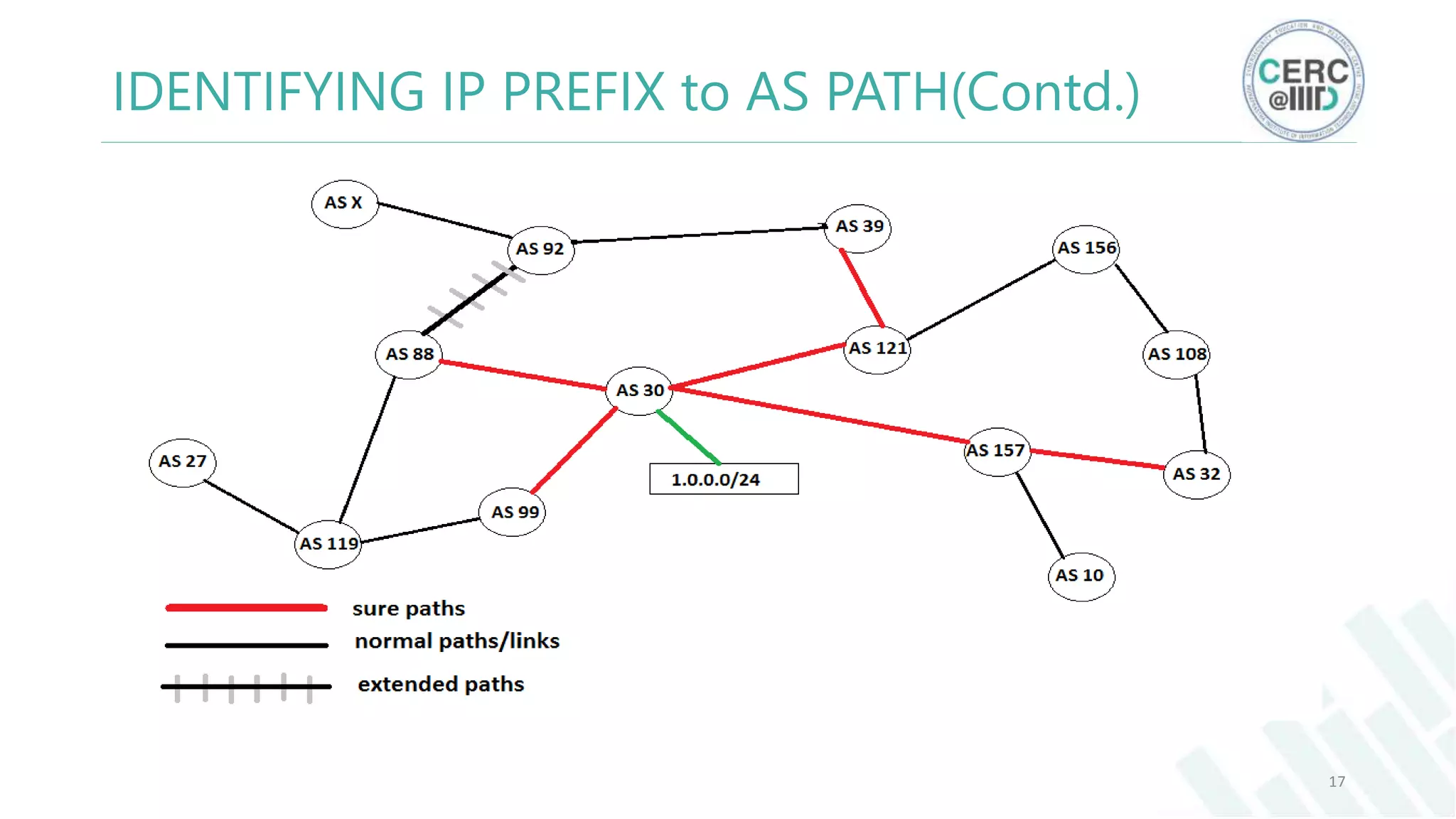
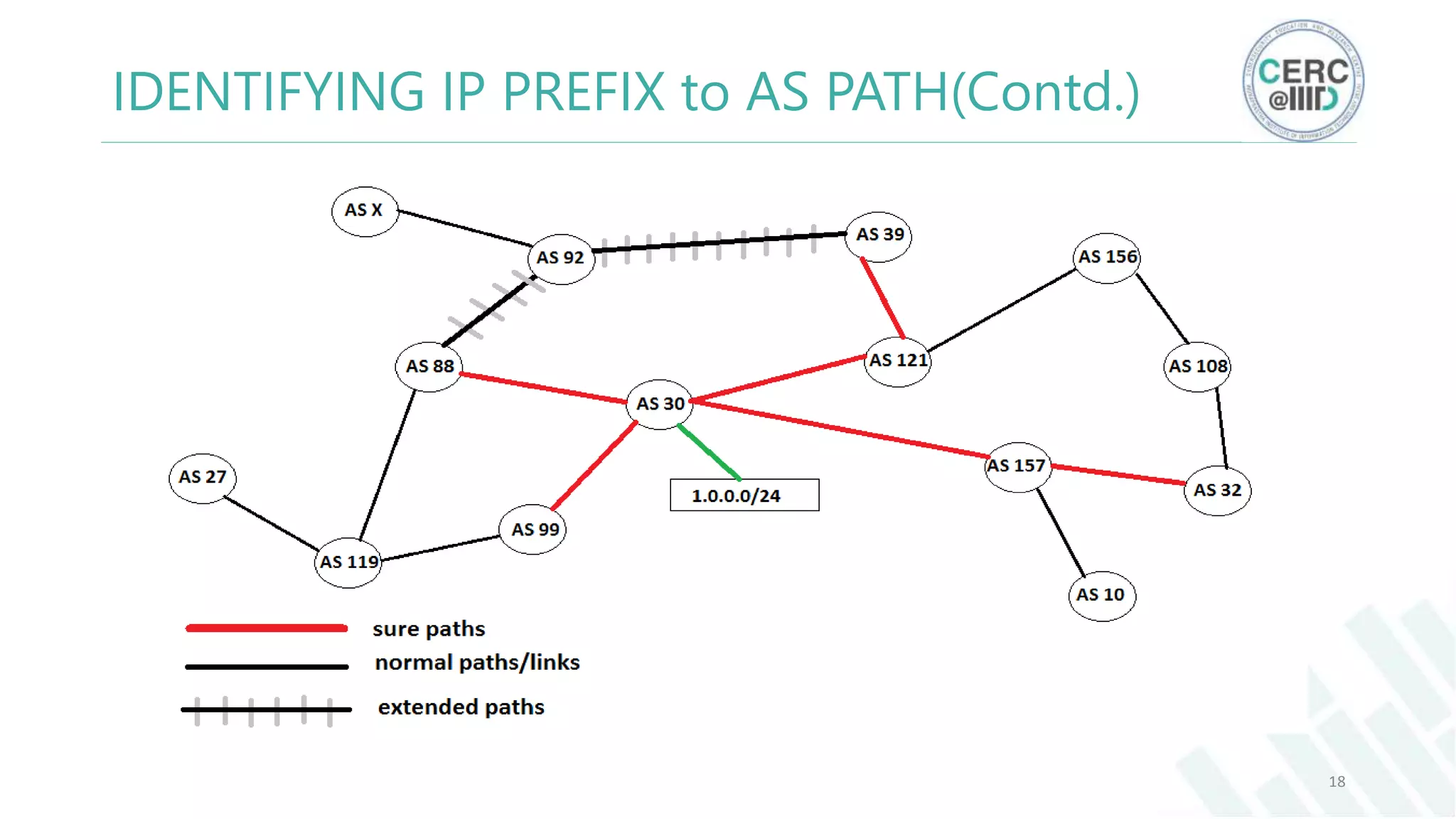
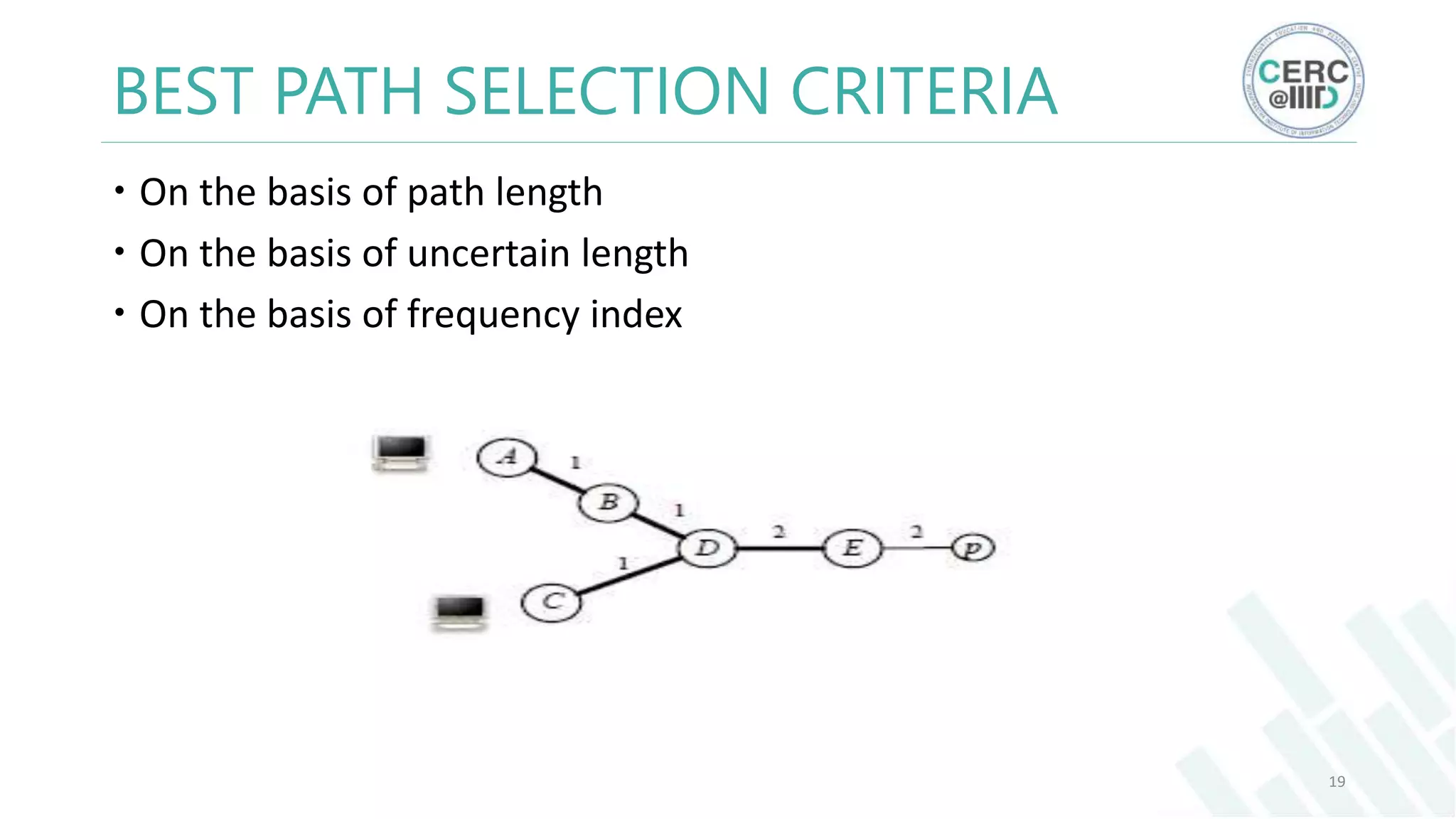
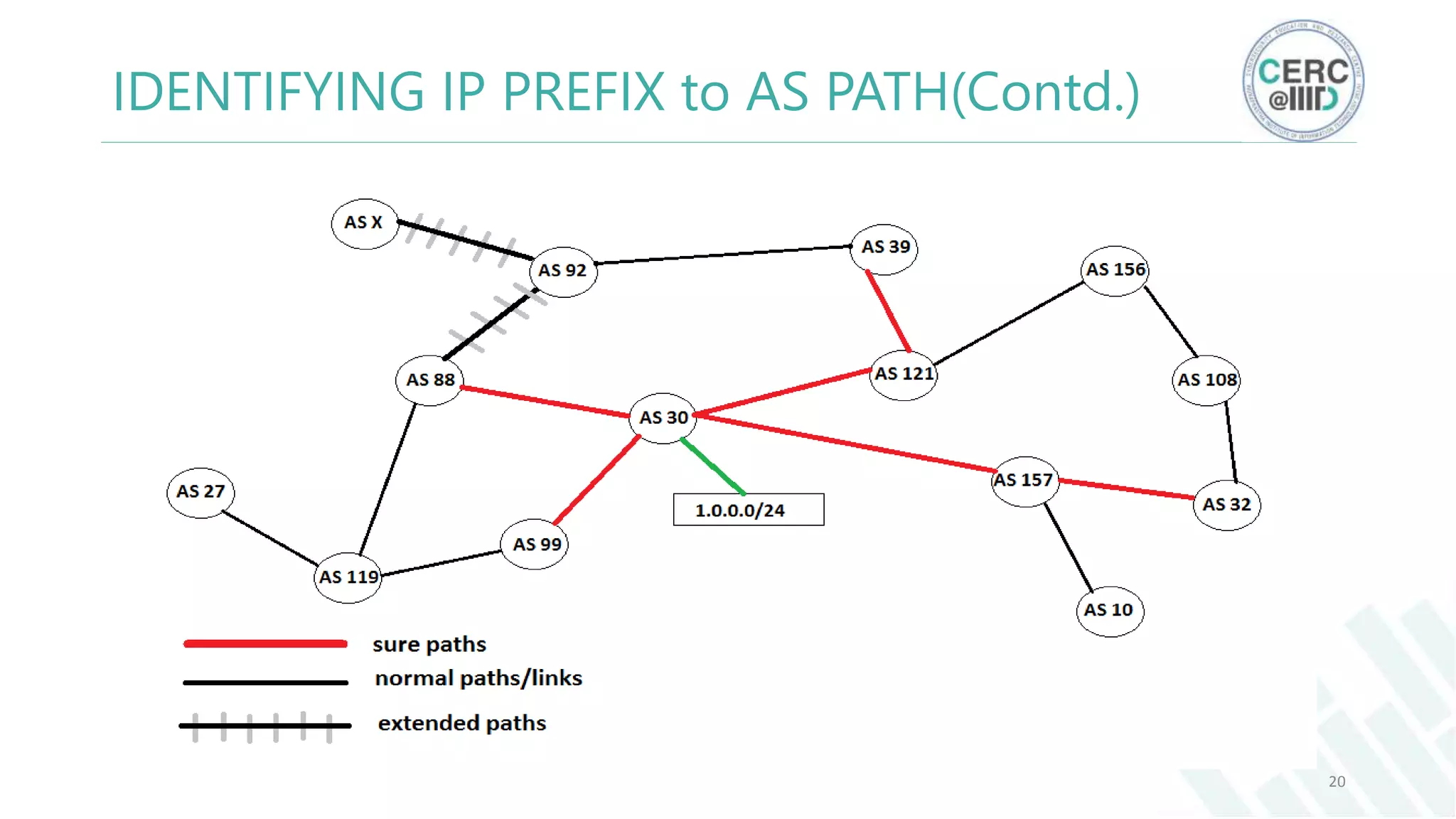
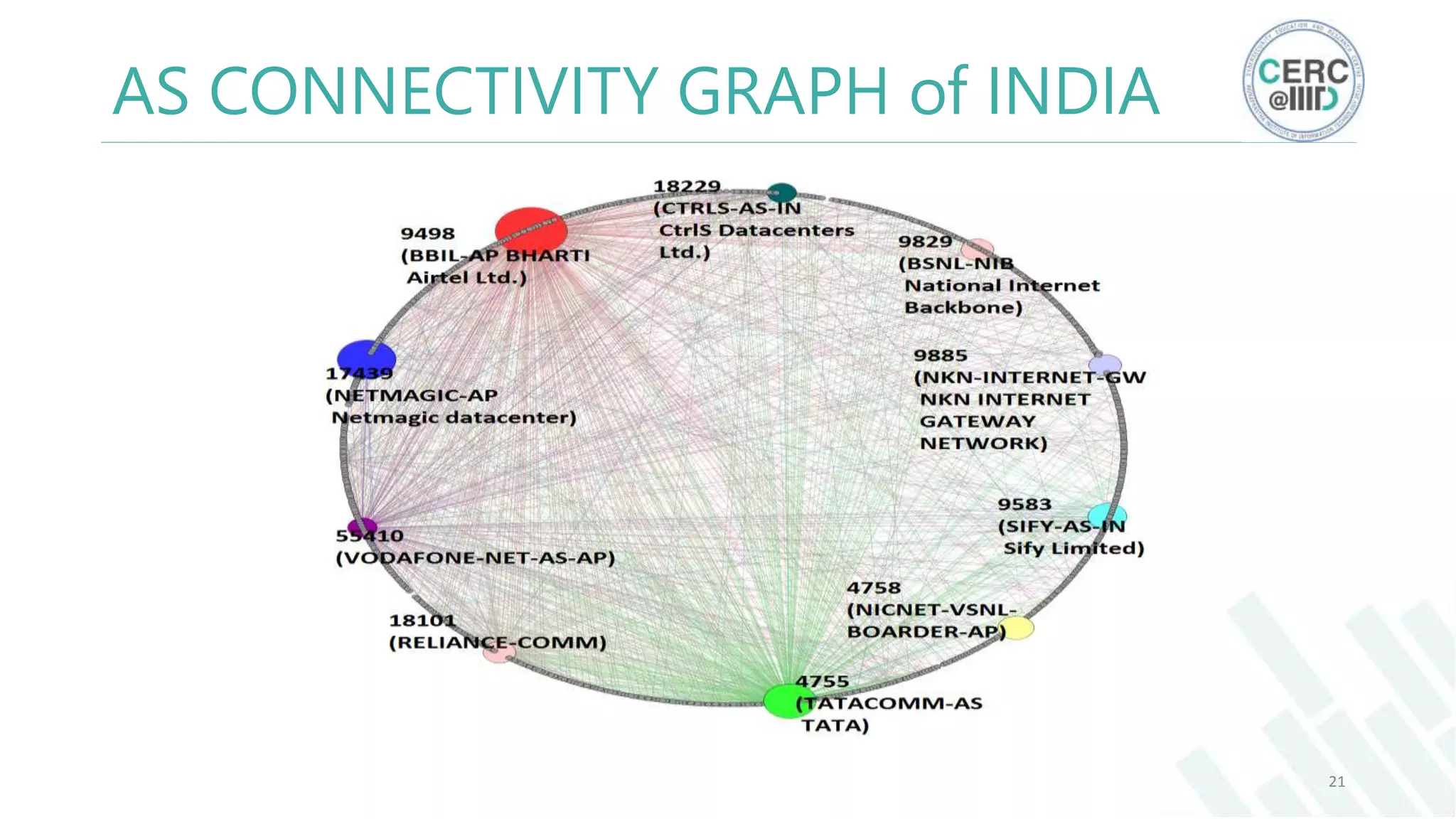
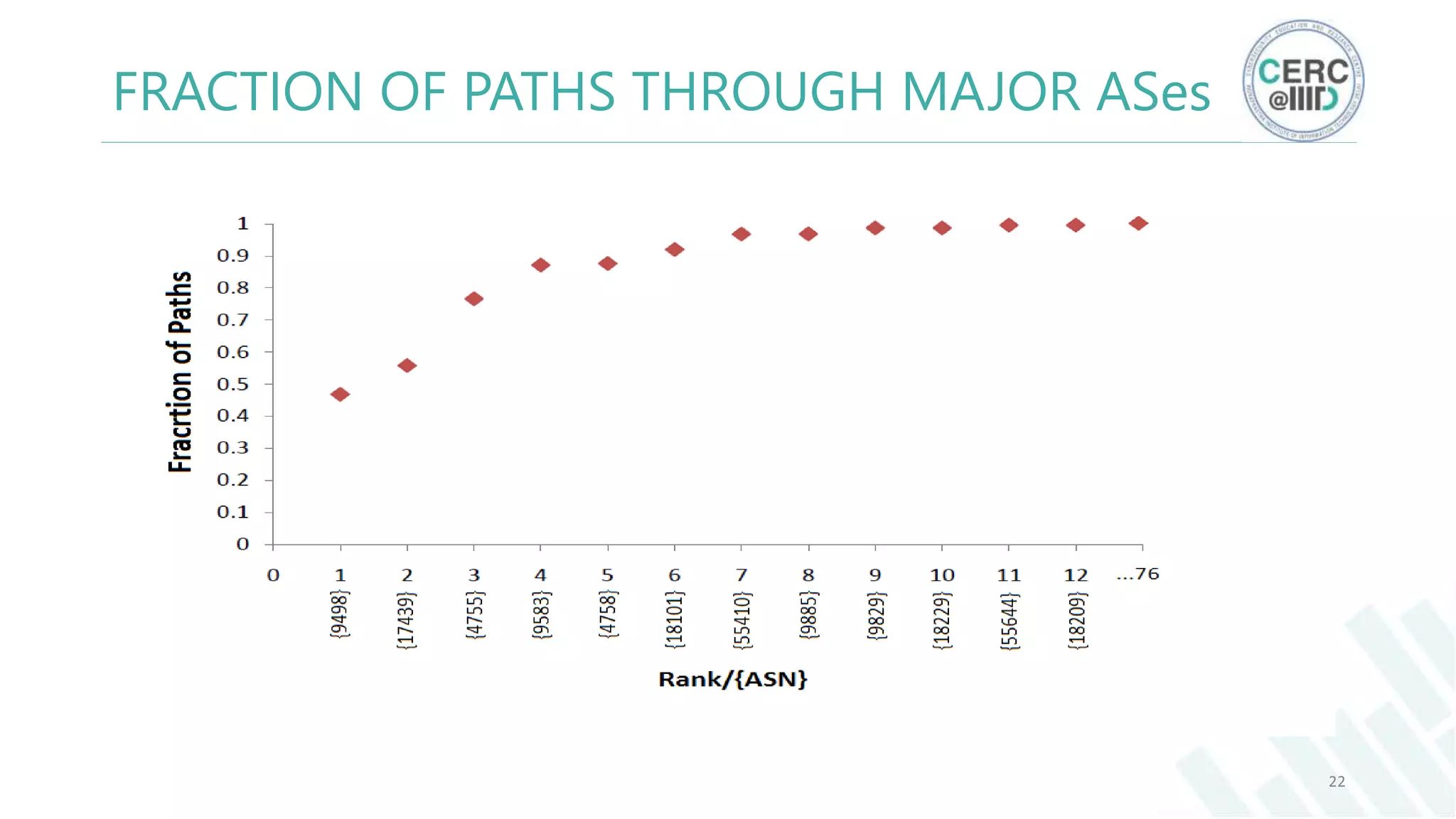
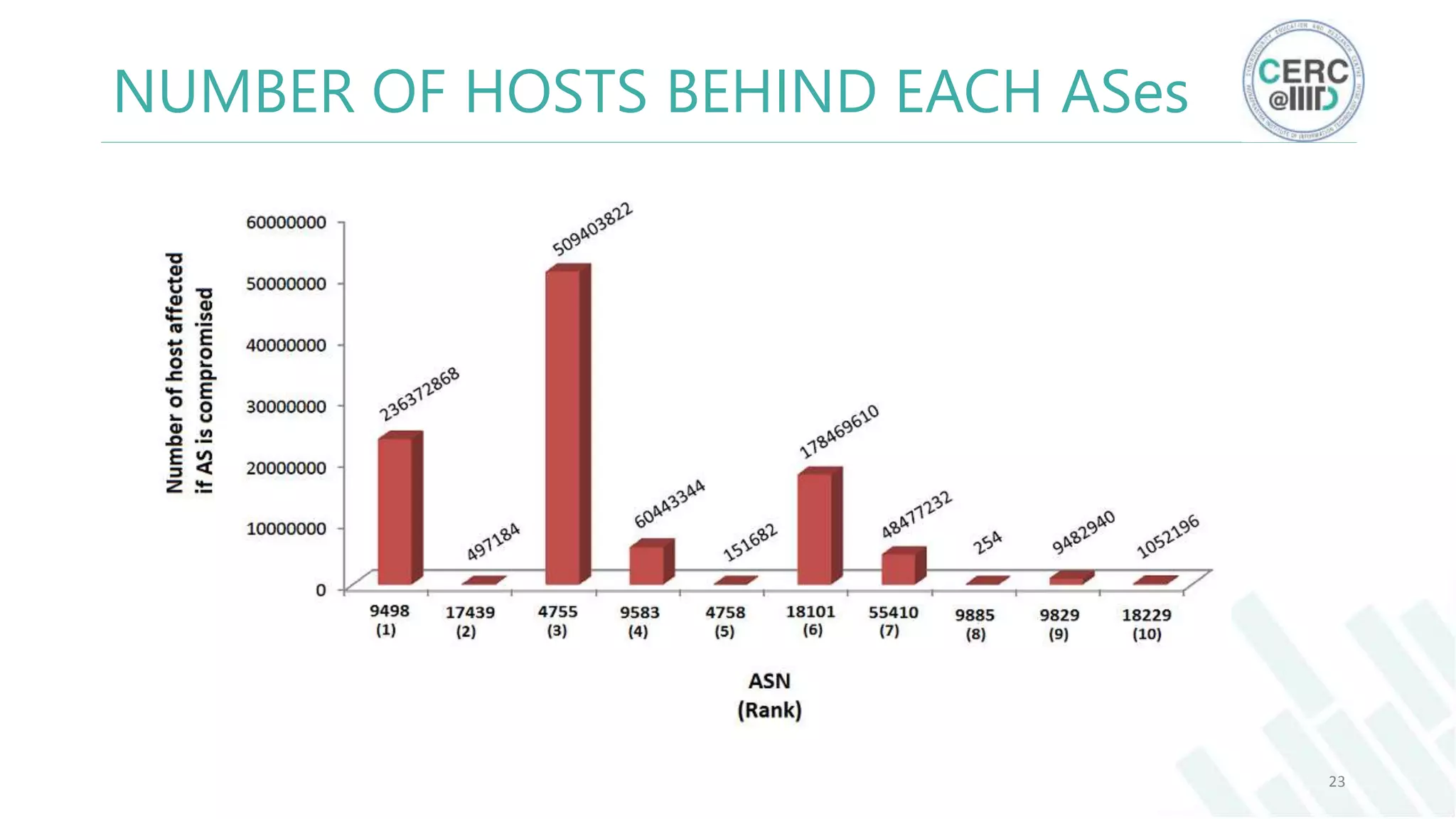
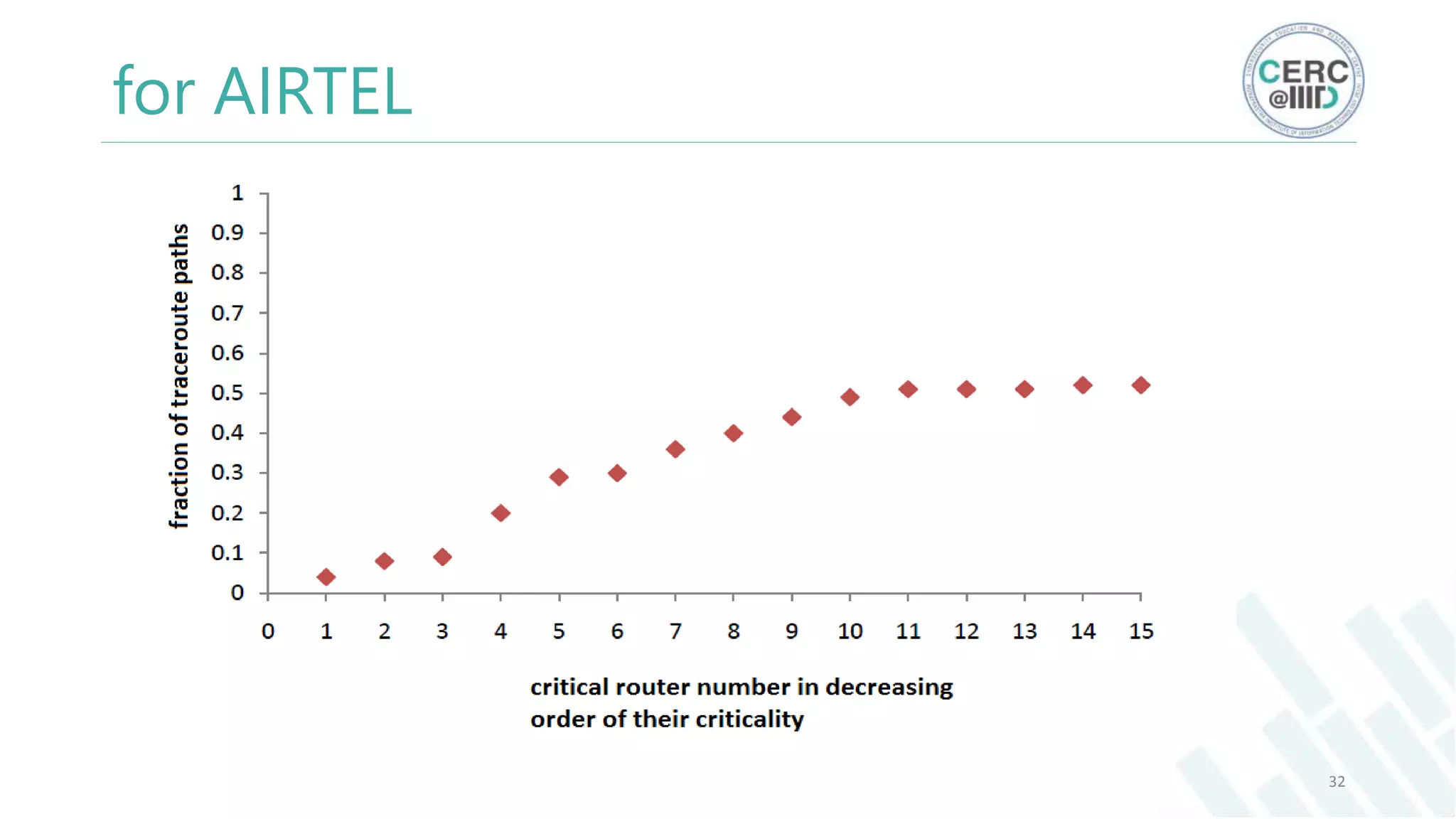
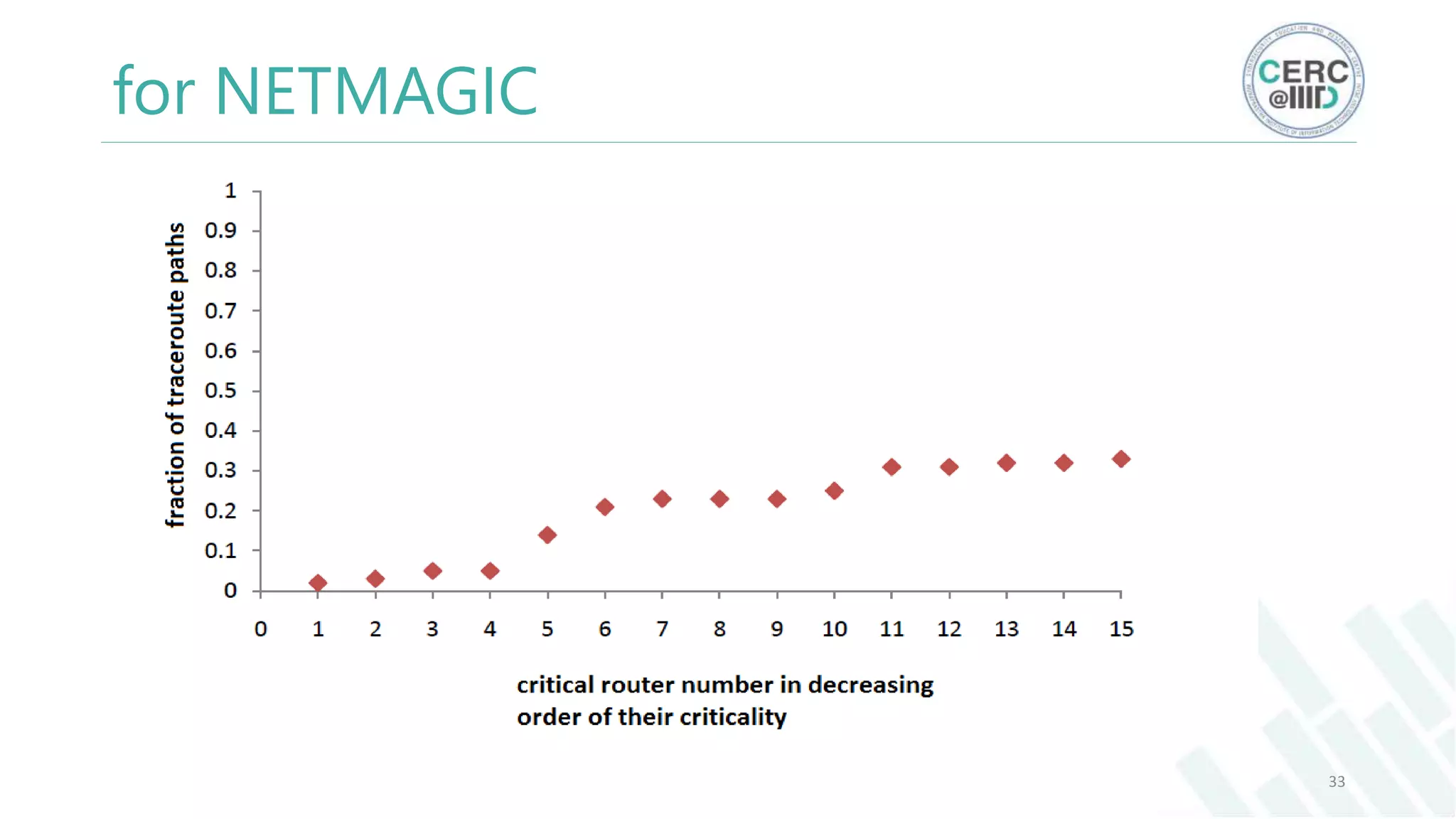
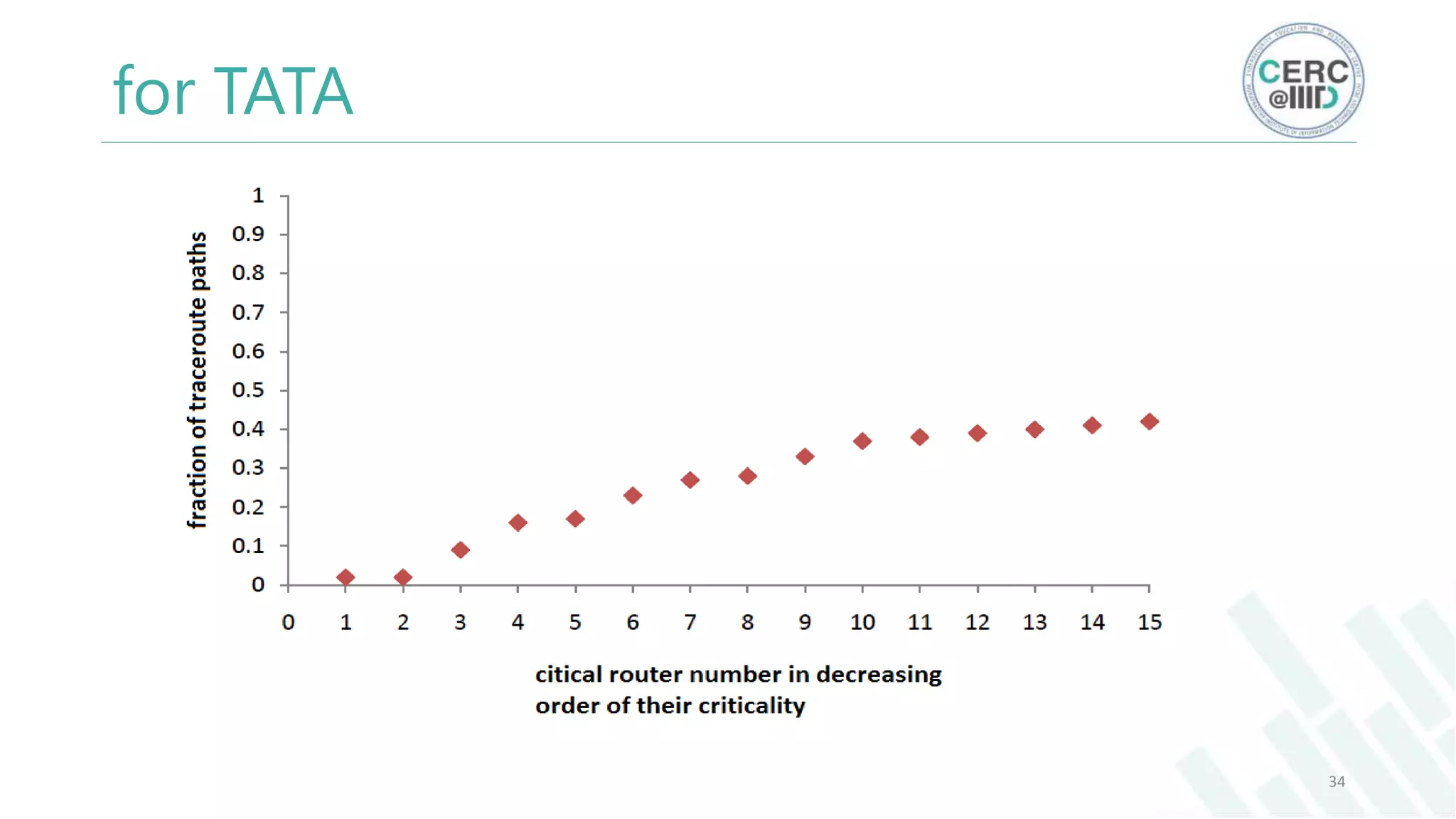
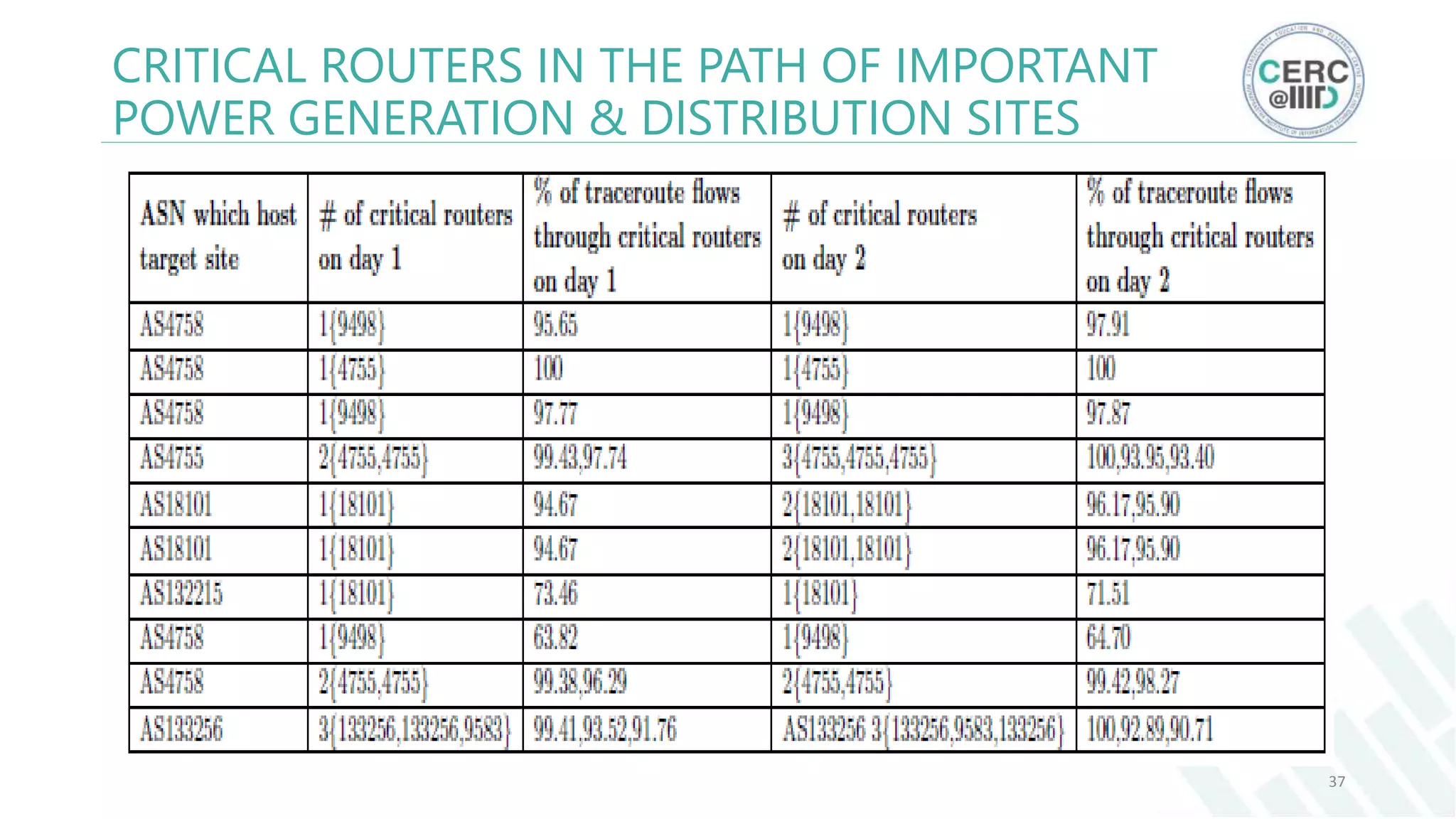
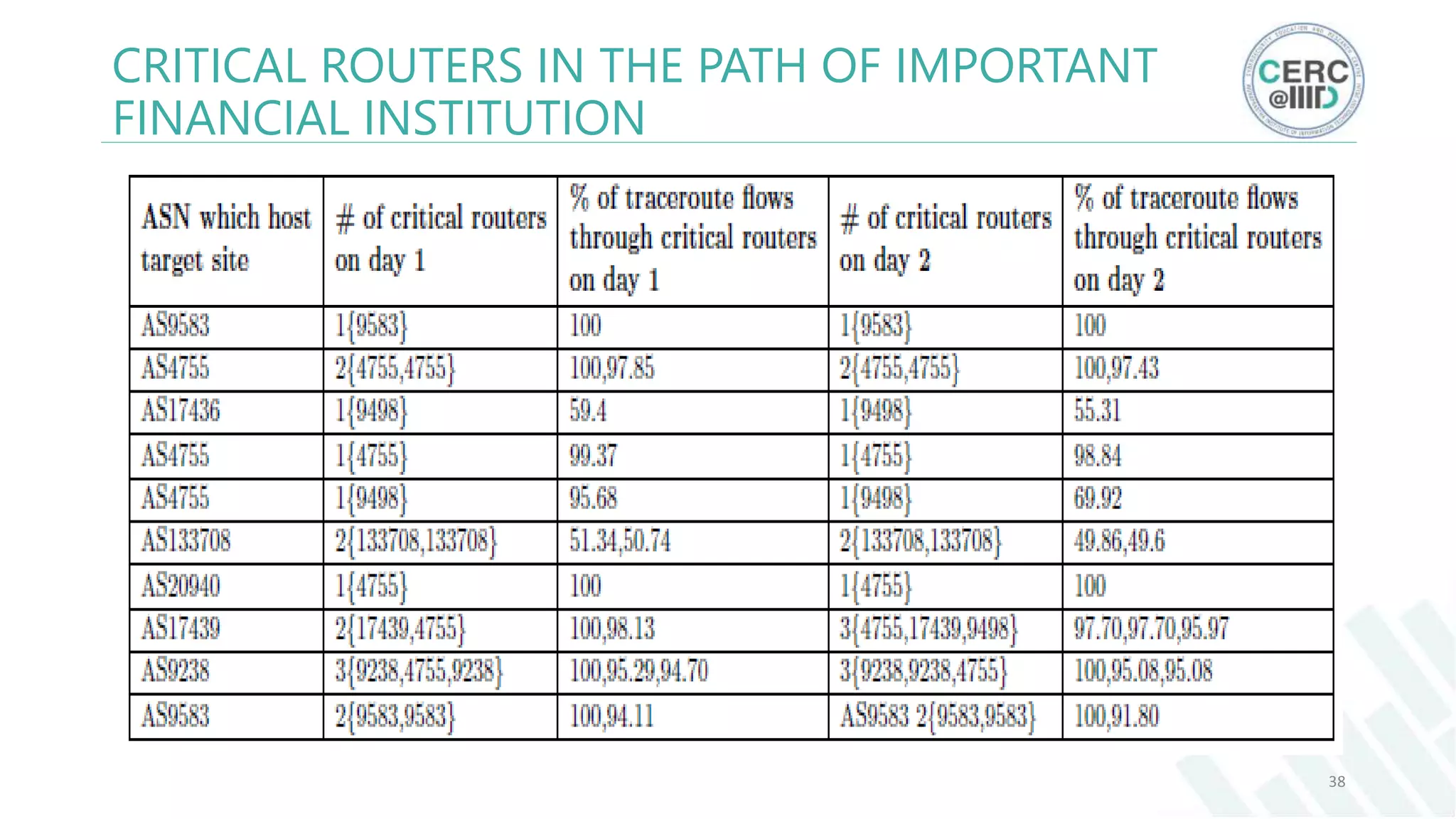
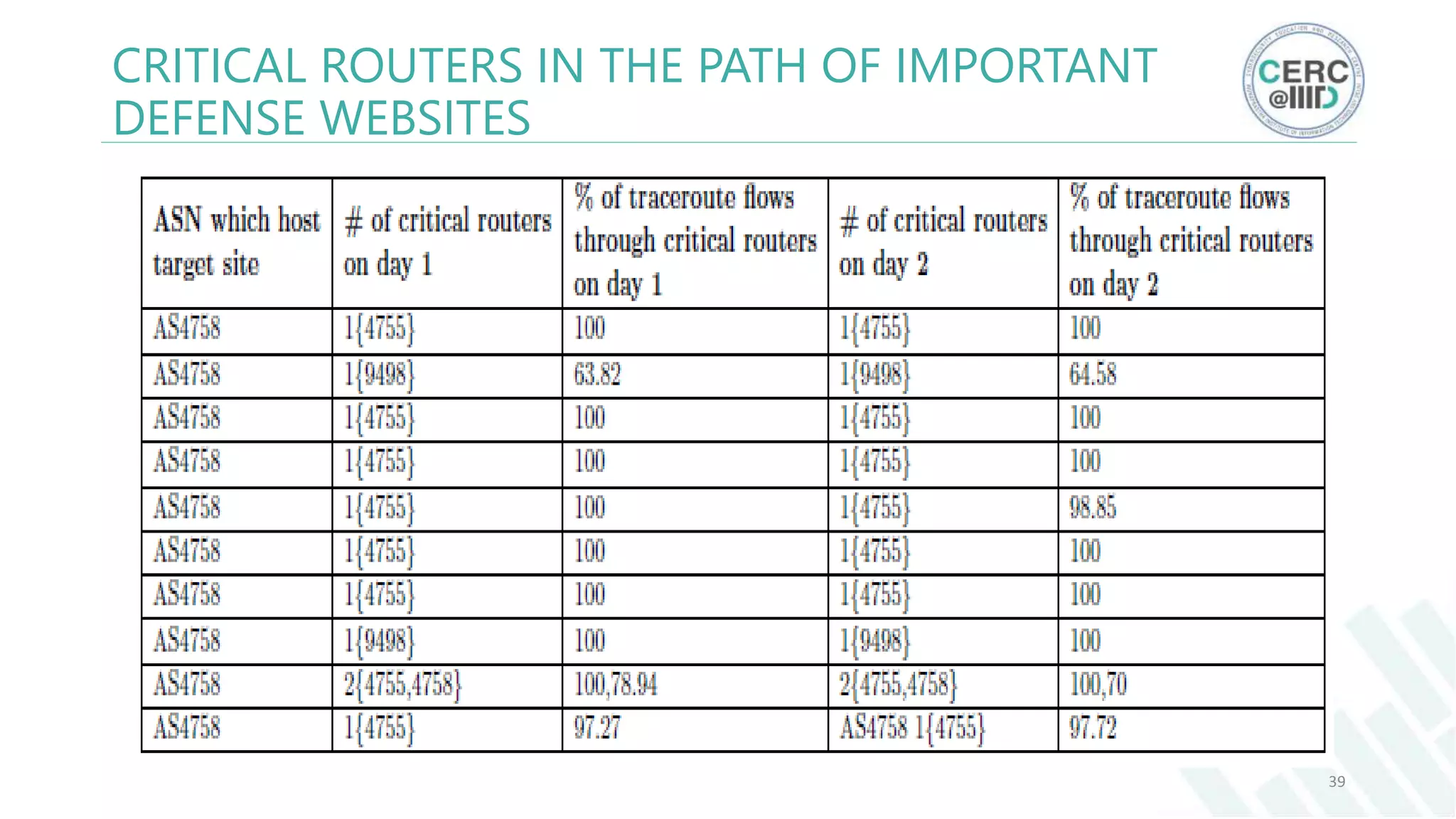
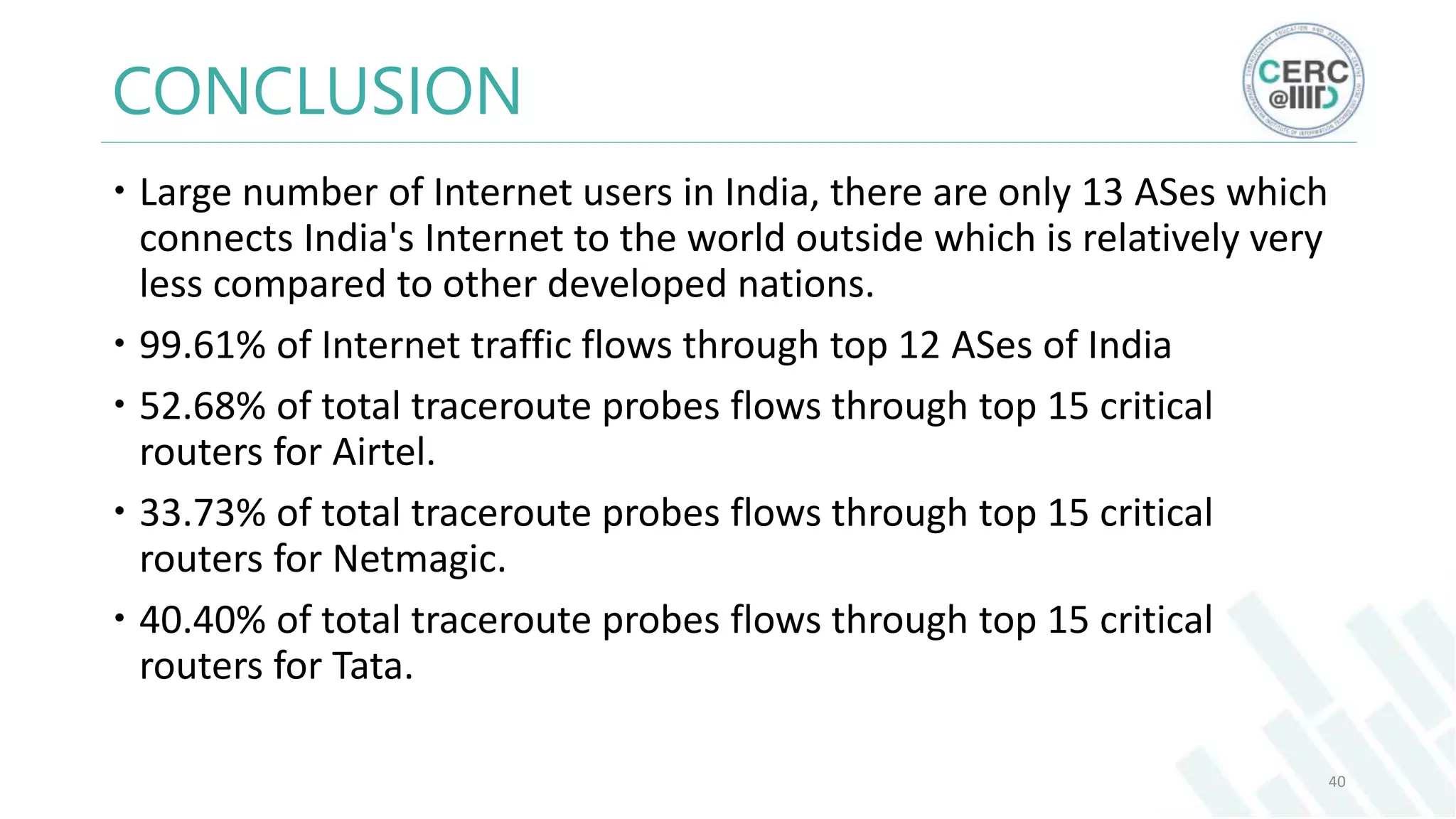
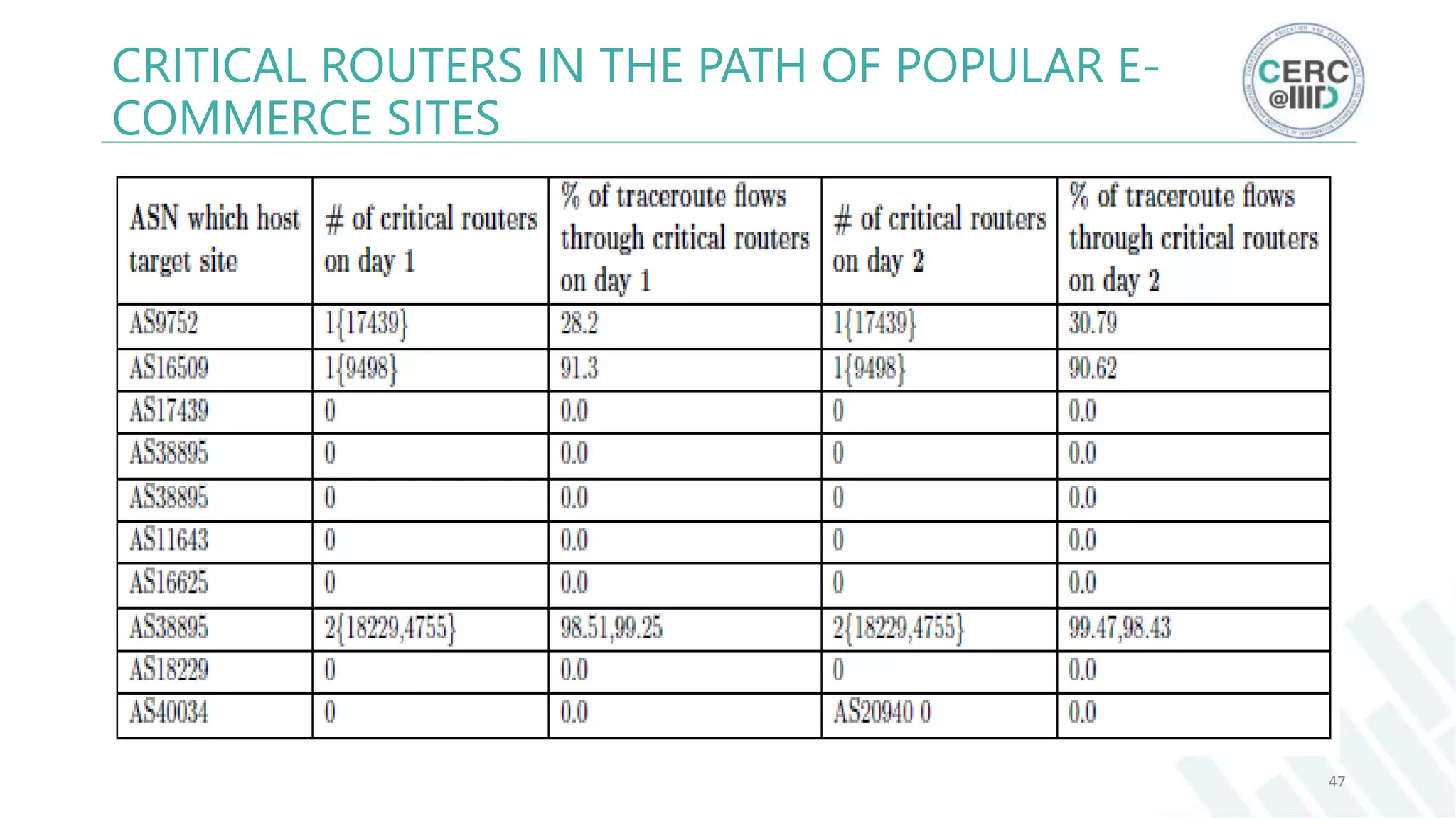
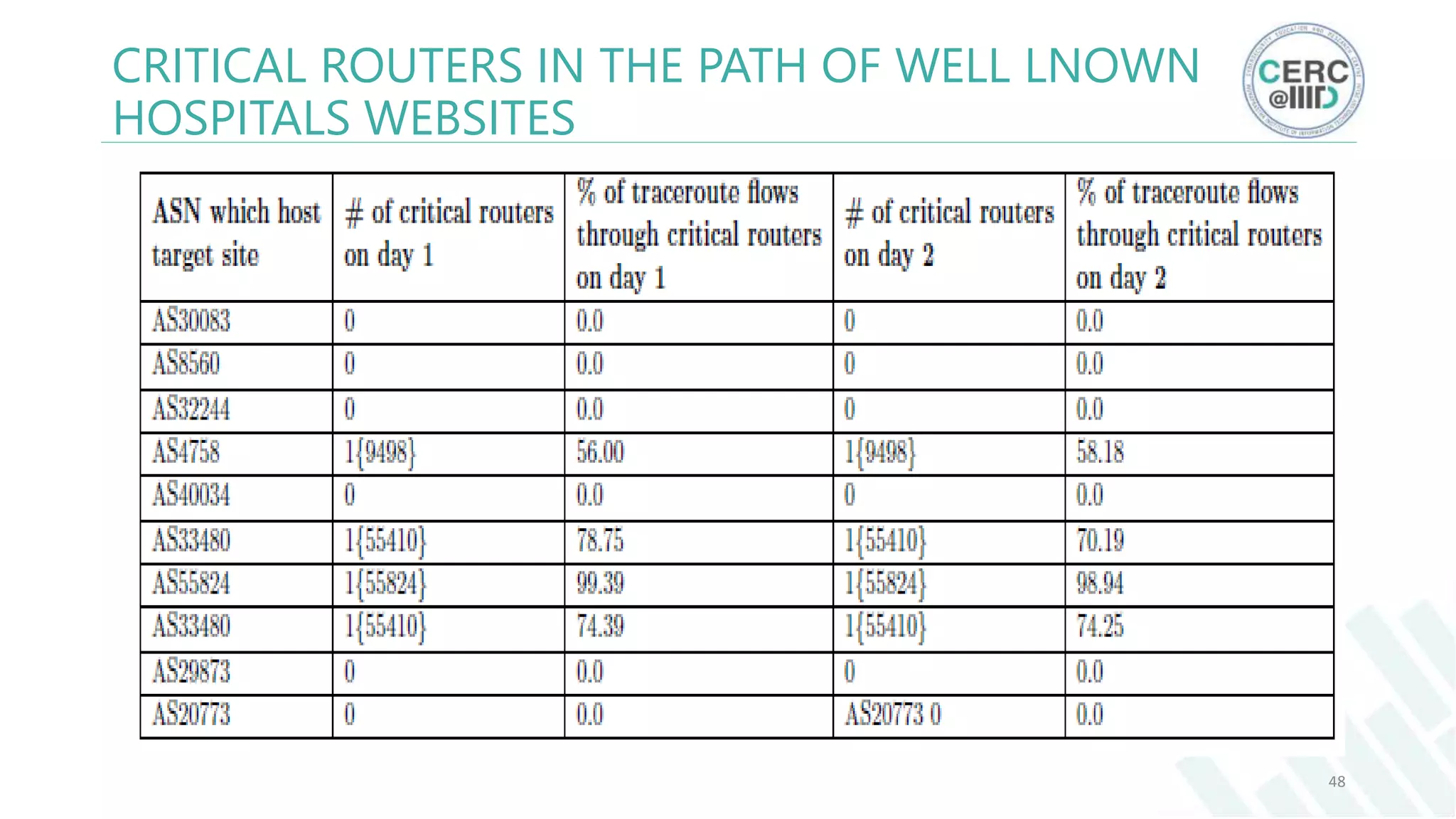
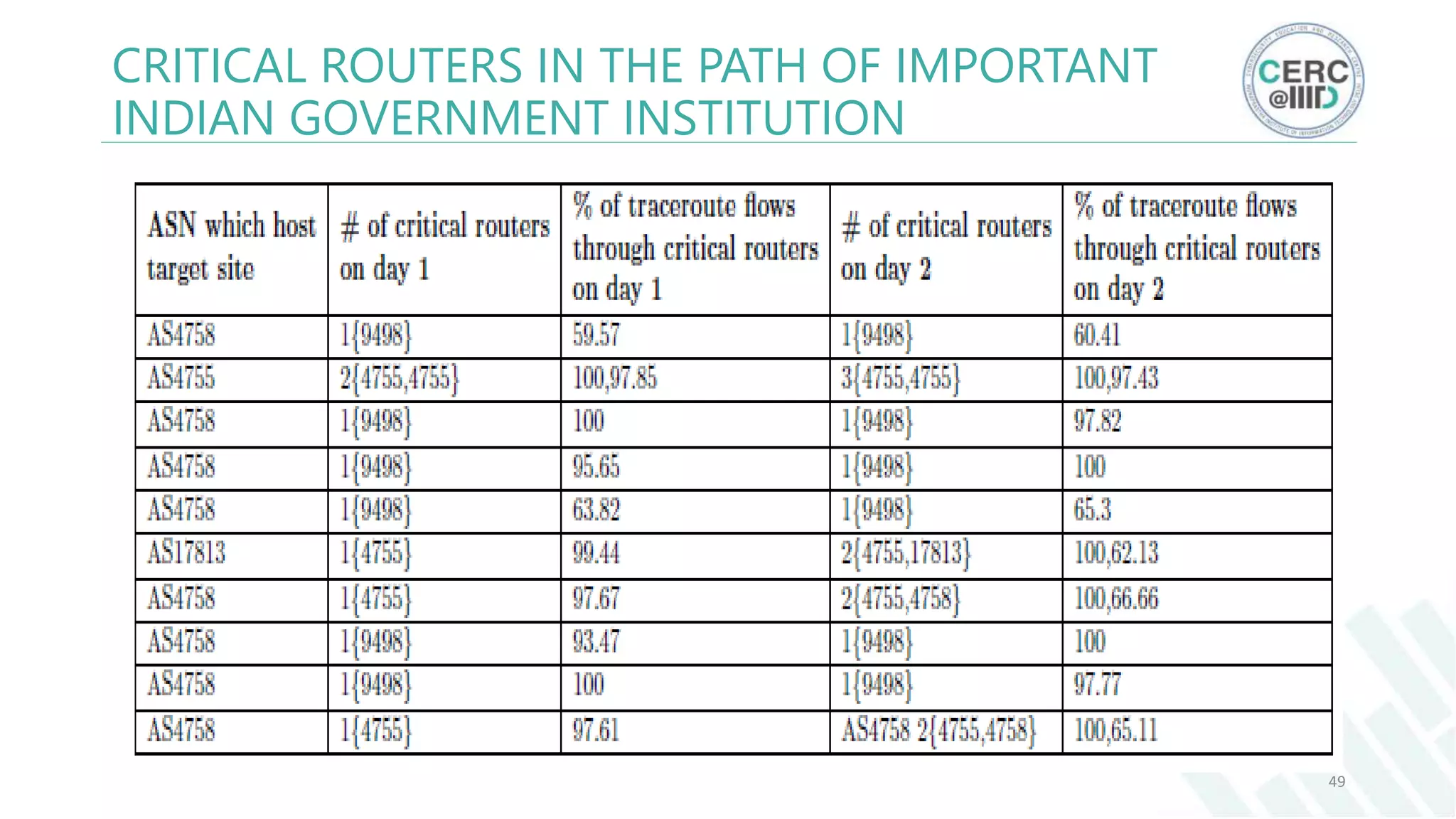
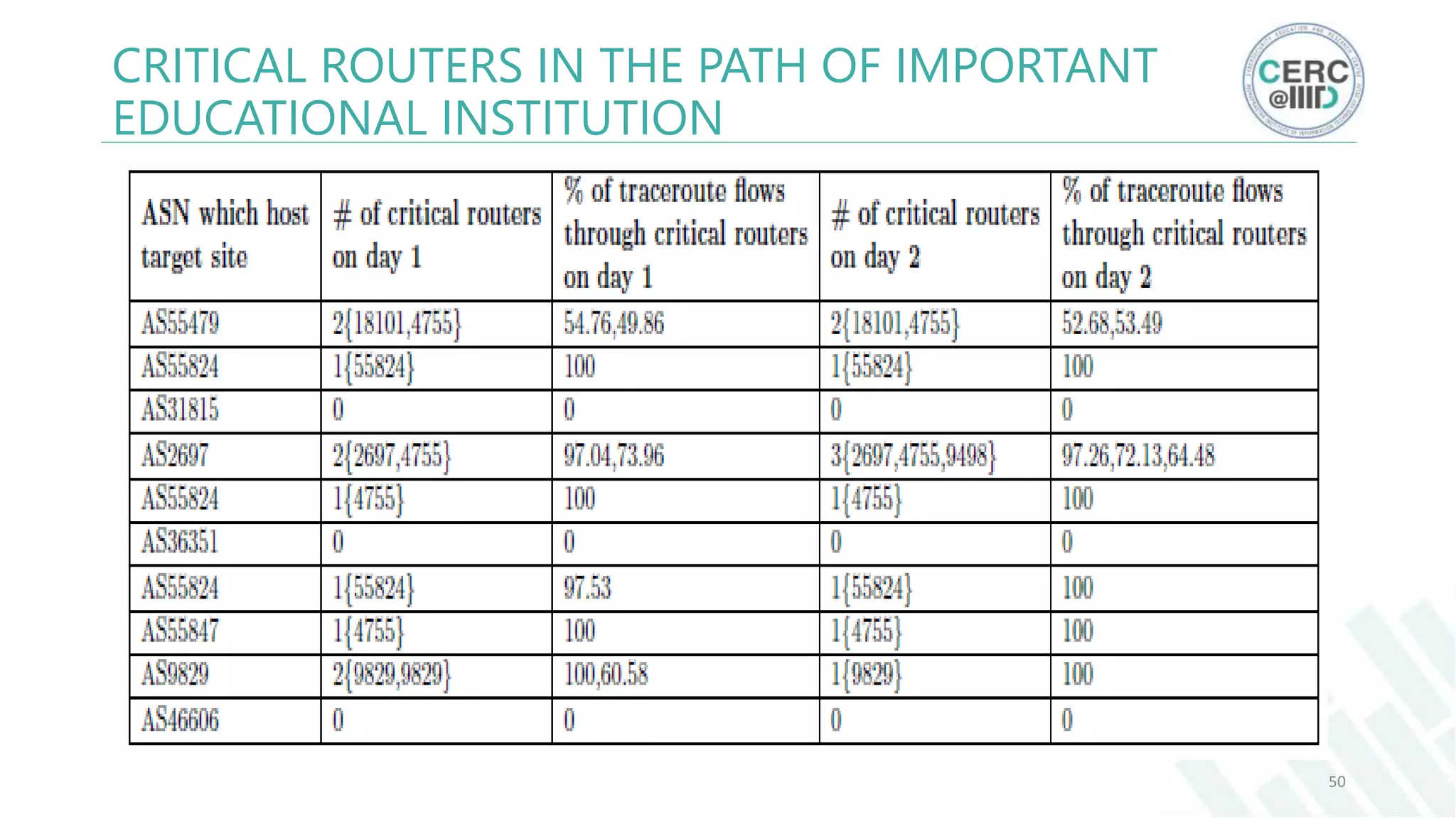
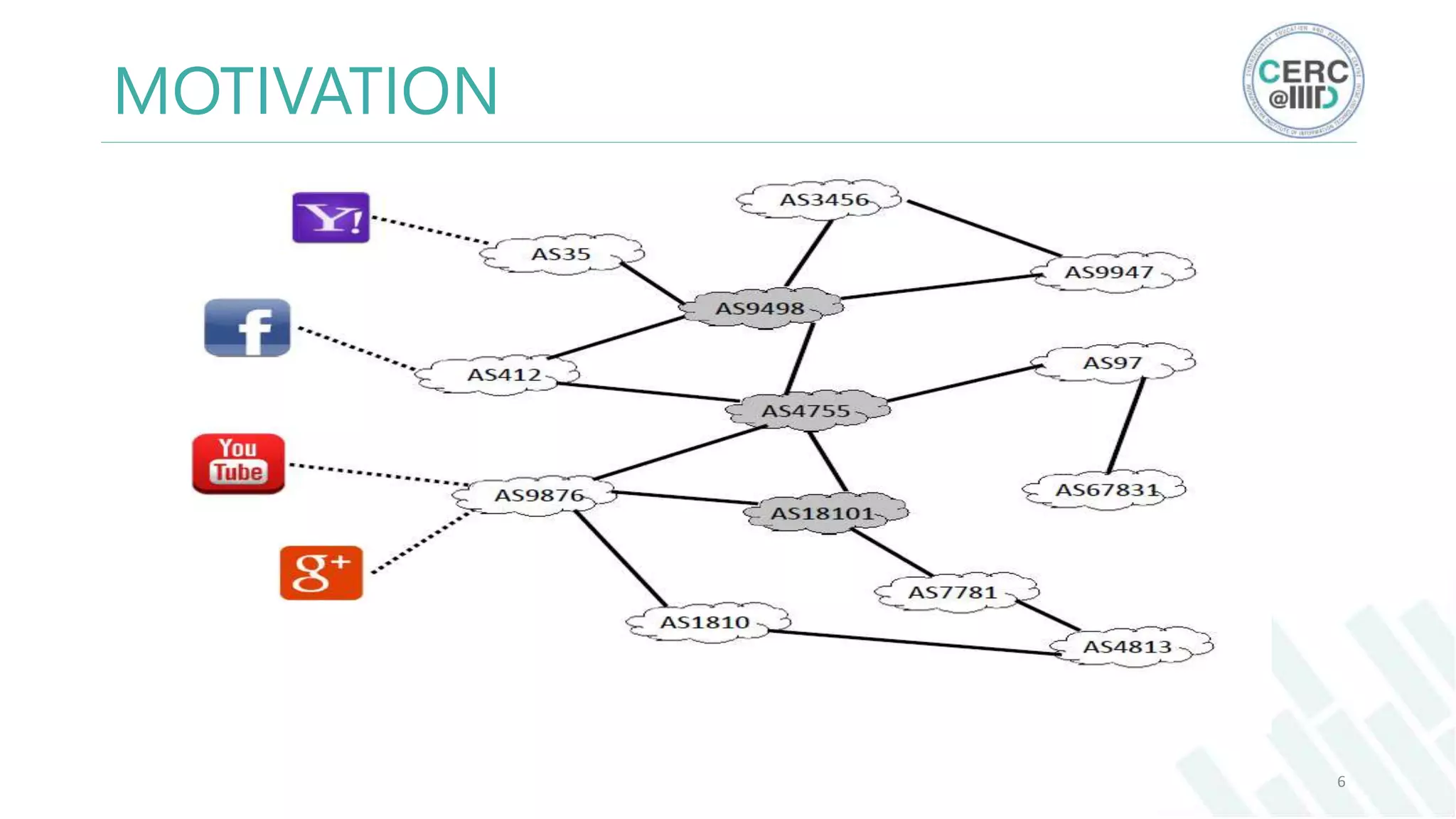
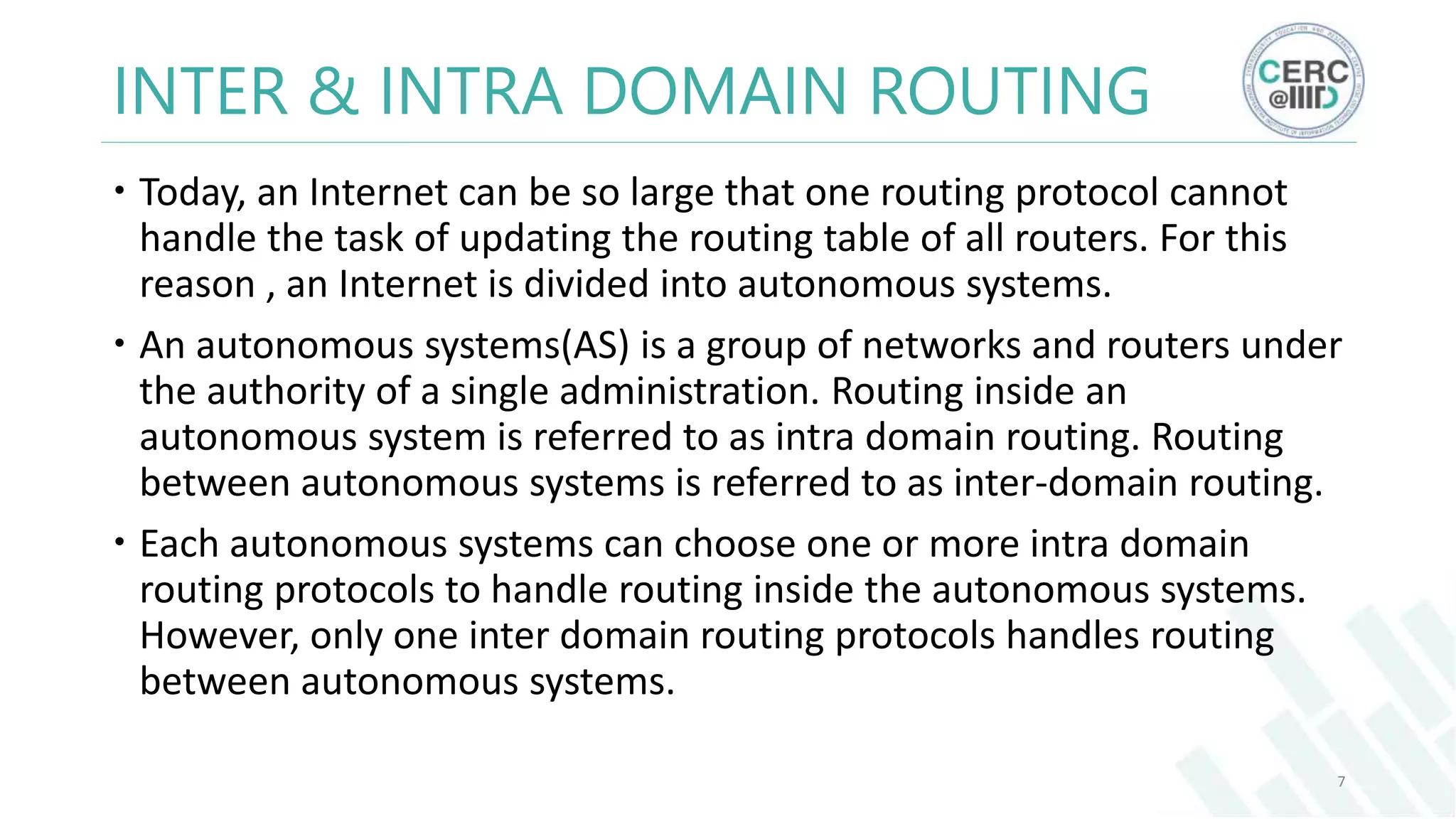
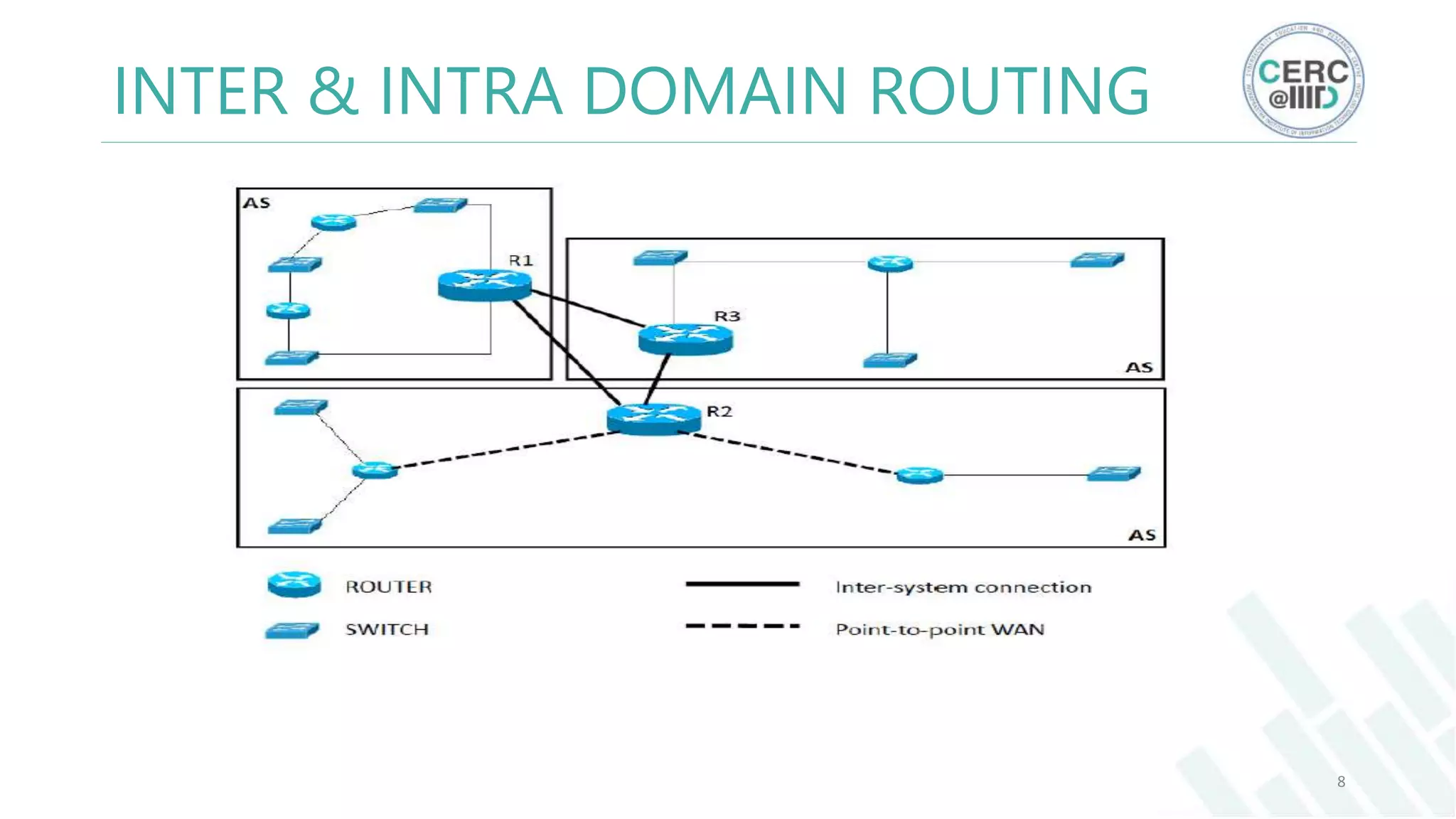
The document is a detailed M.Tech thesis on the topology of India's Internet infrastructure, focusing on the organization of autonomous systems (ASes) and routers. It explores key aspects such as the small number of ASes managing traffic for a large user base, the security implications of network attacks on pivotal nodes, and methodologies for mapping both inter-domain and intra-domain routing. The research findings indicate that a significant fraction of India's internet traffic is funneled through a limited number of ASes and critical routers, raising concerns about the resilience of the network.





![ BGP routing relies on inter AS
relationship[lixin gao, 2001]
the relationships can be classified
into three categories: provider-to-
customer, customer-to-provider
and peer-to-peer.
The customer ISP pays the
provider ISP for transit. A p2p
link connects two ISPs who have
agreed to exchange traffic on a
quid pro quo basis.
9
INTER DOMAIN ROUTING POLICIES a.k.a AS
RELATIONSHIPS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tasveer-150803100415-lva1-app6891/75/TASVEER-Tomography-of-India-s-Internet-Infrastructure-9-2048.jpg)