This document presents an efficient rule-based system for morphological parsing of the Tamil language. It discusses the agglutinative nature of Tamil morphology and the need for morphological analysis in applications such as machine translation. The proposed system uses a combination of rule-based and machine learning approaches to analyze Tamil words and identify their root forms and inflections. It was implemented using resources like the EMILLE corpus and Tamil WordNet and allows for morphological parsing of Tamil texts.





![The problem at handThe problem at hand
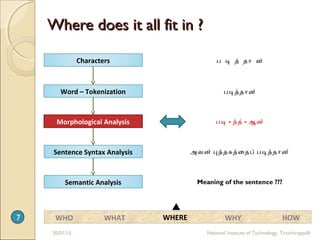
Morphological Analysis of Tamil involves understanding the word structure and its
inflections
AGGLUTINATION IN TAMIL
Agglutination is the morphological process of adding affixes to the base of a word
Typical Tamil verb form will have a number of suffixes showing person, number, mood,
tense and voice.
INFLECTIONS IN TAMIL
Example: vAlntukkontirunt :̣ ̣ ̣ ēṉ [வாழ்ந்துகொகாண்டிருந்ேதேன்]
30/01/15 National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli
WHO WHAT WHYWHERE HOW
vAḷ - வாழ் intu - ந்துக kontụ ̣ - ொகாண்ட irunta - இருந்தே ēn - ஏன்
root voice marker tense marker aspect marker person marker
live past tense
object voice
during past progressive first person,
Singular
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectppt-101107112703-phpapp01/85/Tamil-Morphological-Analysis-6-320.jpg)



![Resources ObtainedResources Obtained
EMILLE – CIIL TAMIL MONOLINGUAL CORPUS
Enabling Minority Language Engineering
Collaborative Venture of
◦ Lancaster University, UK
◦ Central Institute of Indian Languages (CIIL), Mysore, India
Distributed by European Language Resources Association [ELRA]
TAMIL WORDNET
The database is a semantic dictionary that is designed as a lexical network
Developed by
◦ Department of Linguistics ofTamil University
◦ AU-KBC Research Centre, Chennai
Tamil Wordnet resembles a traditional dictionary. It also contains valuable
information about morphologically related words
30/01/15 National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli
WHO WHAT WHYWHERE HOW9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectppt-101107112703-phpapp01/85/Tamil-Morphological-Analysis-11-320.jpg)




![ReferencesReferences
A Novel Approach to Morphological Analysis forTamil Language
◦ Anand kumar M1, DhanalakshmiV1, Rajendran S2, Soman K P
Nannool and Tholkaapiyam
◦ Tamil Grammar texts
The Morphological Generator and Parsing Engine forTamilVerb Forms.
◦ Ultimate Software Solution, Dindigul
Morphological Analyzer forTamil
◦ Anandan. P, Ranjani Parthasarathy, Geetha T.V. [2002]
◦ ICON 2002, RCILTS-Tamil,Anna University, India.
Morphology.A Handbook on Inflection andWord Formation
◦ Daelemans Walter, G. Booij, Ch. Lehmann, and J. Mugdan (eds.) [2004]
Tamil Part-of-Speech tagger based on SVMTool
◦ DhanalakshmiV,Anandkumar M,Vijaya M.S, Loganathan R, Soman K.P, Rajendran S [2008]
◦ Proceedings of the COLIPS International Conference on Asian Language Processing 2008 (IALP).
Unsupervised Learning of the Morphology of a Natural Language.
◦ John Goldsmith. [2001]
◦ Computational Linguistics, 27(2):153–198.
Computational morphology of verbal complex
◦ Rajendran, S.,Arulmozi, S., Ramesh Kumar,Viswanathan, S. [2001]
◦ Paper read in Conference at Dravidan University, Kuppam, December 26-29, 2001.
30/01/15 National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectppt-101107112703-phpapp01/85/Tamil-Morphological-Analysis-17-320.jpg)
