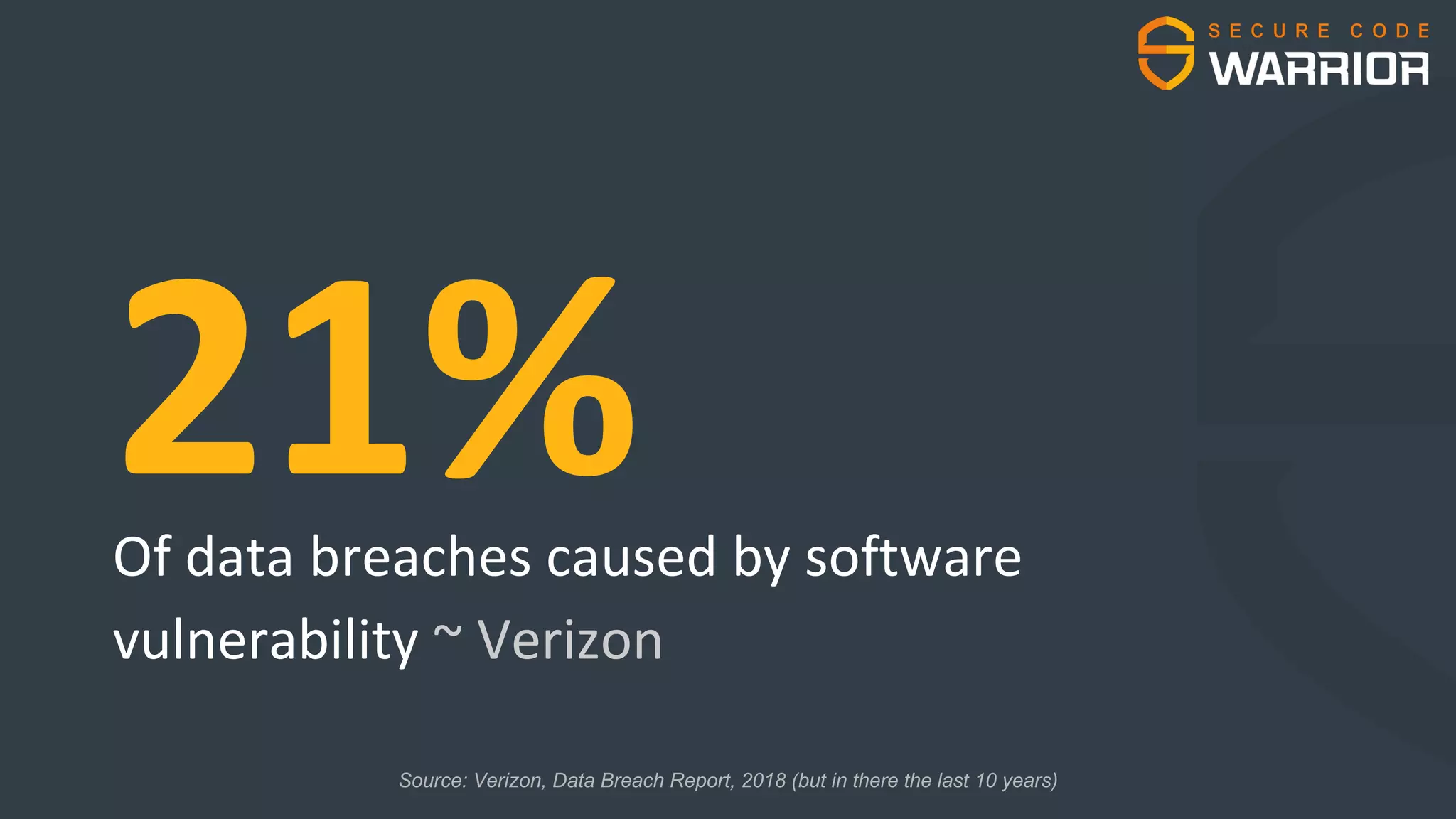
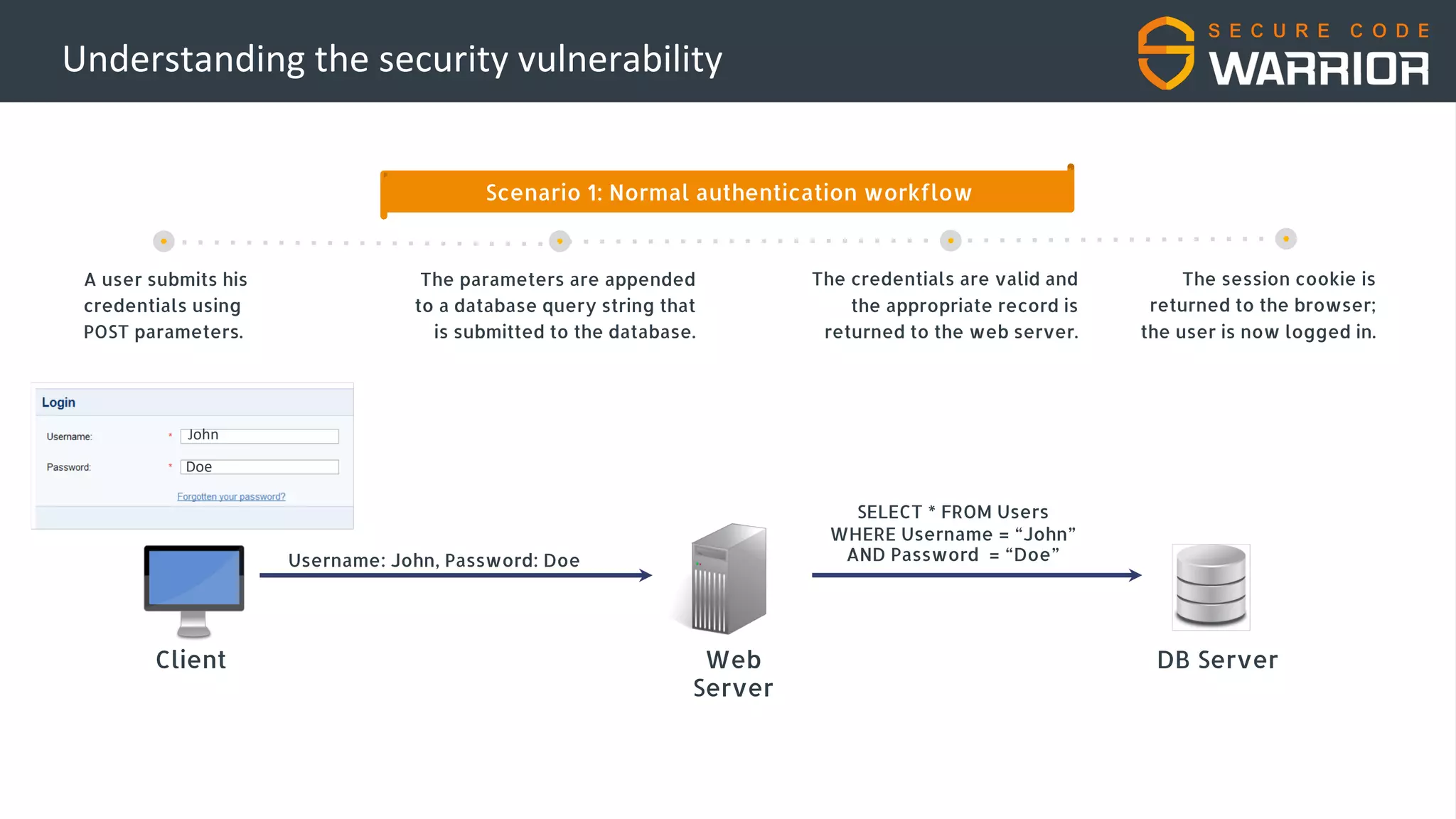
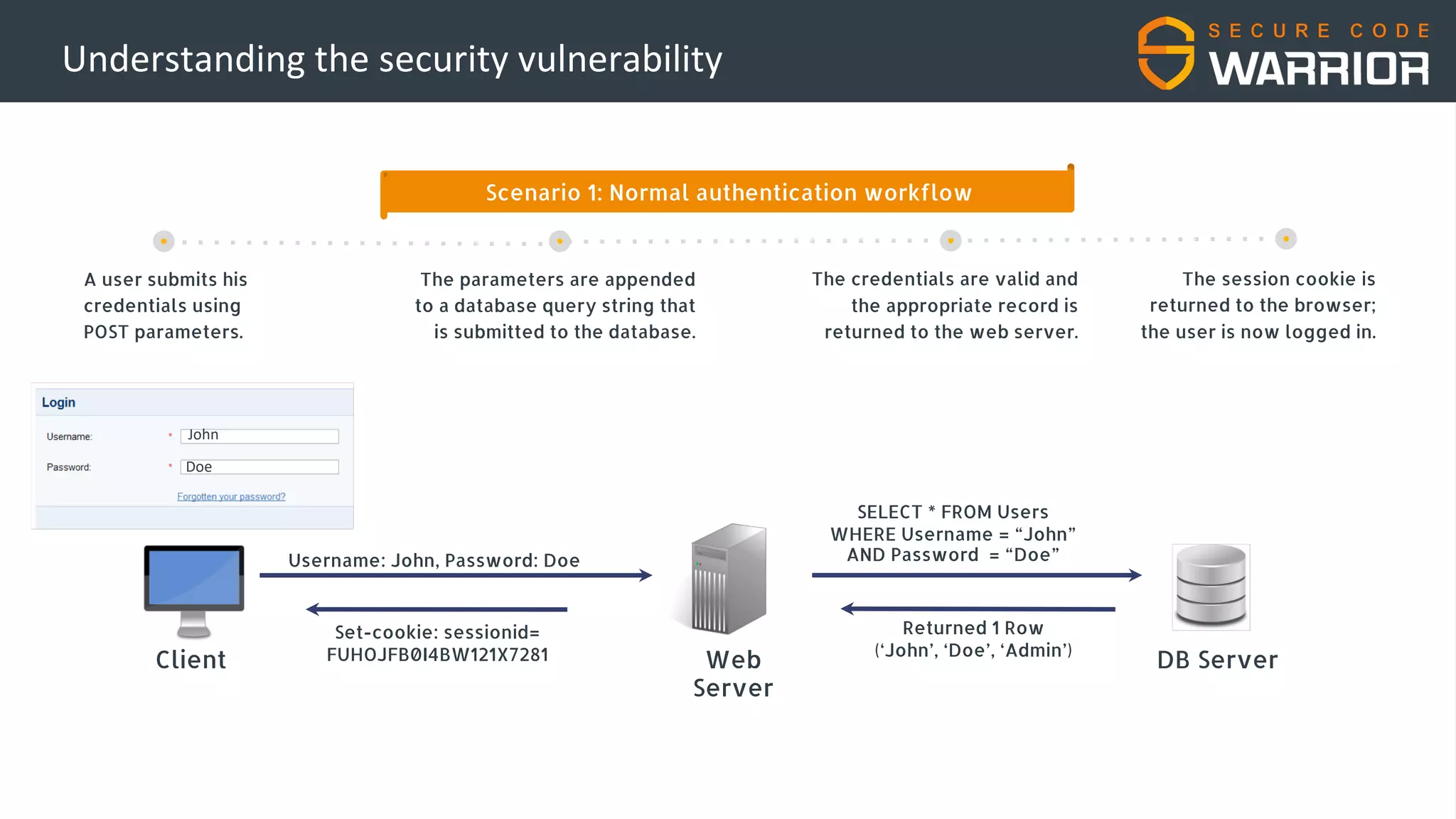
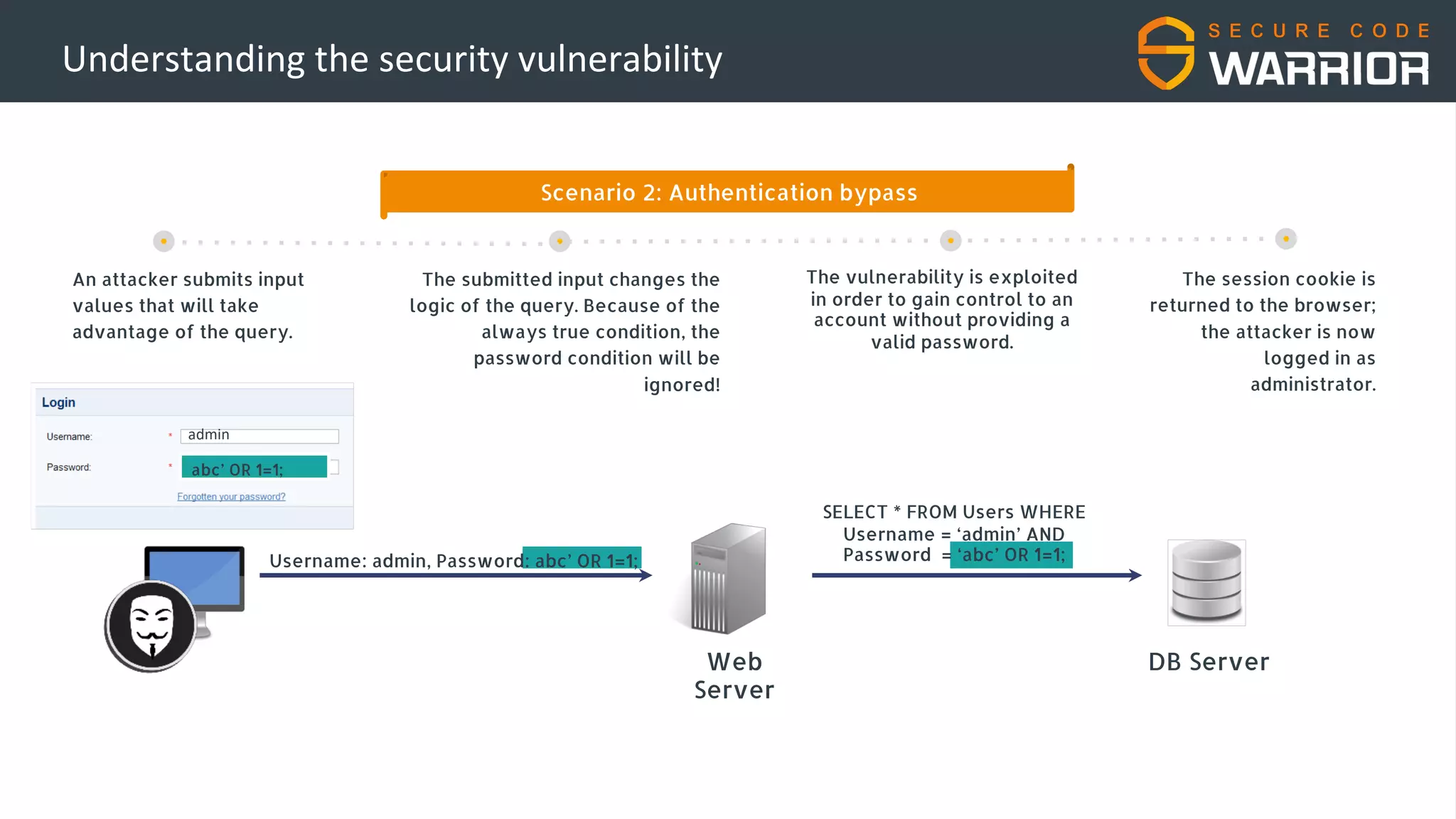
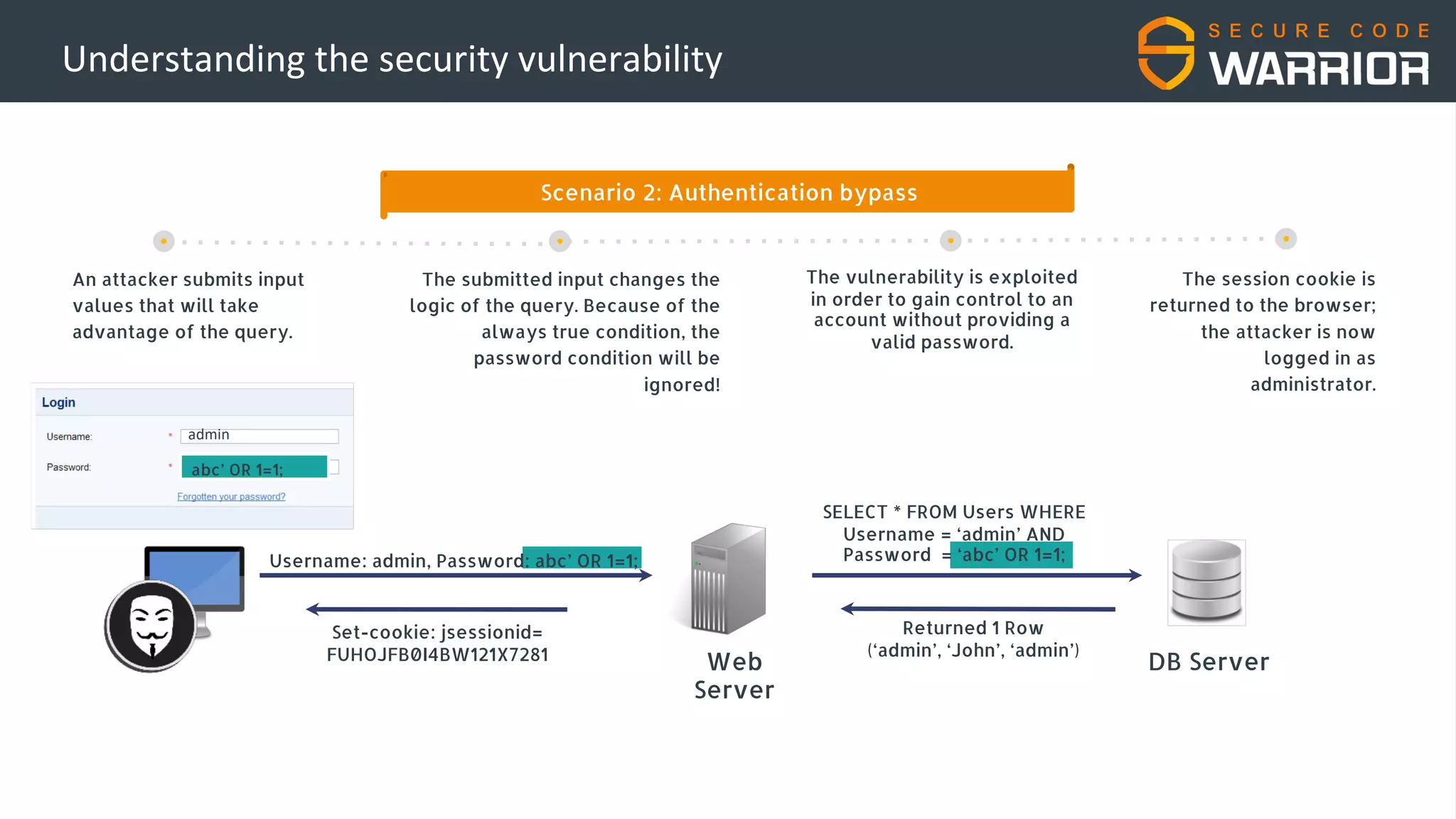
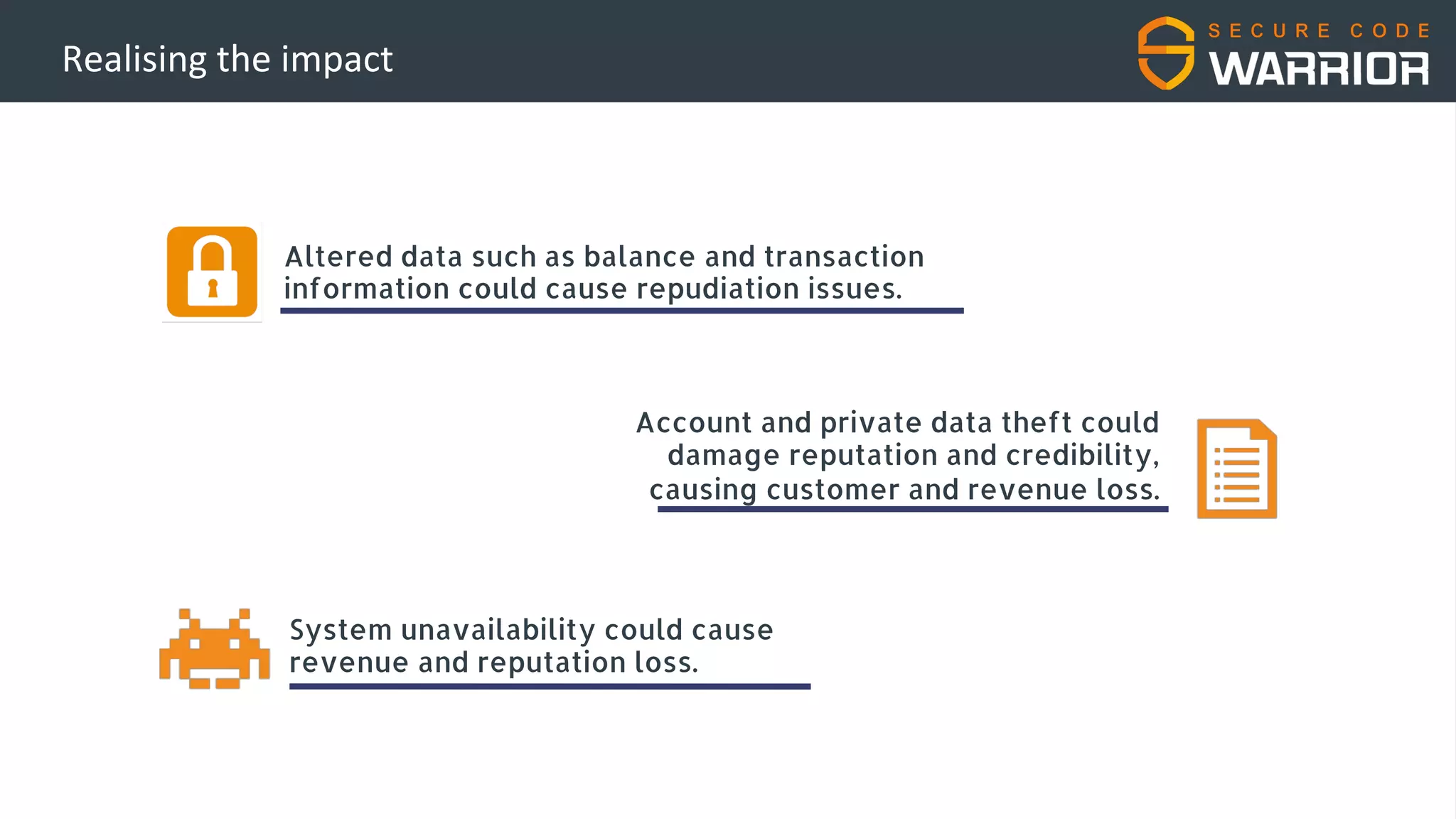
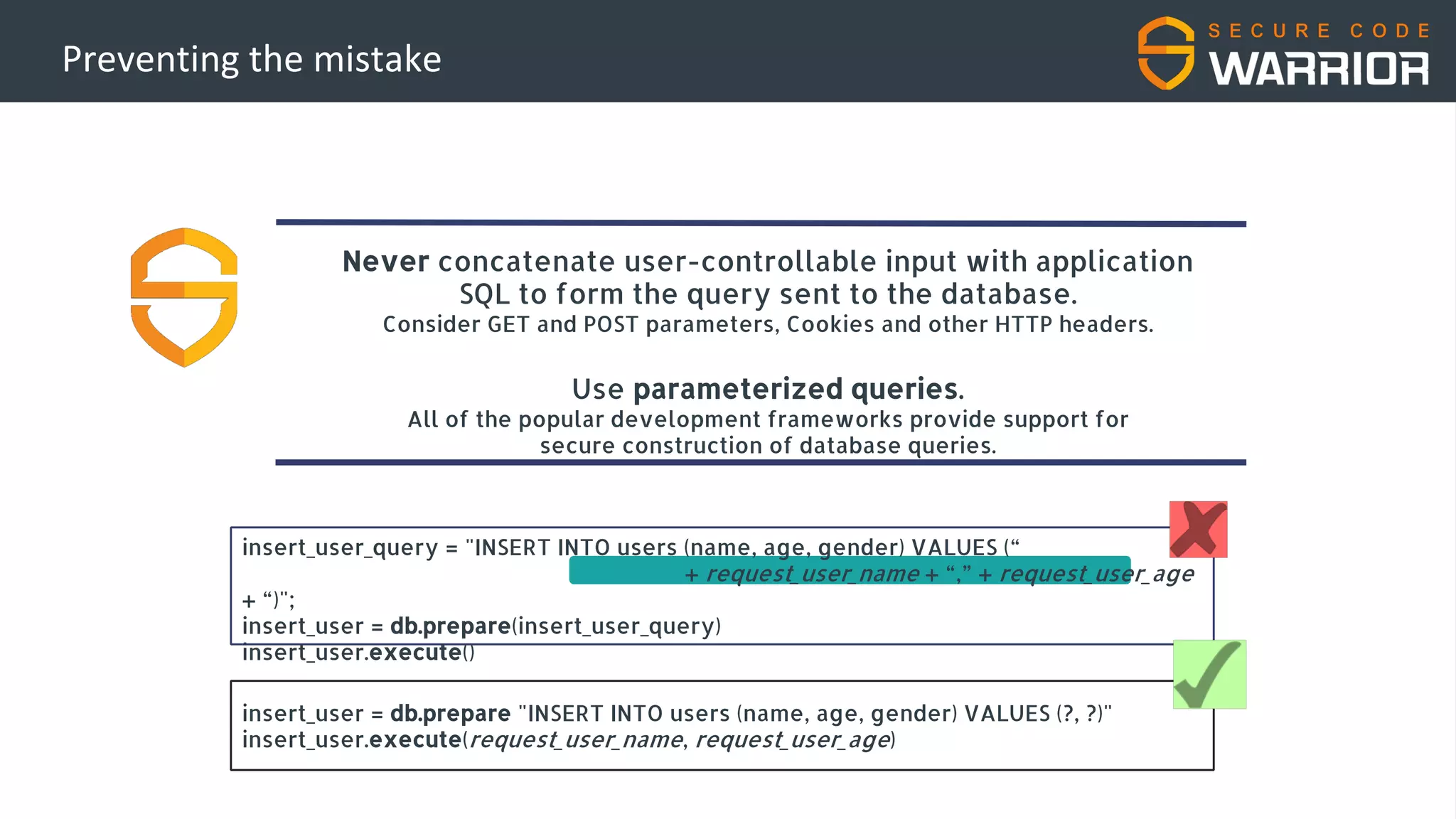
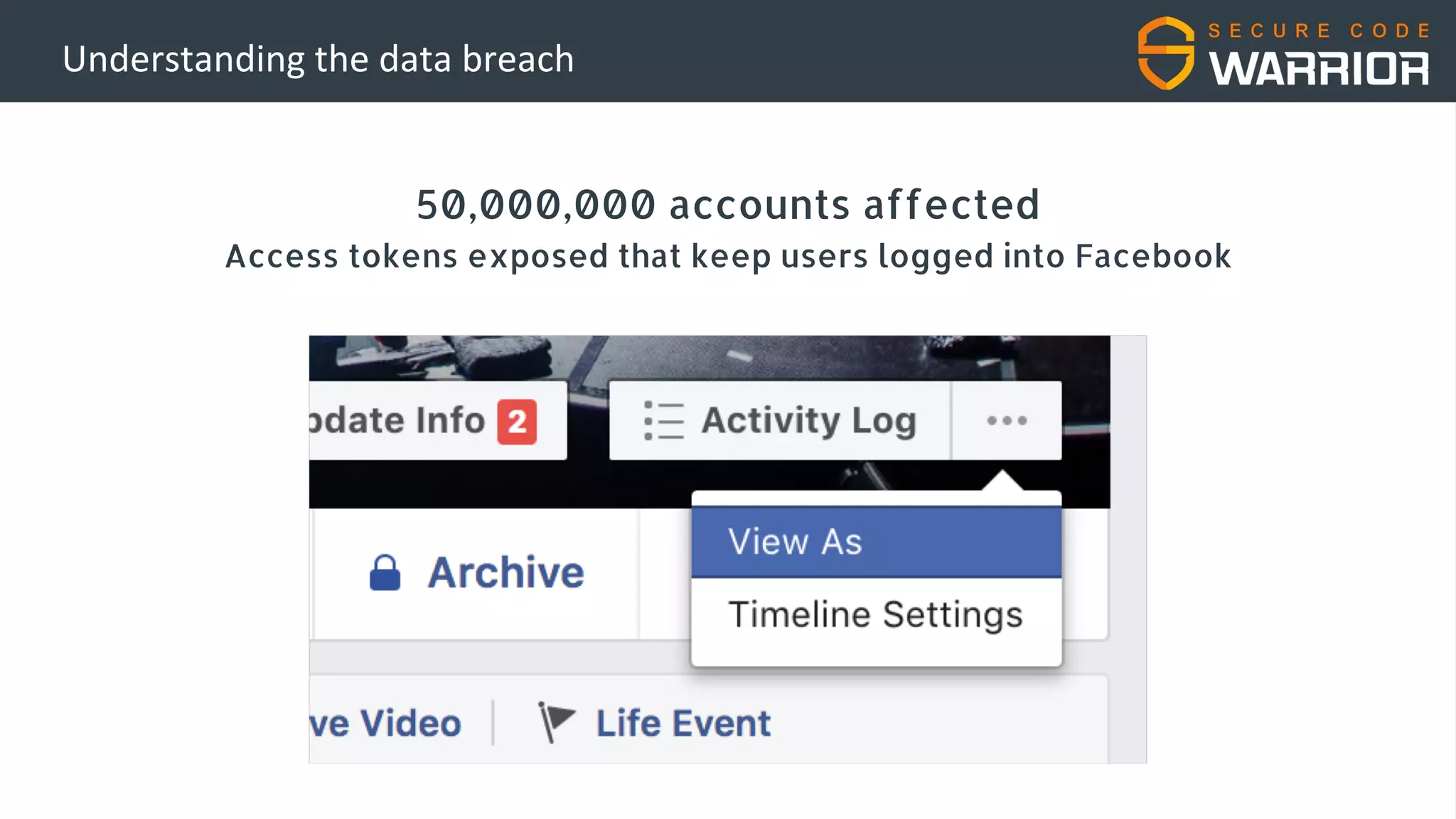
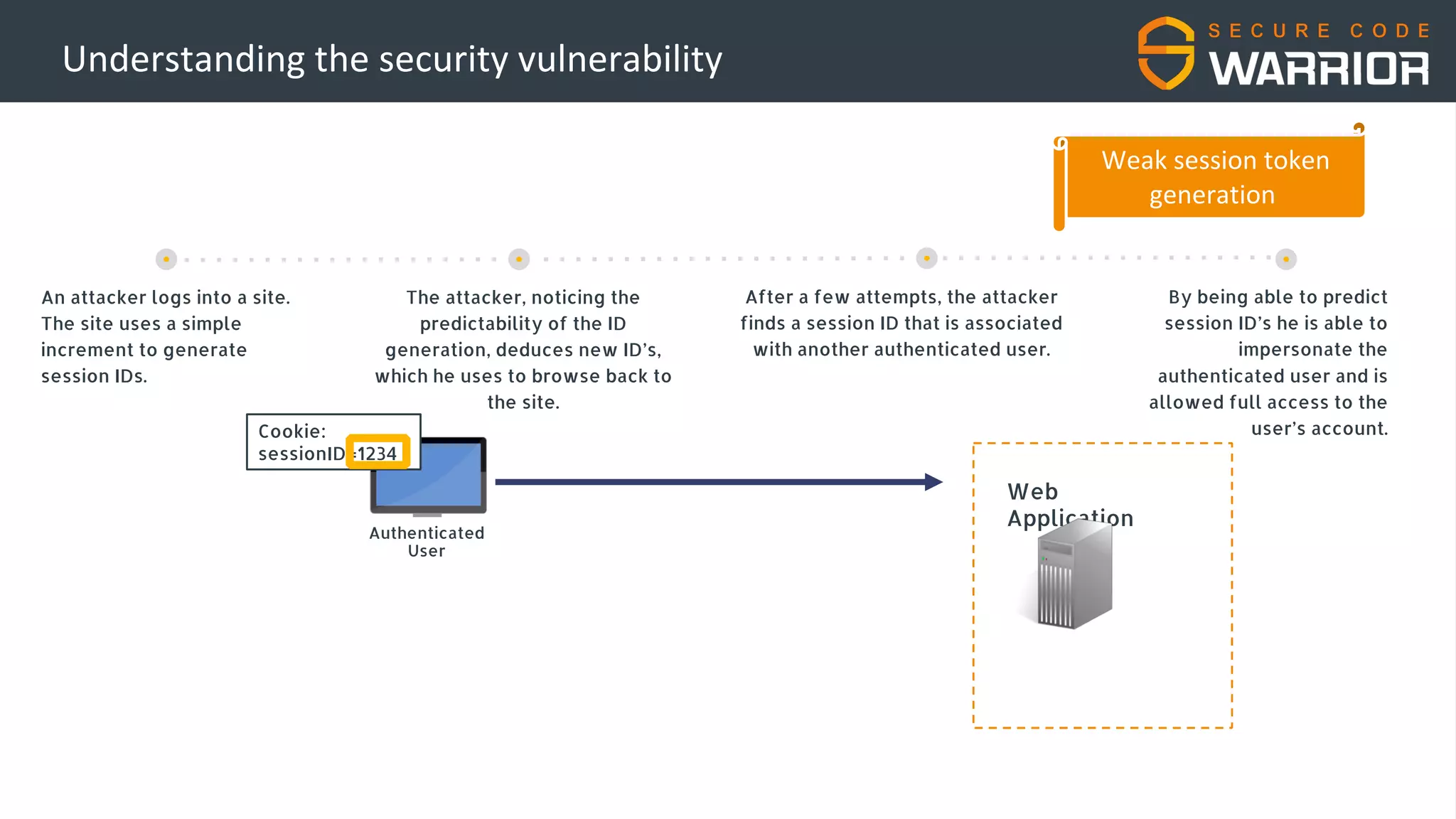
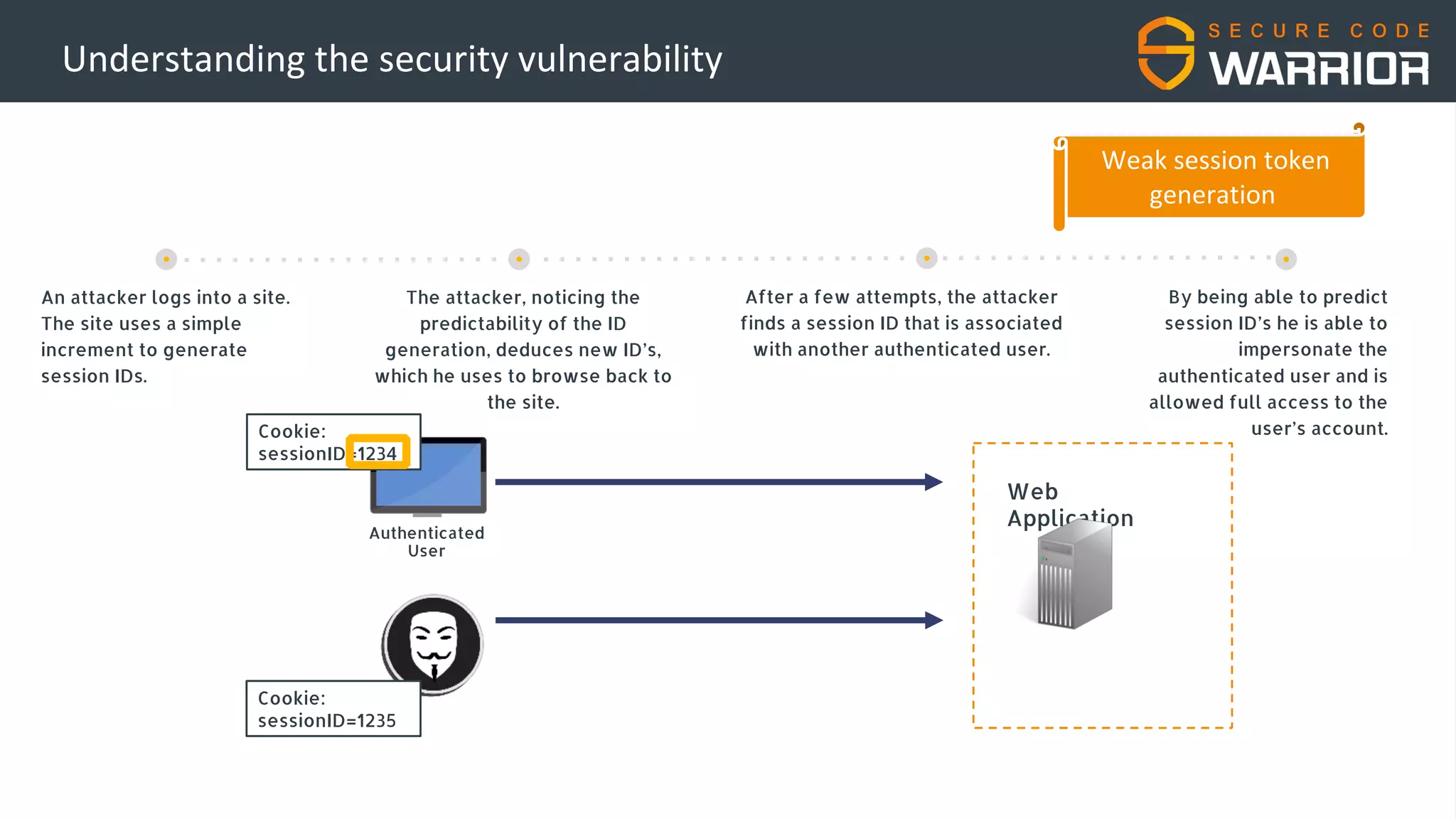
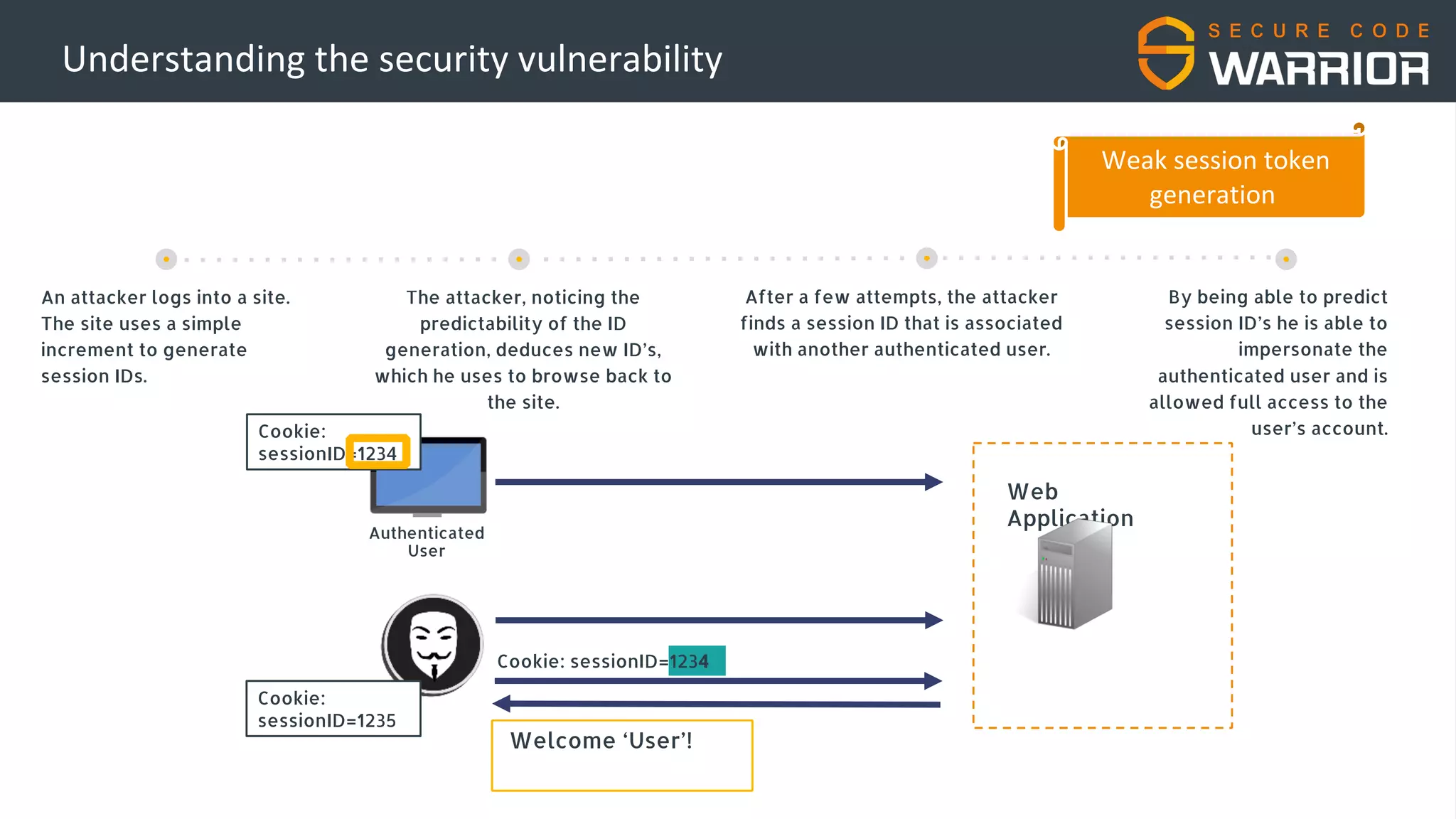
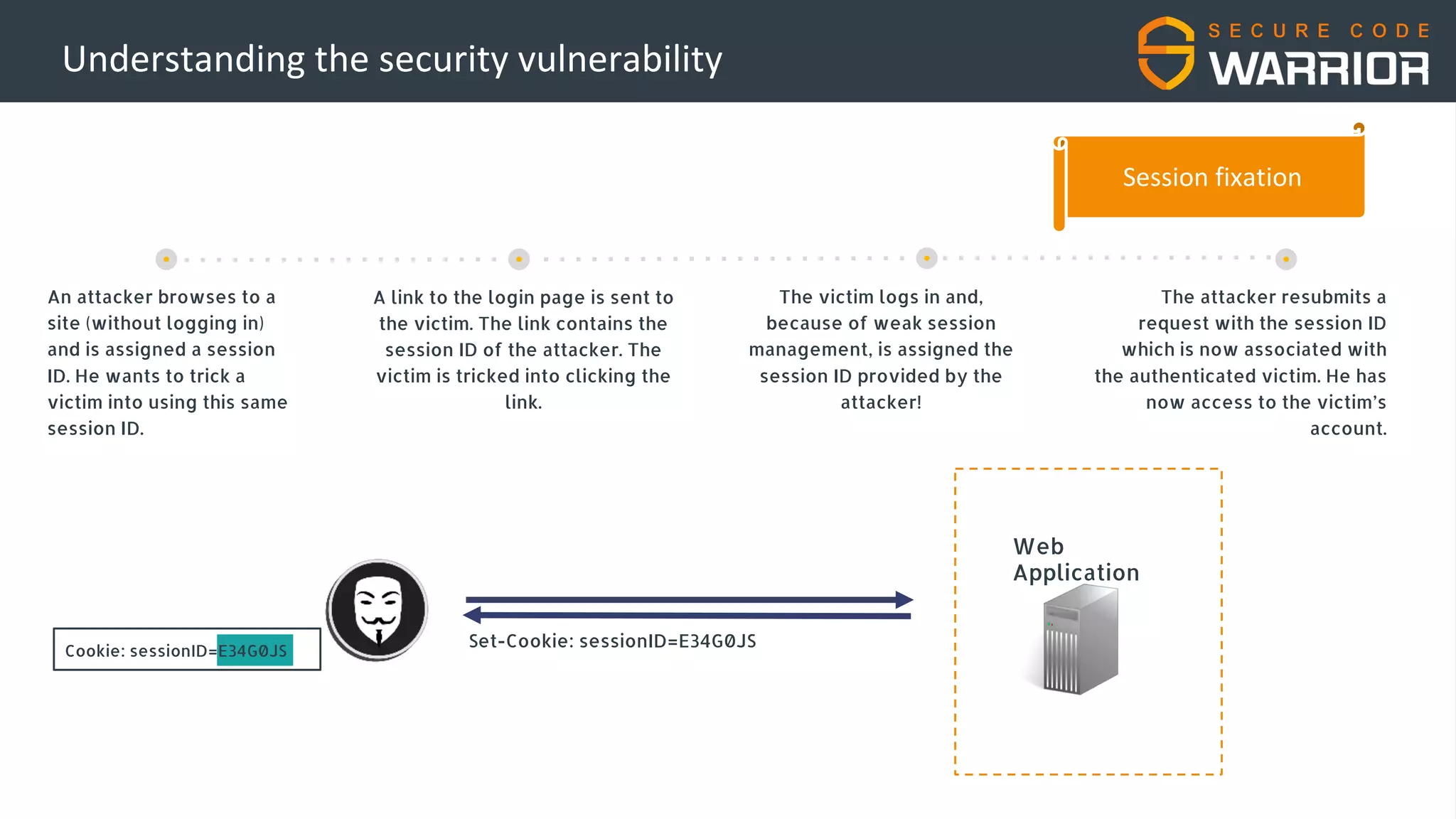
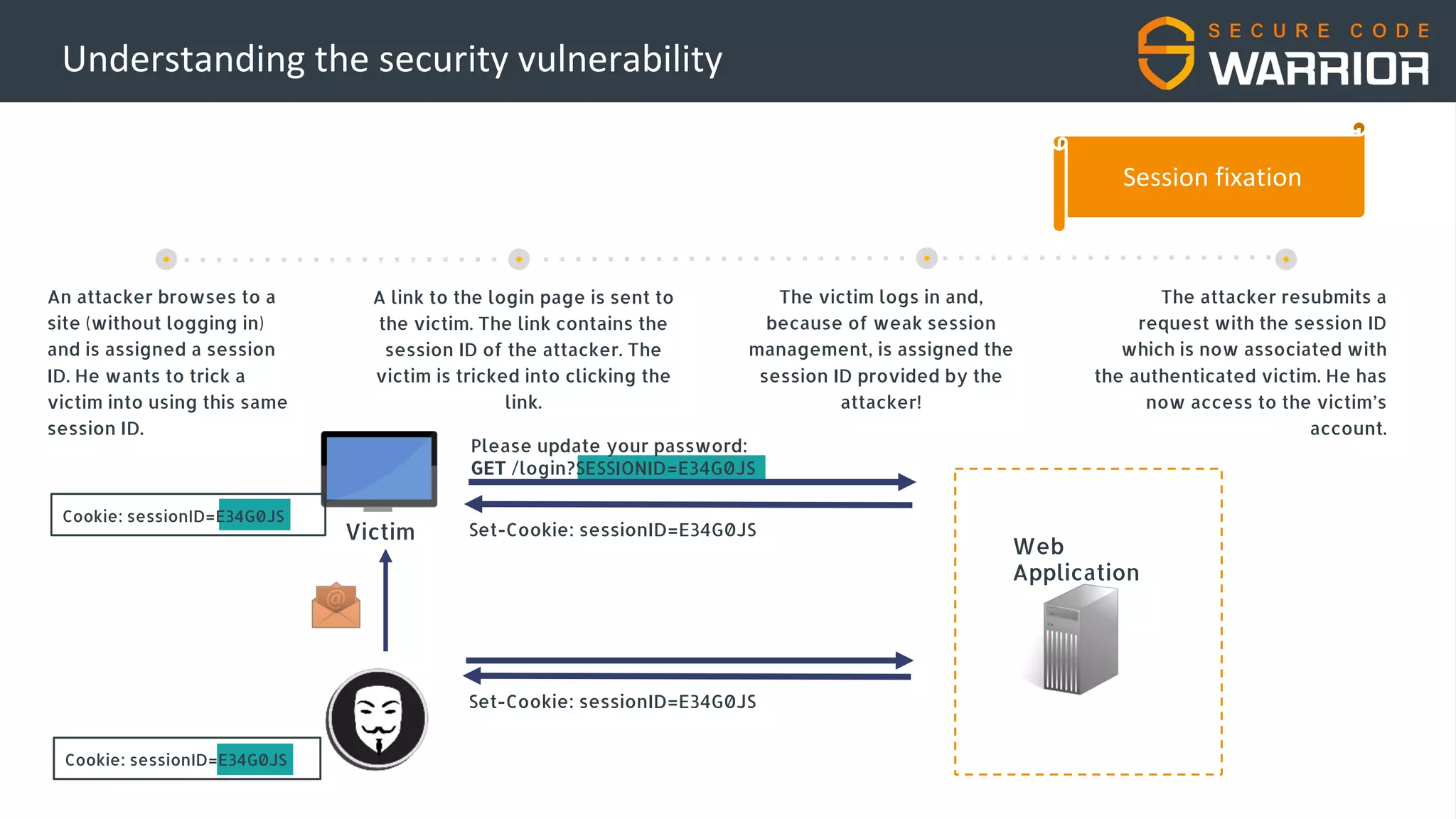
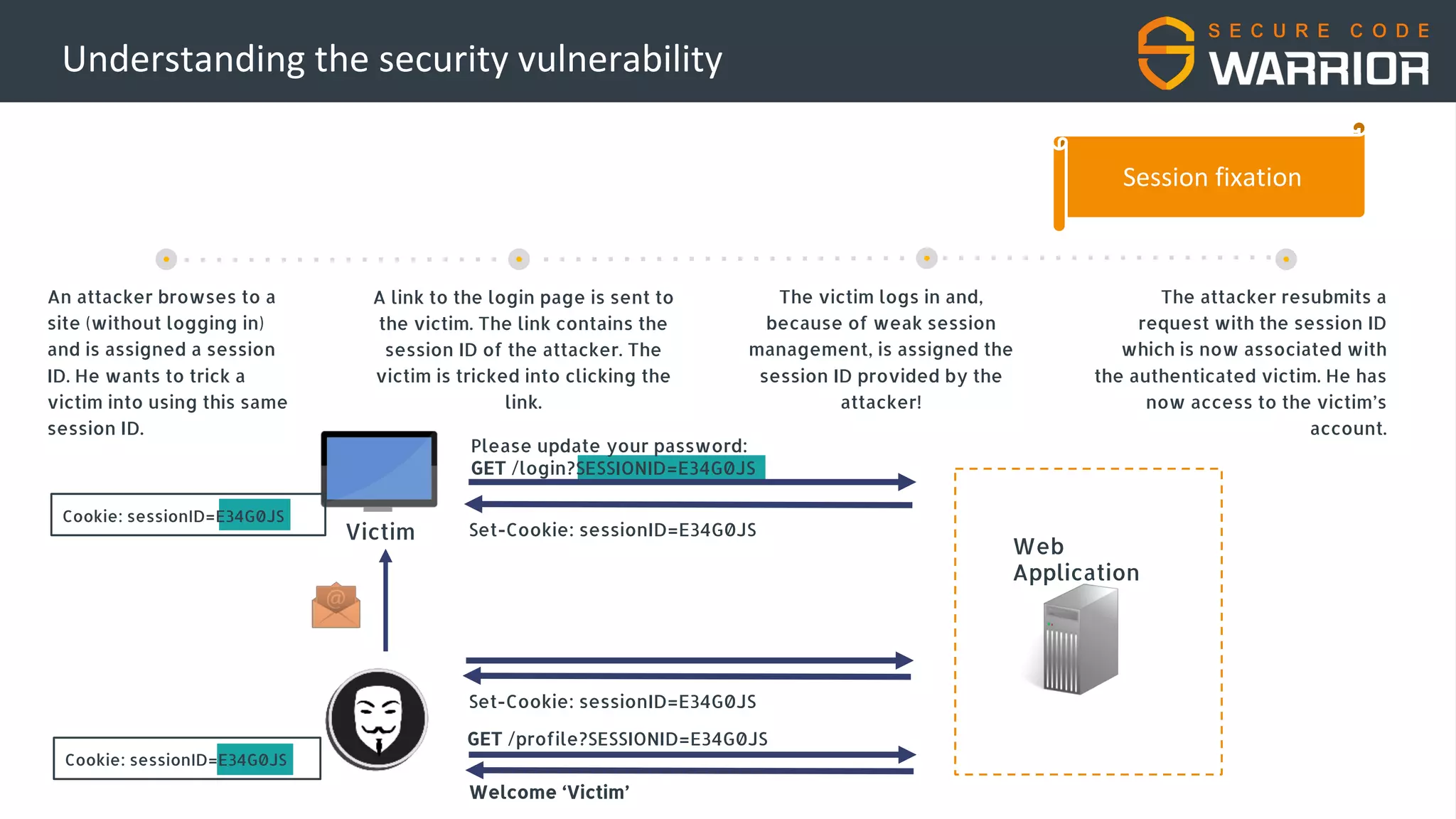
This document discusses common web application security vulnerabilities like SQL injection and insecure session management that can lead to data breaches. It provides examples of how vulnerabilities in user authentication and session handling can be exploited to compromise accounts or perform account takeovers. The key lessons are that all user input should be sanitized and parameterized queries used to prevent SQL injection. Session IDs also need to be unpredictable, time limited, and their transport secured to prevent session hijacking attacks. Secure development practices like least privilege access and secure coding guidelines are recommended to build applications securely.