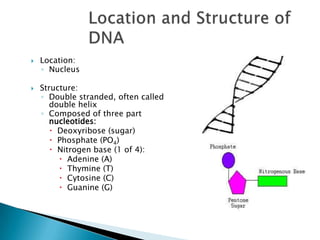
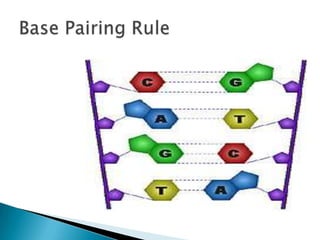
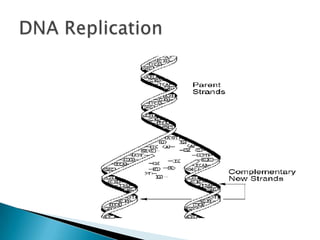
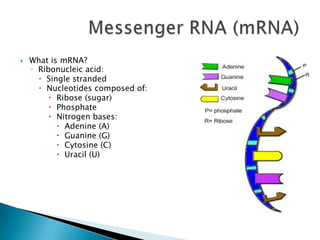
DNA contains the genetic blueprint for making proteins and is located in the cell nucleus. It is made up of nucleotides with one of four nitrogen bases. During cell replication, DNA unzips and makes copies of itself. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the DNA instructions from the nucleus to the ribosomes, where proteins are assembled based on the mRNA code. The mRNA code uses three-nucleotide sequences called codons to specify the 20 different amino acids used to build proteins. Mutations in DNA can occur from changes in single nucleotides or the insertion/deletion of bases, altering the genetic code.