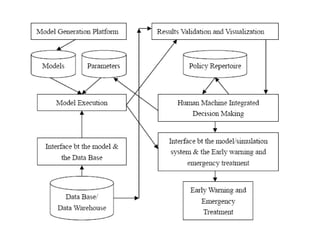
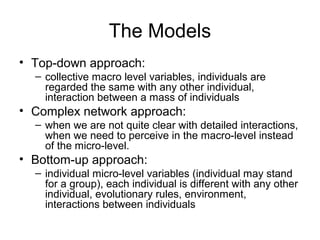
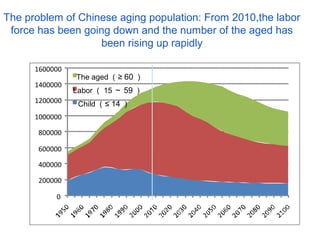
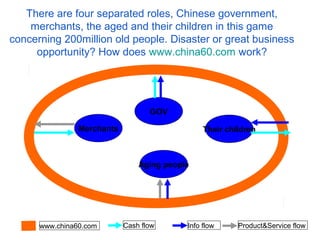
The document discusses challenges facing China including balancing economic growth with social issues like inequality and an aging population. It proposes developing an integrated decision making support system to address complex, interconnected problems. Such a system would collect data from various fields, develop multidisciplinary models, evaluate policy alternatives, and incorporate feedback to support decision makers in managing issues with global impacts like climate change, resource scarcity, and more. Developing such a system poses challenges around facilitating collaboration across disciplines and scales.