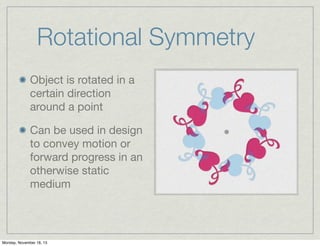
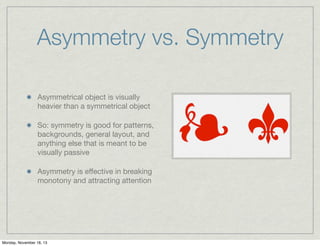
Symmetry is an ordering principle where there is balance between opposing sides. It exists precisely in nature, which humans mimic in design. There are different types of symmetry including translation, reflection, and rotation. Asymmetry lacks symmetry and can be used as a design tool to create visual hierarchy and points of interest.