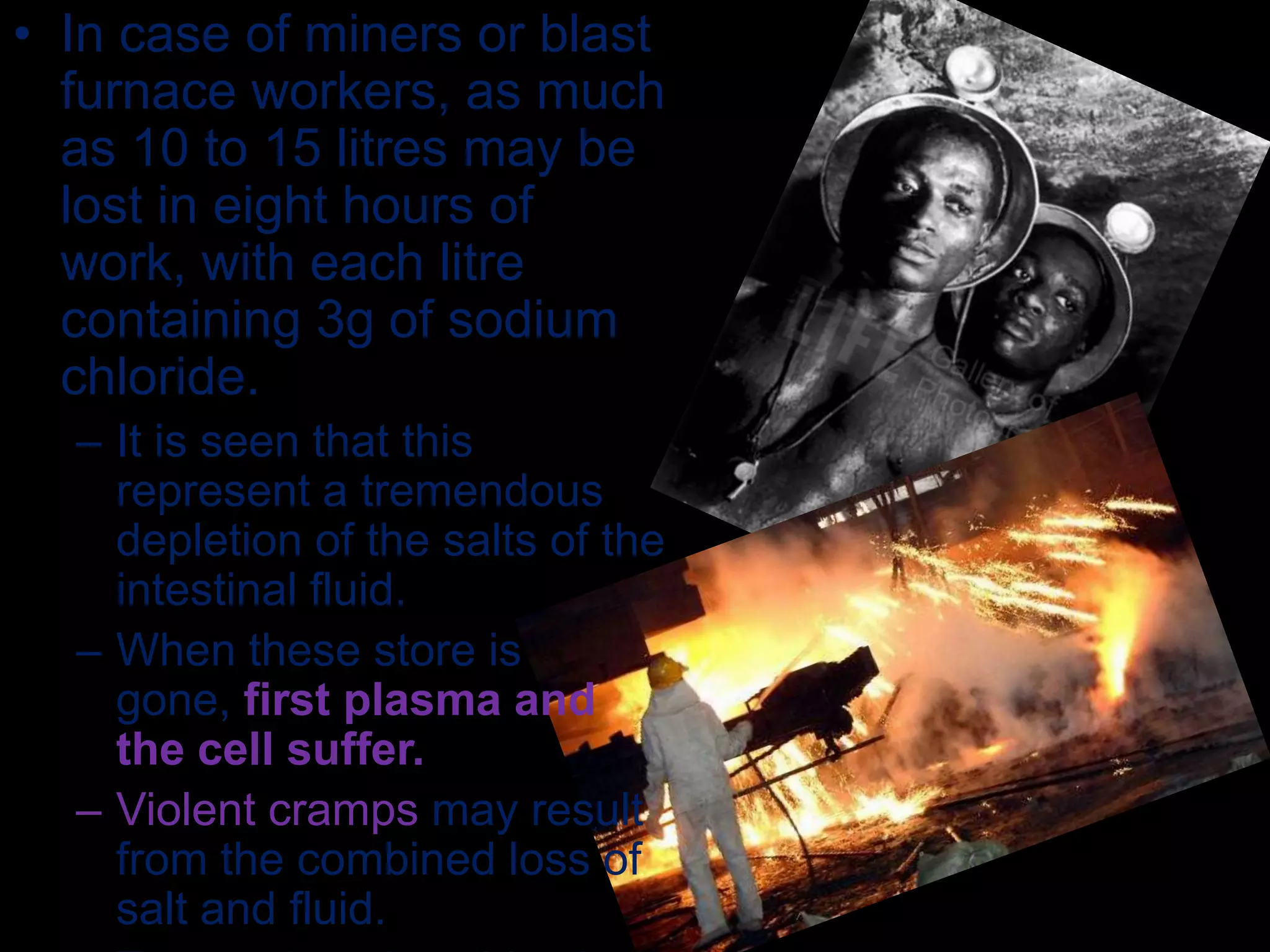
Sweat is a colorless saline moisture excreted by sweat glands that helps regulate body temperature through evaporation. The rate of sweating is affected by temperature, humidity, and muscular activity, with high temperatures and activity increasing sweating. Sweat contains water, urea, sodium chloride, potassium salts, and loses up to 0.2g of nitrogen daily during profuse sweating. Loss of large amounts of sweat can deplete the body's stores of salts and fluids, potentially causing cramps, so workers losing over 10 liters daily should drink water with 0.1% sodium chloride to replenish electrolytes.