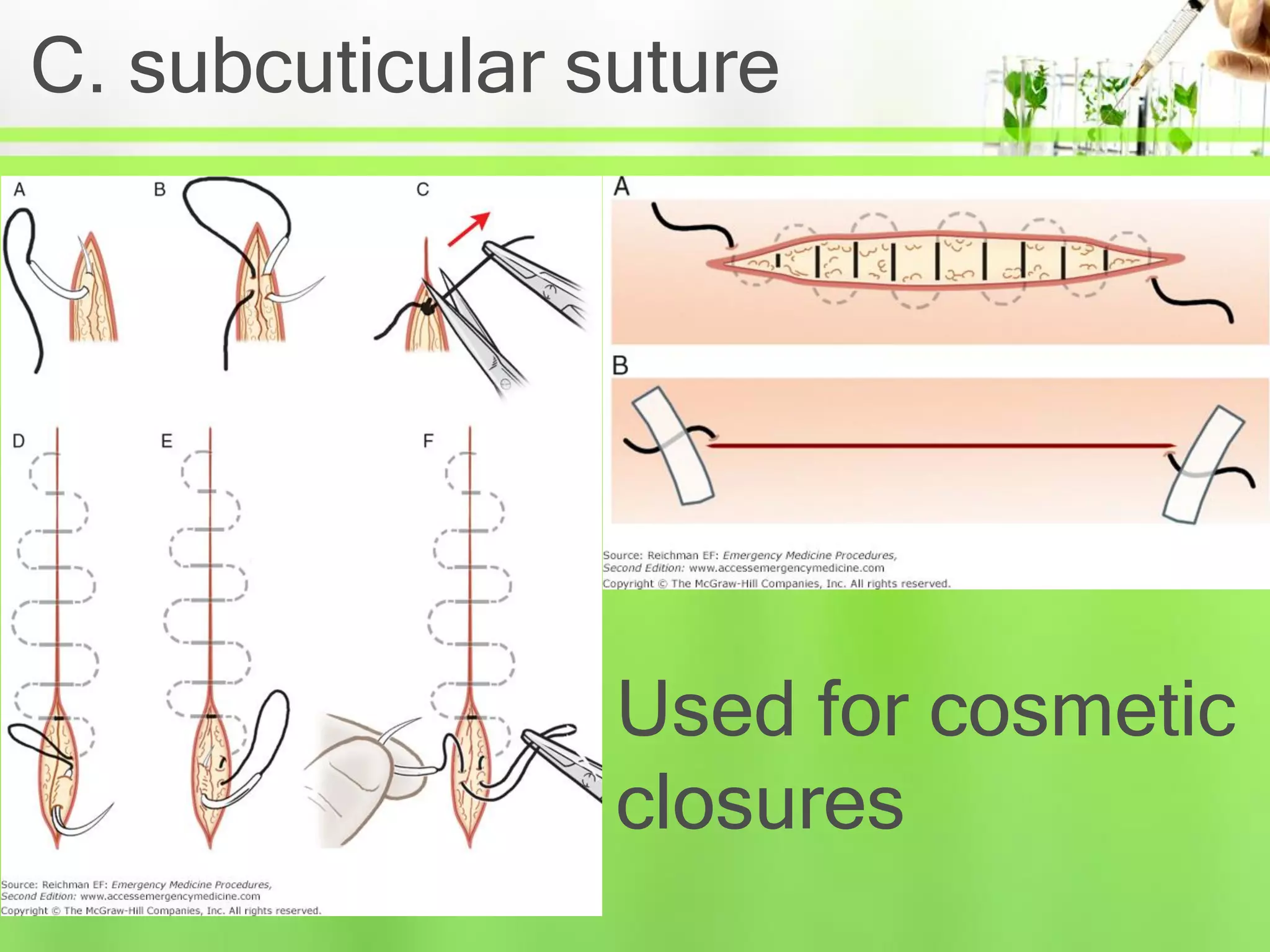
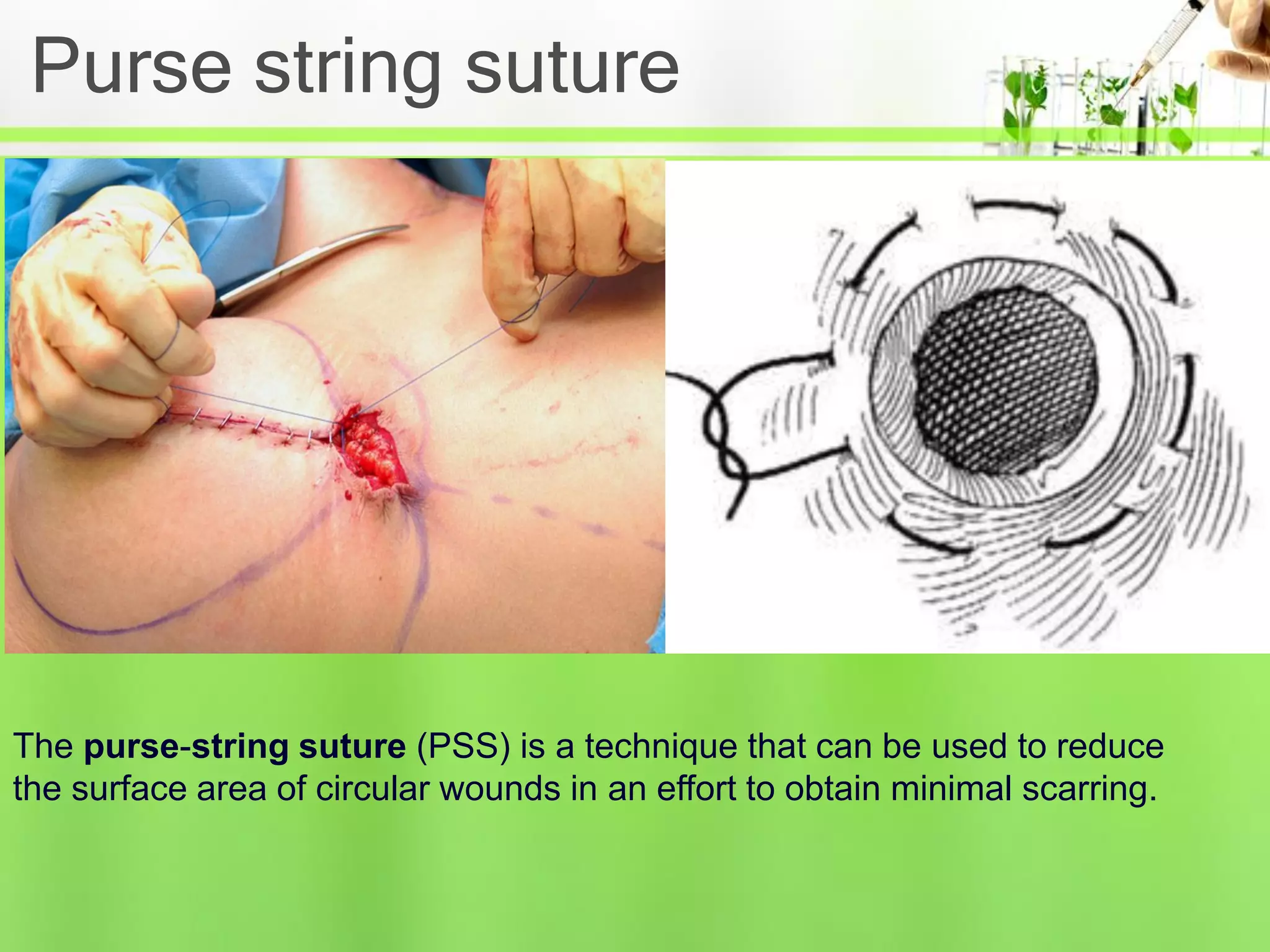
This document discusses suture materials and basic suturing techniques. It describes the ideal characteristics of suture materials, the goals of suturing, and different classifications of suture materials including absorbable natural and synthetic materials as well as non-absorbable options. Common suturing techniques like continuous, interrupted, and mattress sutures are outlined. The document provides a helpful overview of fundamental concepts in suturing.