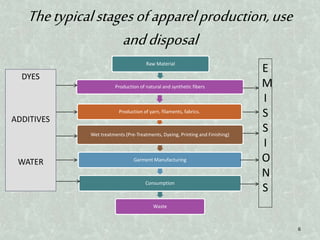
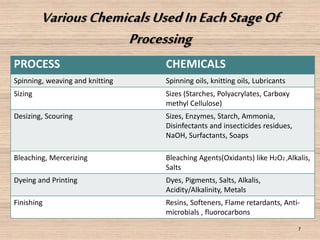
This document discusses sustainability in the apparel industry. It defines sustainability as meeting present needs without compromising future generations' ability to meet their own needs. The apparel industry uses large amounts of resources and chemicals that harm the environment. The document recommends more sustainable practices like using organic cotton and recycling textiles. It provides examples of companies like Levi's and Nike that are developing sustainable apparel lines using recycled materials and reducing water and waste.