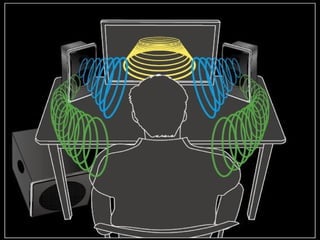
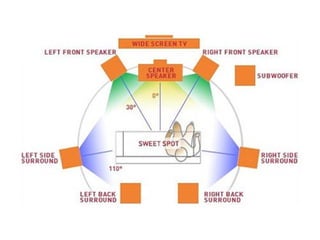
Surround sound uses multiple audio channels to immerse the listener in the sound environment. It originated in movie theaters using many speakers to diffuse sound throughout the cinema. Modern home theater systems use 5.1 or 7.1 channel configurations with speakers in front, center, and surround positions. Surround sound formats have evolved from mono to stereo to surround formats like Dolby Digital and DTS that add discrete channels for an immersive 3D soundfield.