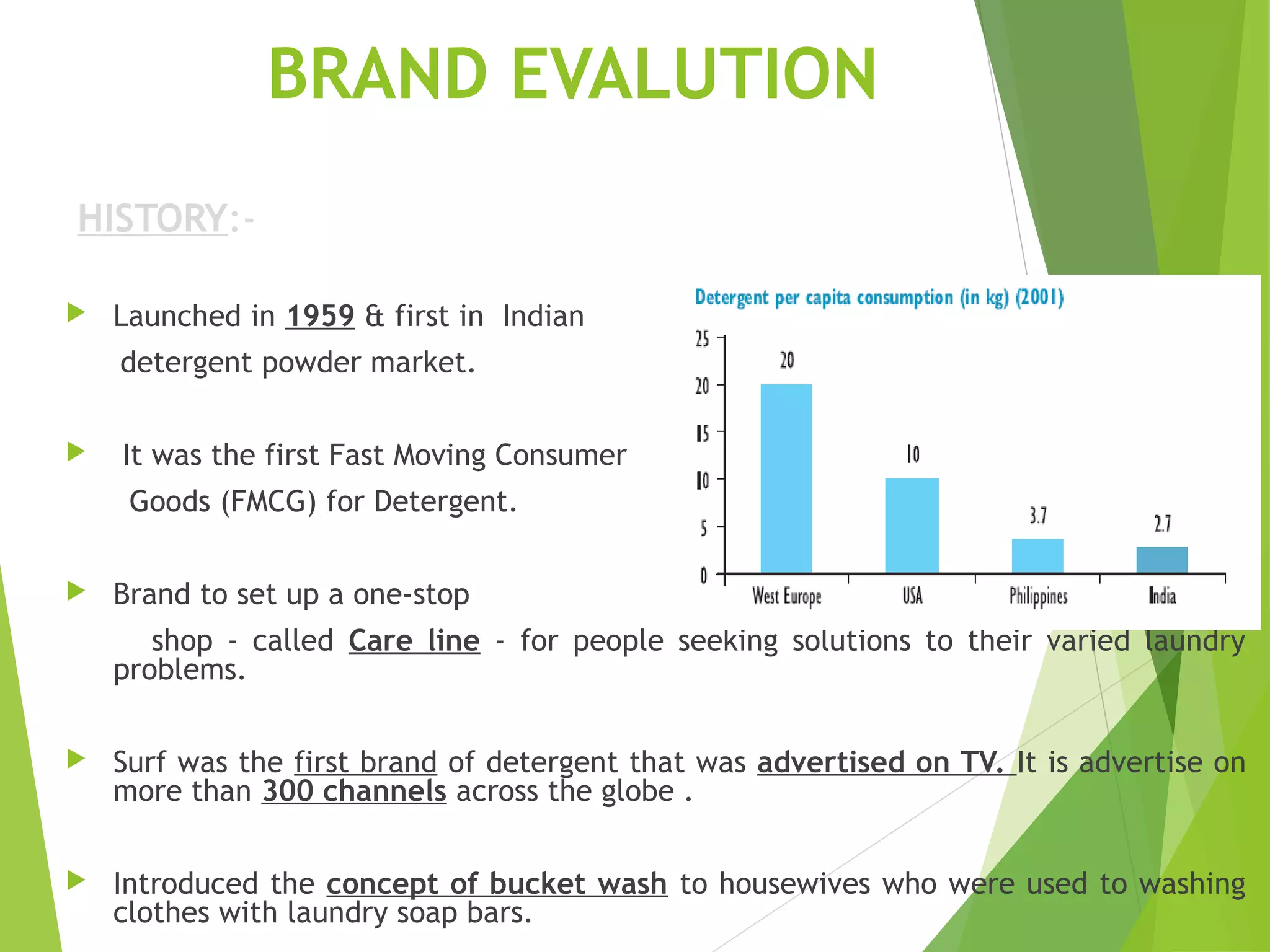
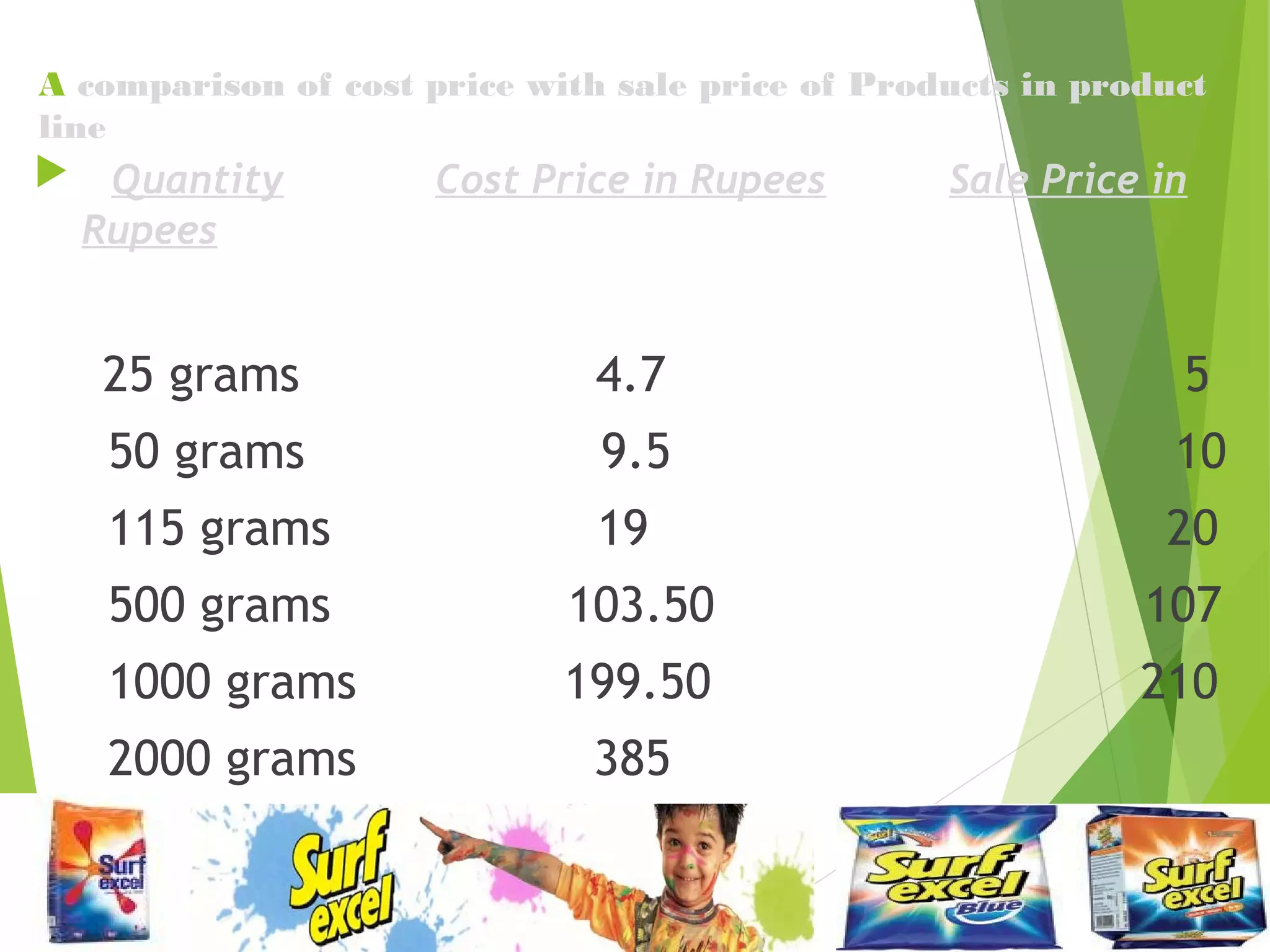
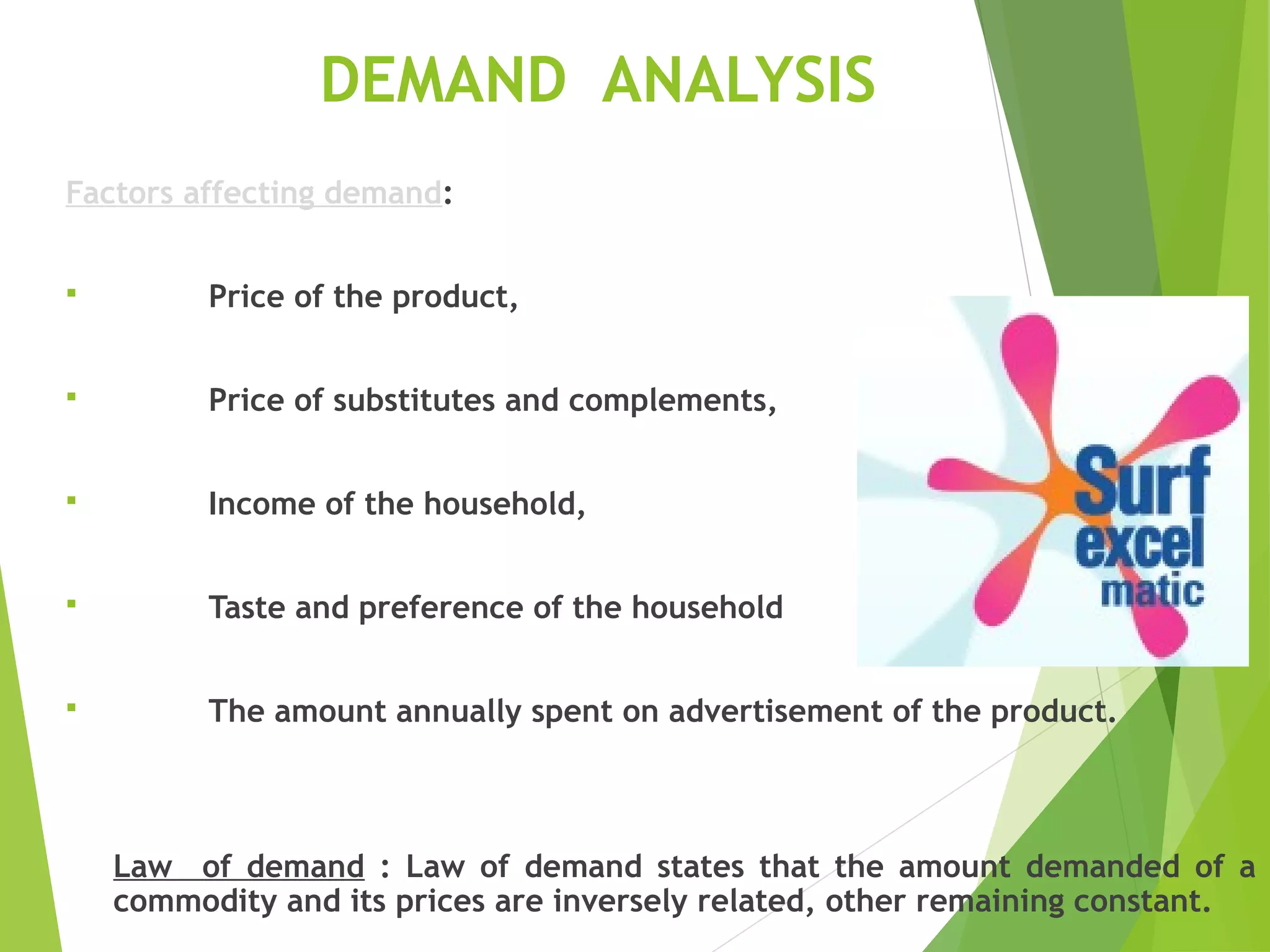
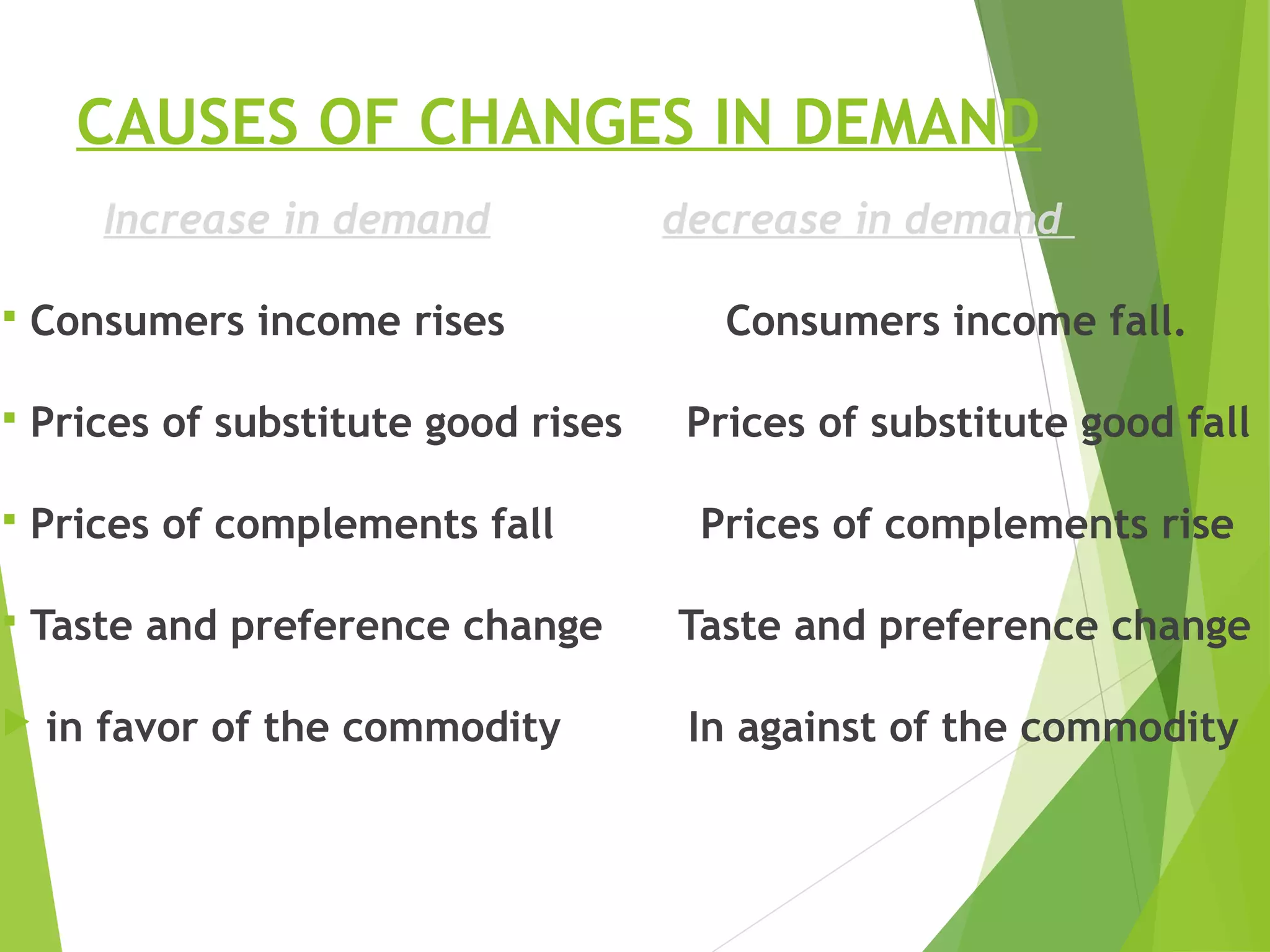
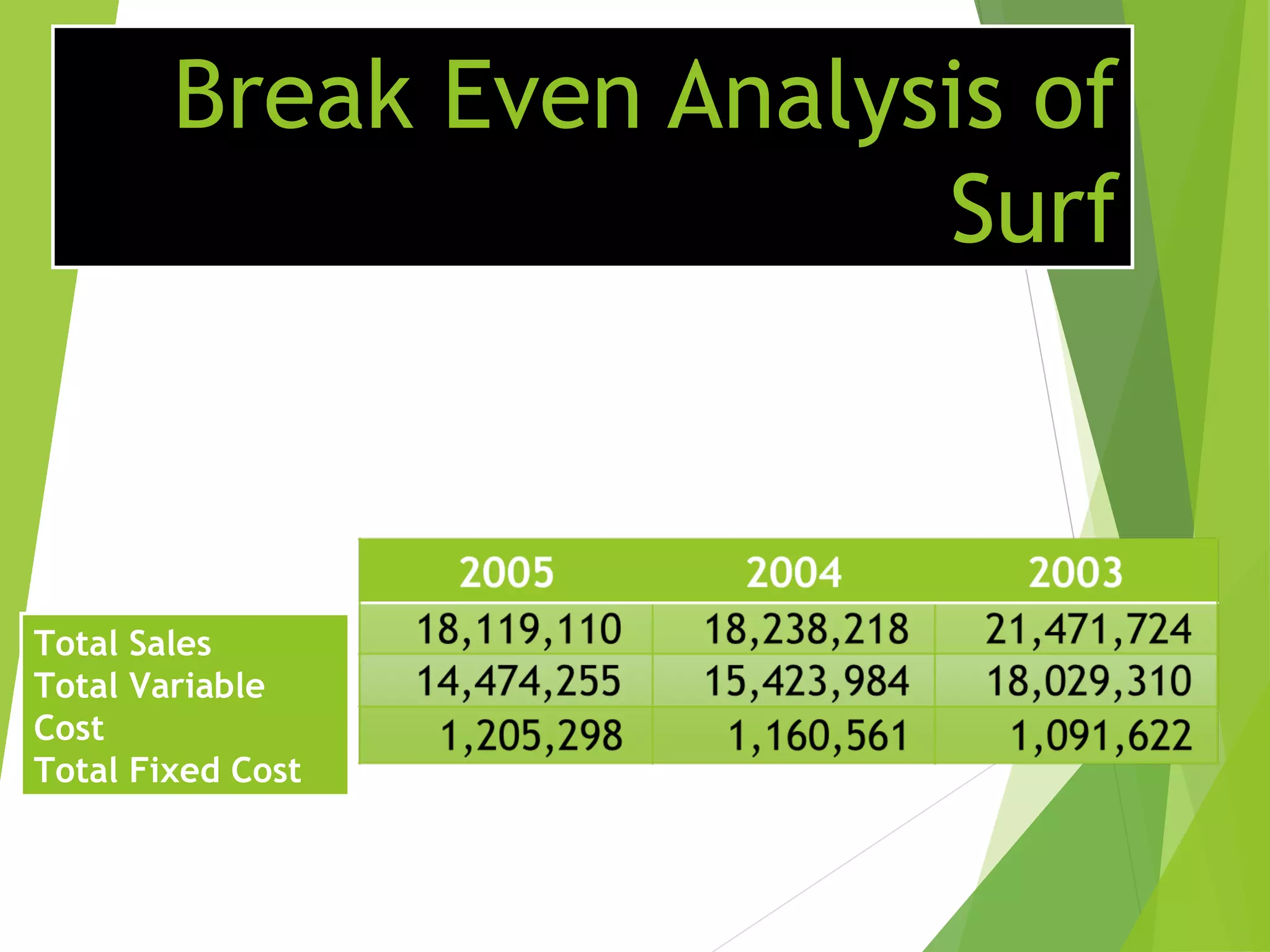
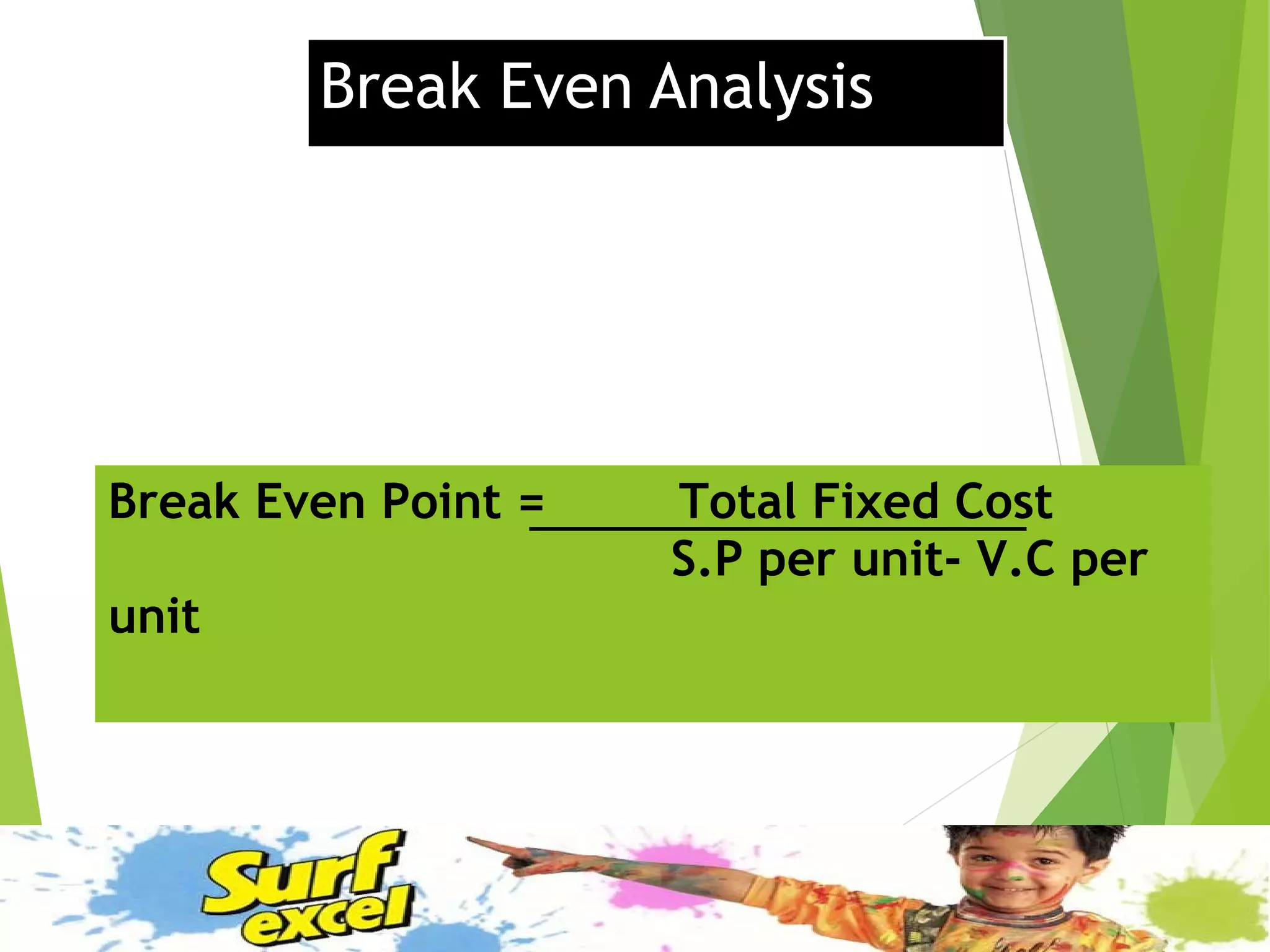
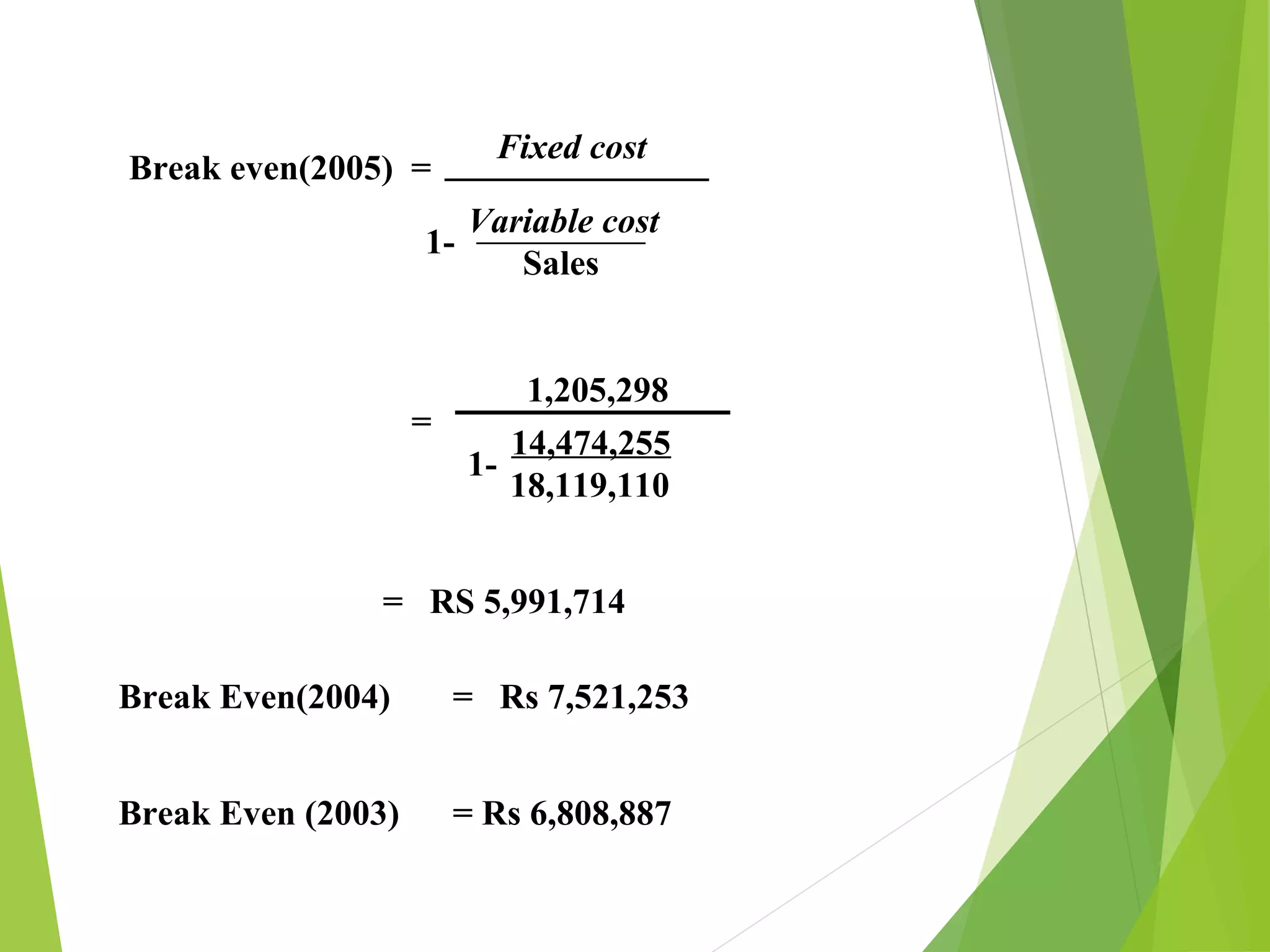
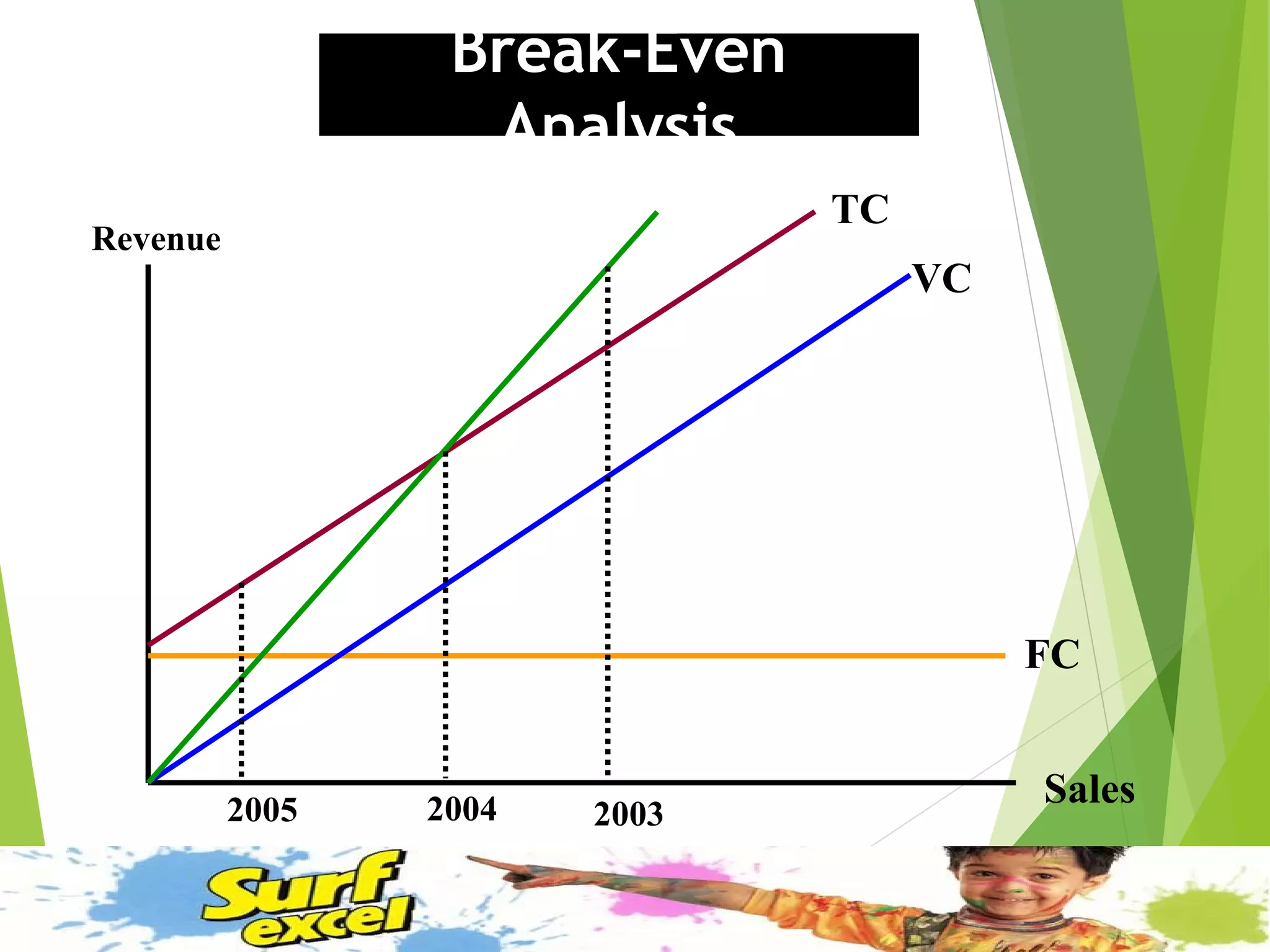
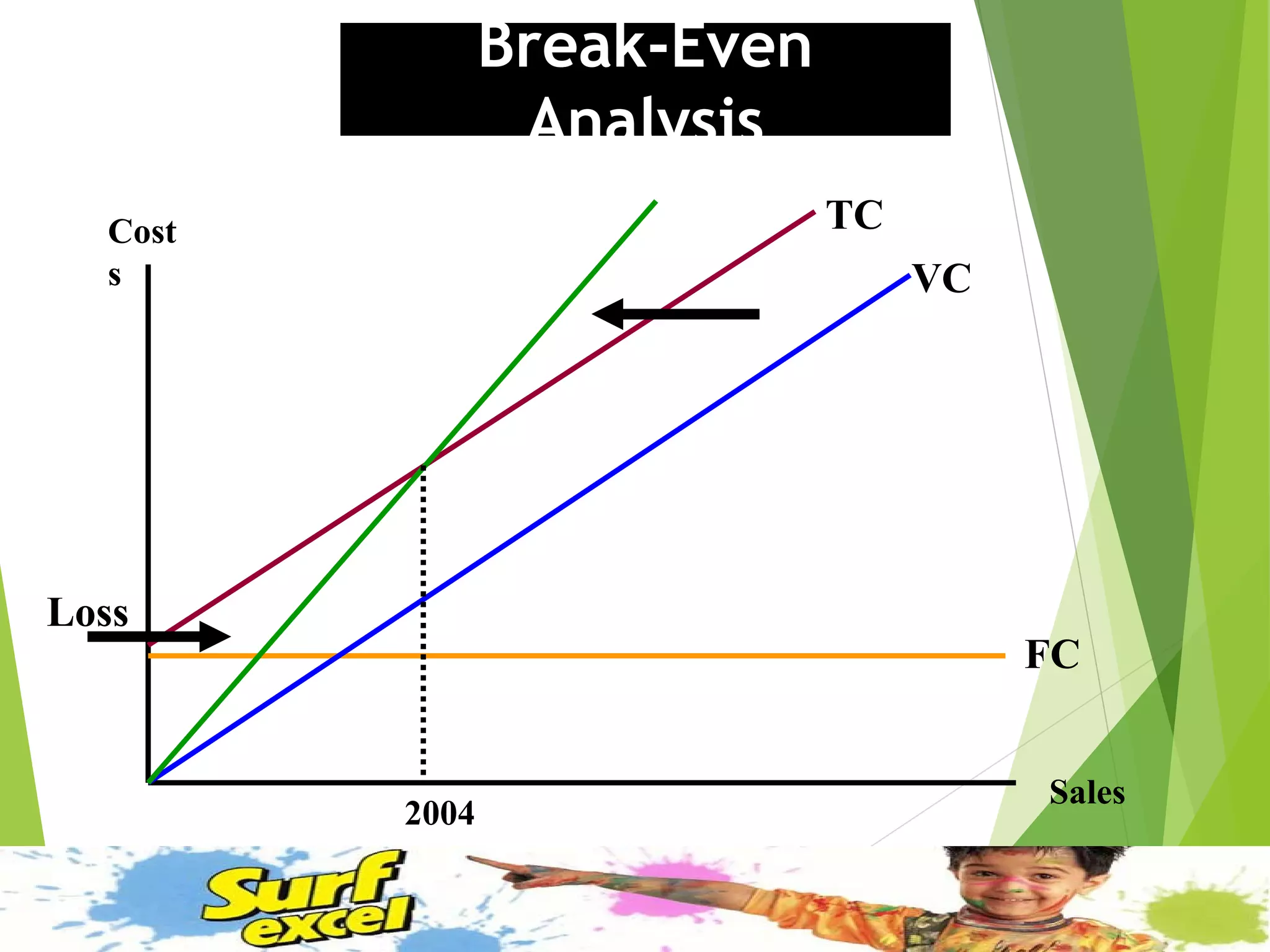
This document discusses Surf Excel, a detergent brand owned by Unilever that has been in the Indian market since 1960. It provides details on Surf Excel's product history and innovations, including being the first detergent brand advertised on TV in India. Financial information is presented on Surf Excel's pricing and costs. The document analyzes the demand and supply factors for Surf Excel and the Indian detergent market. It describes the oligopolistic market structure and provides a break-even analysis for Surf Excel. In conclusion, recommendations are made around forecasting demand and achieving market leadership in the large Indian detergent market.