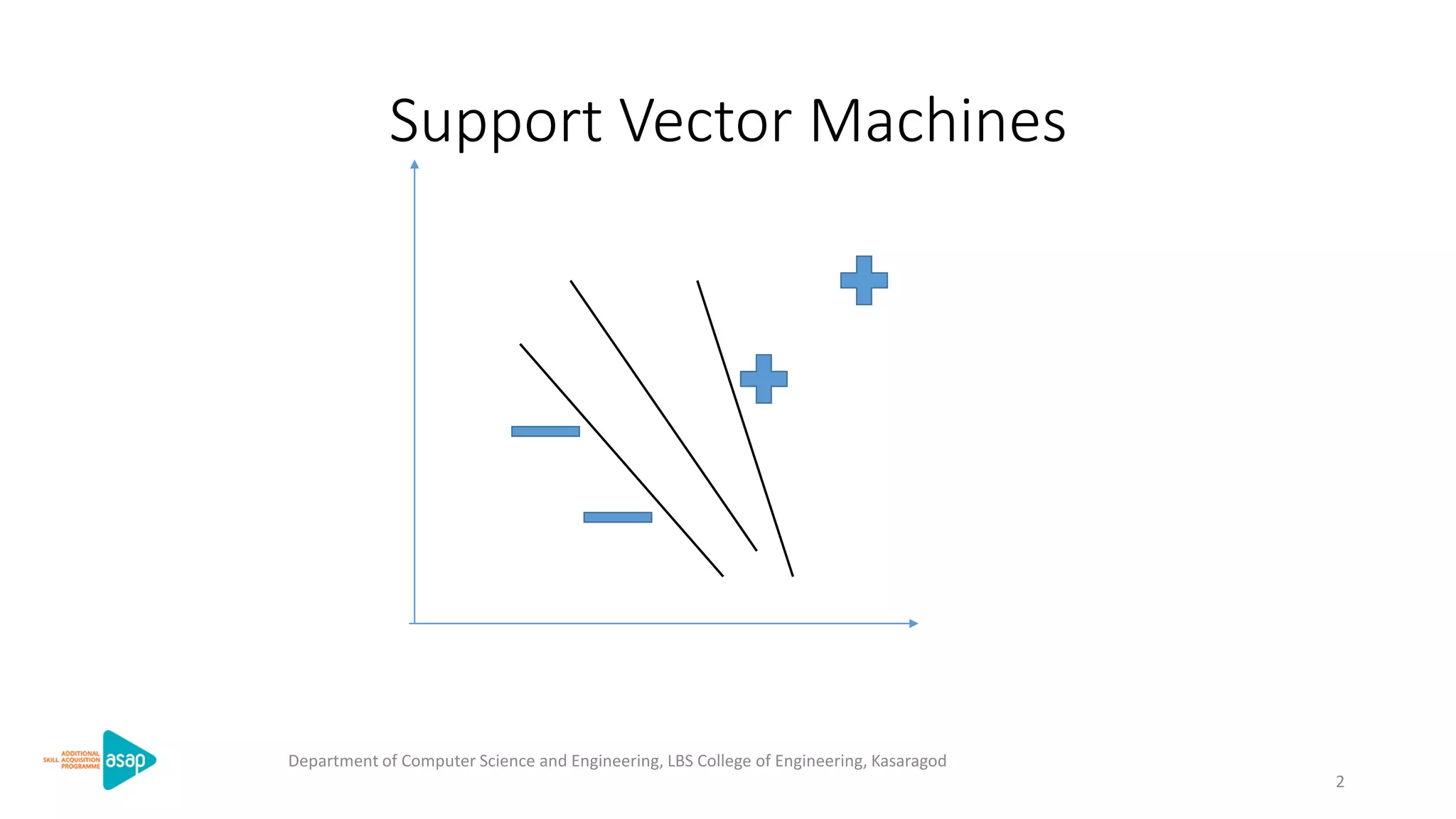
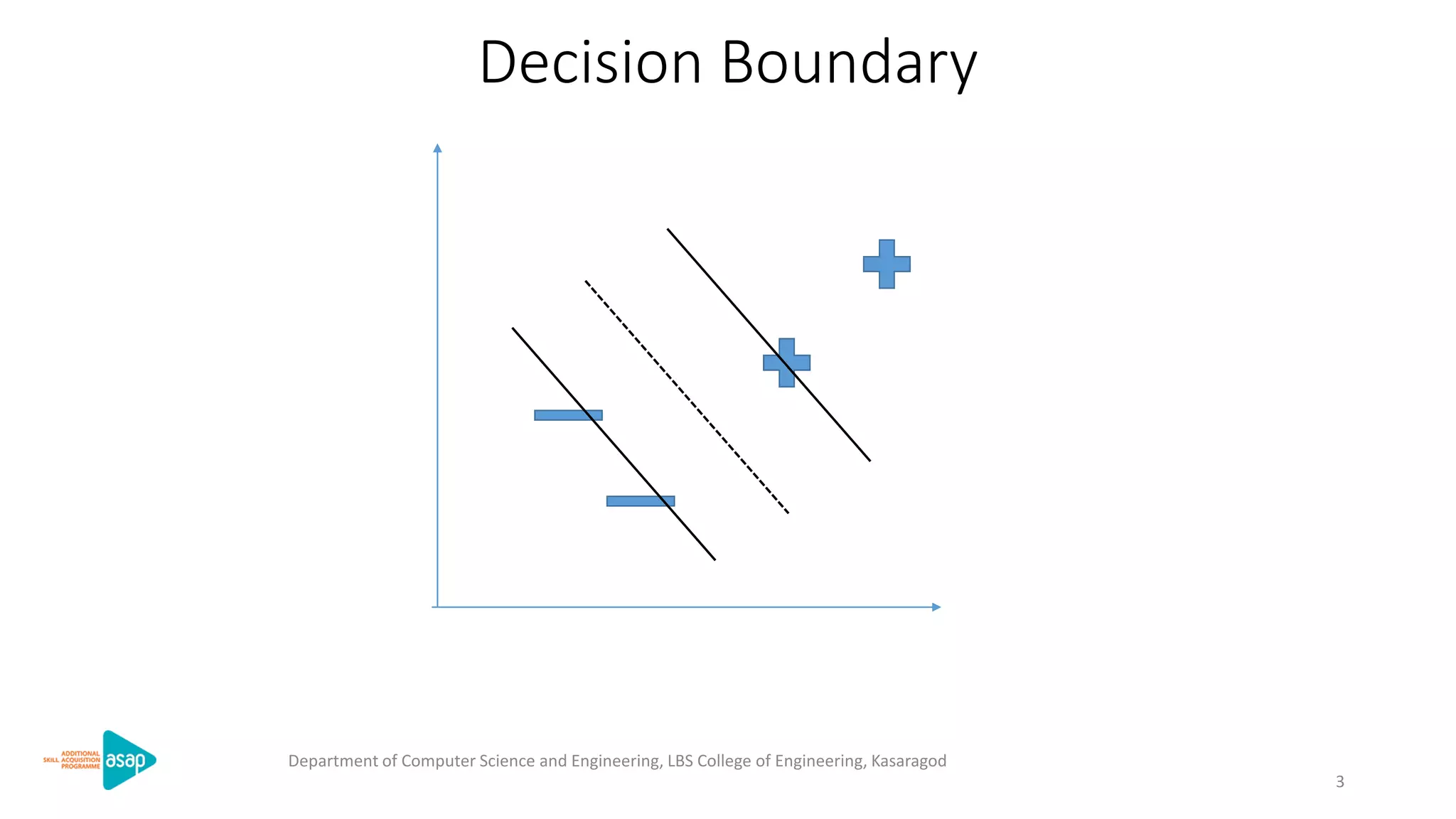
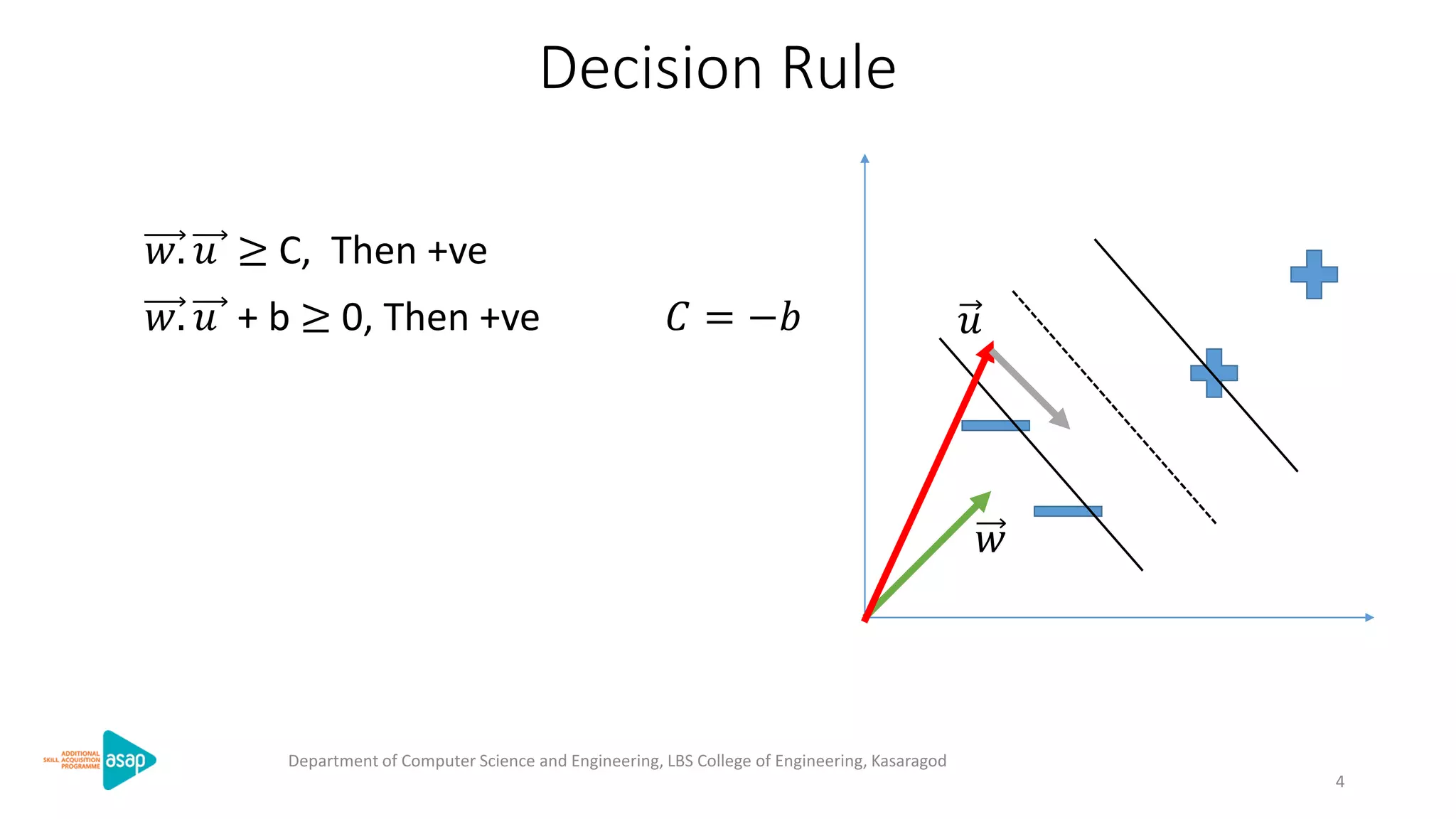
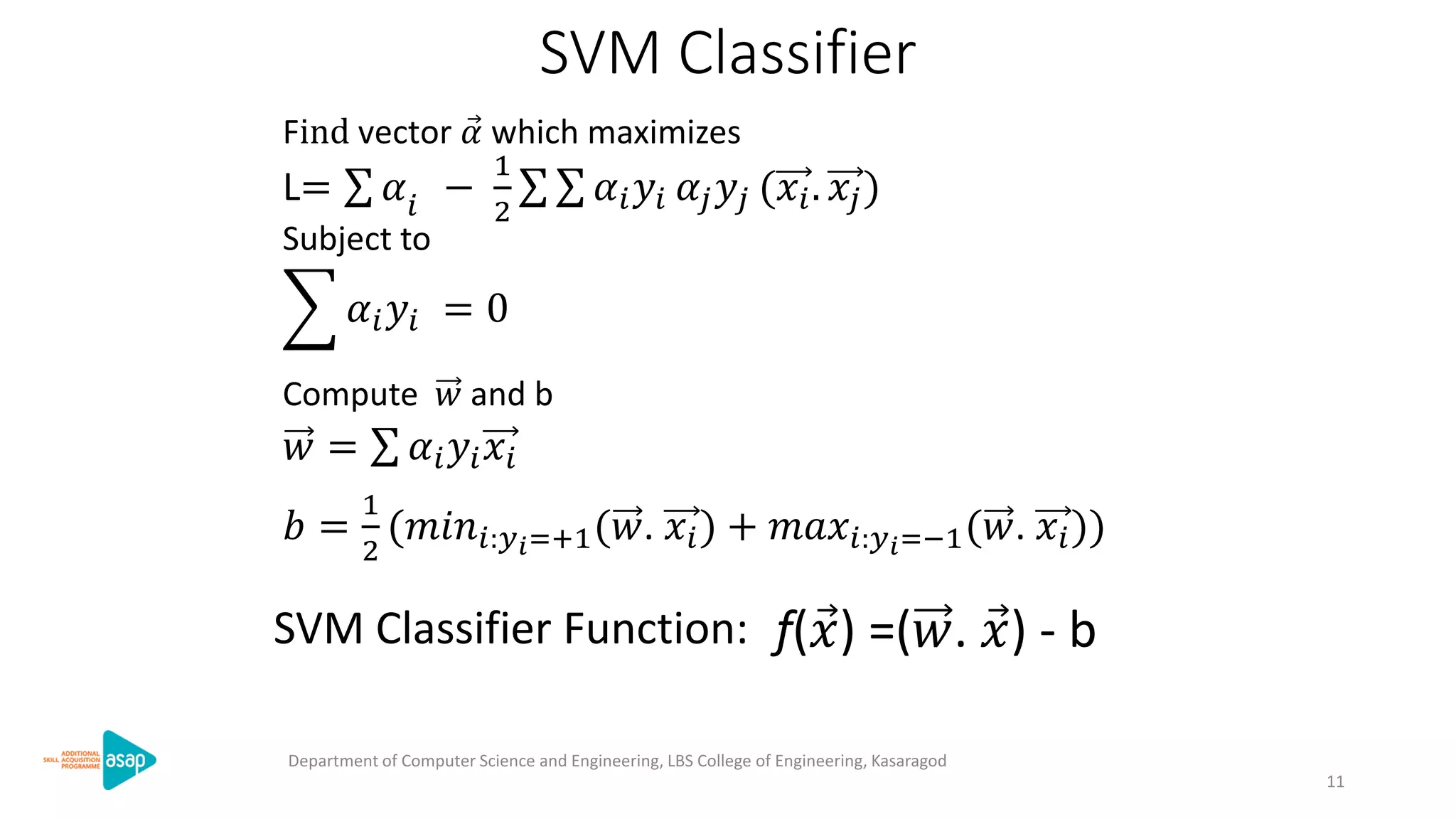
The document discusses support vector machines (SVMs), a supervised machine learning algorithm used for classification and regression. It describes how SVMs find the optimal separating hyperplane that maximizes the margin between the two classes of data points. The document provides the optimization formulation using Lagrange multipliers to find the separating hyperplane and defines the decision function to classify new data points. It also includes an example applying SVMs to classify a sample dataset.
![Optimization using Lagrange multipliers
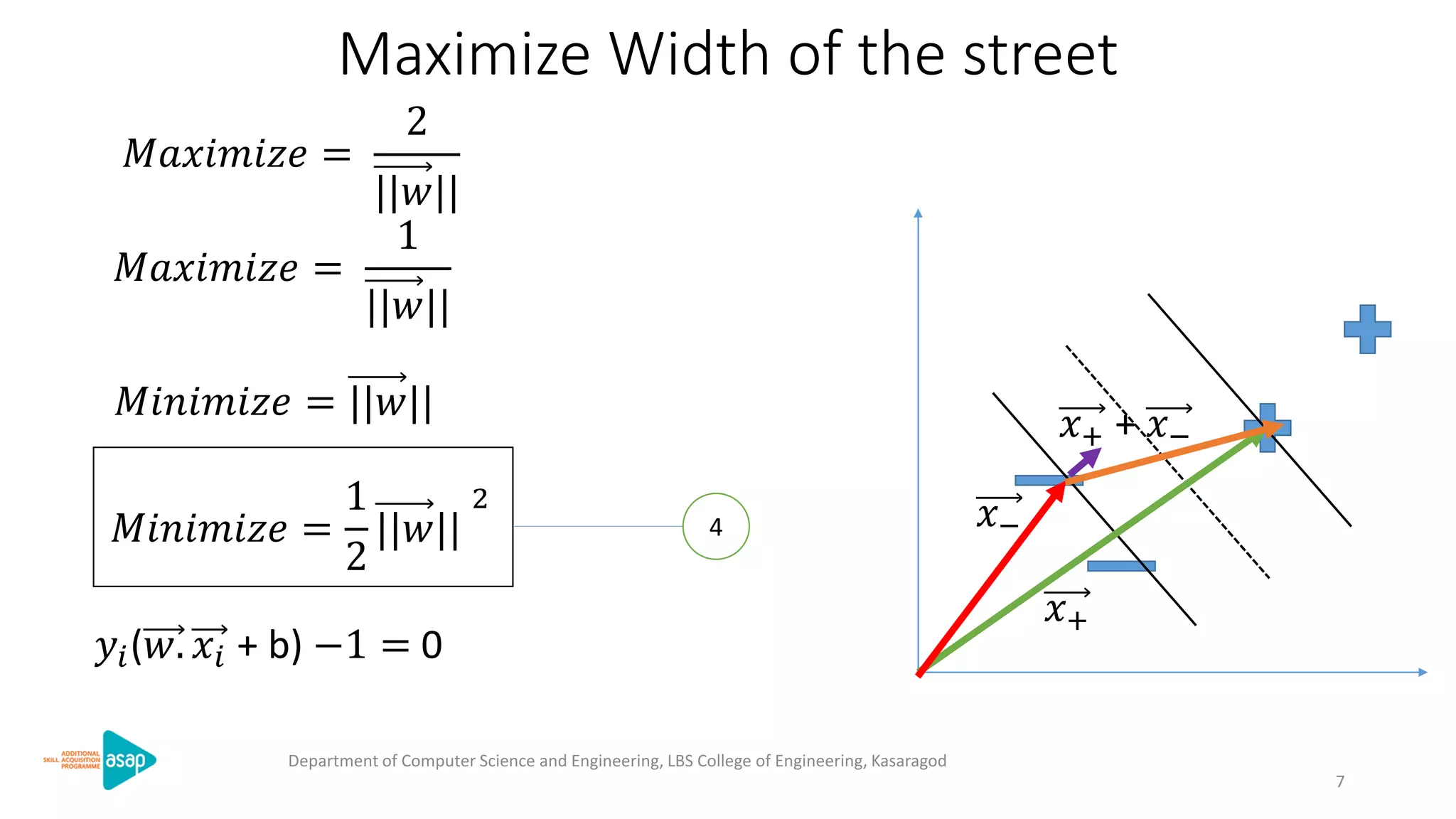
Expression: 𝑀𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑚𝑖𝑧𝑒 =
1
2
||𝑤||
2
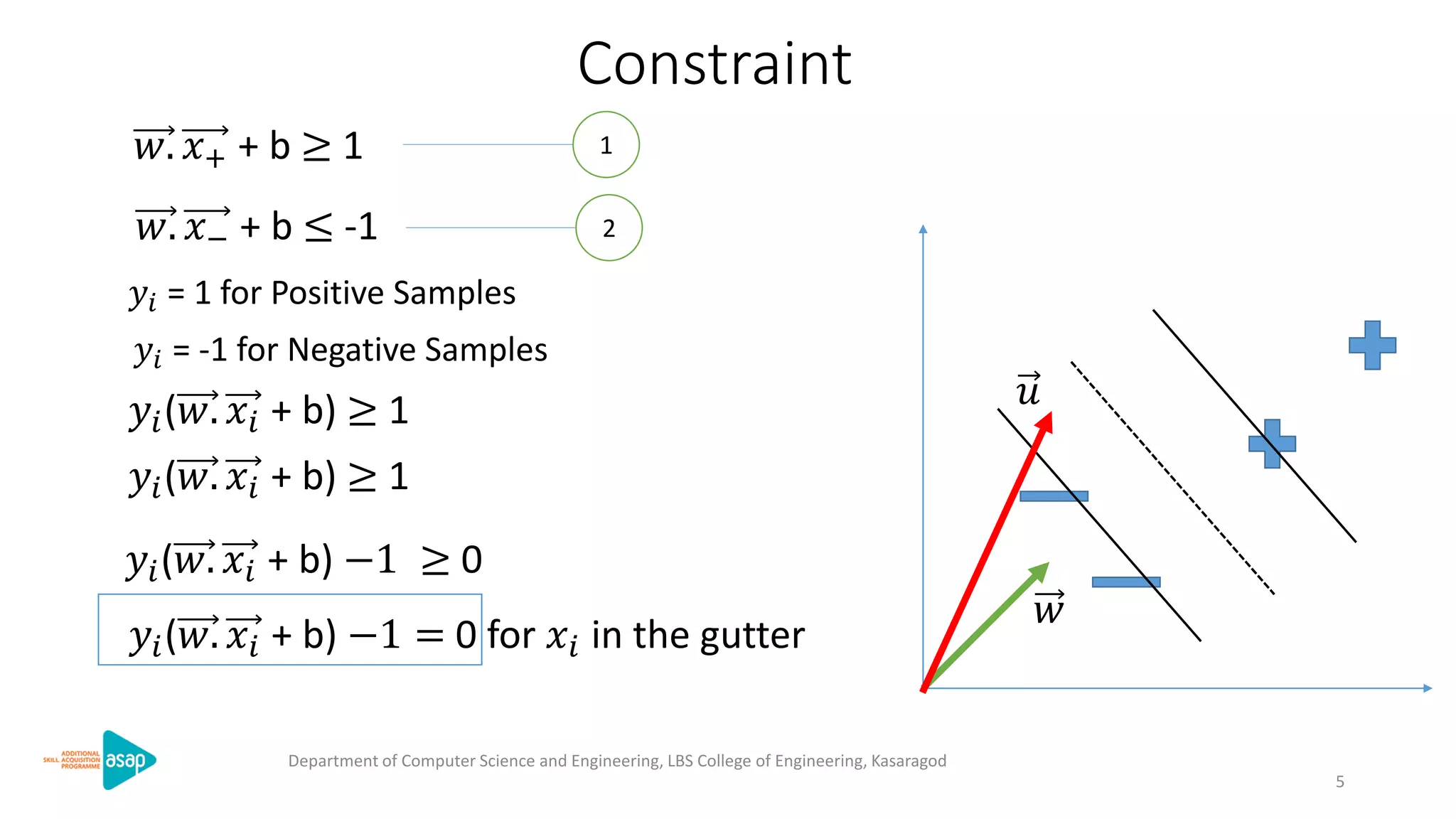
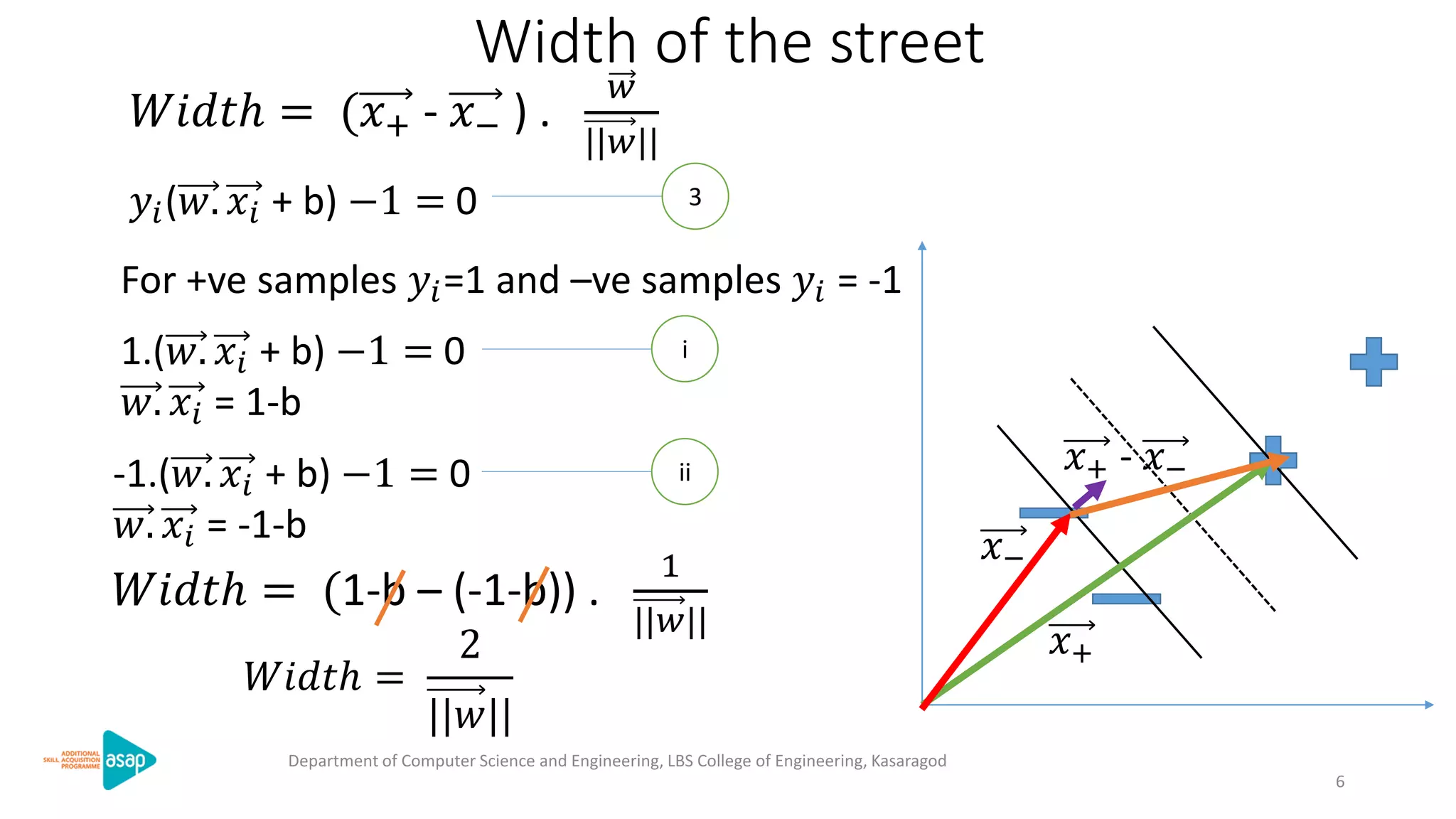
Constraint: 𝑦𝑖(𝑤. 𝑥𝑖 + b) −1 = 0
L=
1
2
||𝑤||
2
- 𝛼𝑖 [𝑦𝑖(𝑤. 𝑥𝑖 + b) − 1]
𝜕𝐿
𝜕𝑤
= 𝑤- 𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 𝑥𝑖 = 0
𝑤 = 𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 𝑥𝑖 6
𝜕𝐿
𝜕𝑏
= - 𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 = 0
𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 = 0 7
5
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, LBS College of Engineering, Kasaragod
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/svm-200515172618/75/Support-Vector-Machines-8-2048.jpg)
![Optimization using Lagrange multipliers
7
L=
1
2
||𝑤||
2
- 𝛼𝑖 [𝑦𝑖(𝑤. 𝑥𝑖 + b) − 1]
𝑤 = 𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 𝑥𝑖
5
6
𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 = 0
L=
1
2
( 𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 𝑥𝑖 ).( 𝛼𝑗 𝑦𝑗 𝑥𝑗 )- 𝛼𝑖 [𝑦𝑖(( 𝛼𝑗 𝑦𝑗 𝑥𝑗 )𝑥𝑖 + b) − 1]
L=
1
2
( 𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 𝑥𝑖 ).( 𝛼𝑗 𝑦𝑗 𝑥𝑗 )- ( 𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 𝑥𝑖). ( 𝛼𝑗 𝑦𝑗 𝑥𝑗) − 𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 b + 𝛼𝑖
= 0
L= 𝛼𝑖 +
1
2
( 𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 𝑥𝑖 ).( 𝛼𝑗 𝑦𝑗 𝑥𝑗 )- ( 𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 𝑥𝑖). ( 𝛼𝑗 𝑦𝑗 𝑥𝑗)
L= 𝛼𝑖 −
1
2
𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 𝛼𝑗 𝑦𝑗 (𝑥𝑖. 𝑥𝑗)
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, LBS College of Engineering, Kasaragod
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/svm-200515172618/75/Support-Vector-Machines-9-2048.jpg)
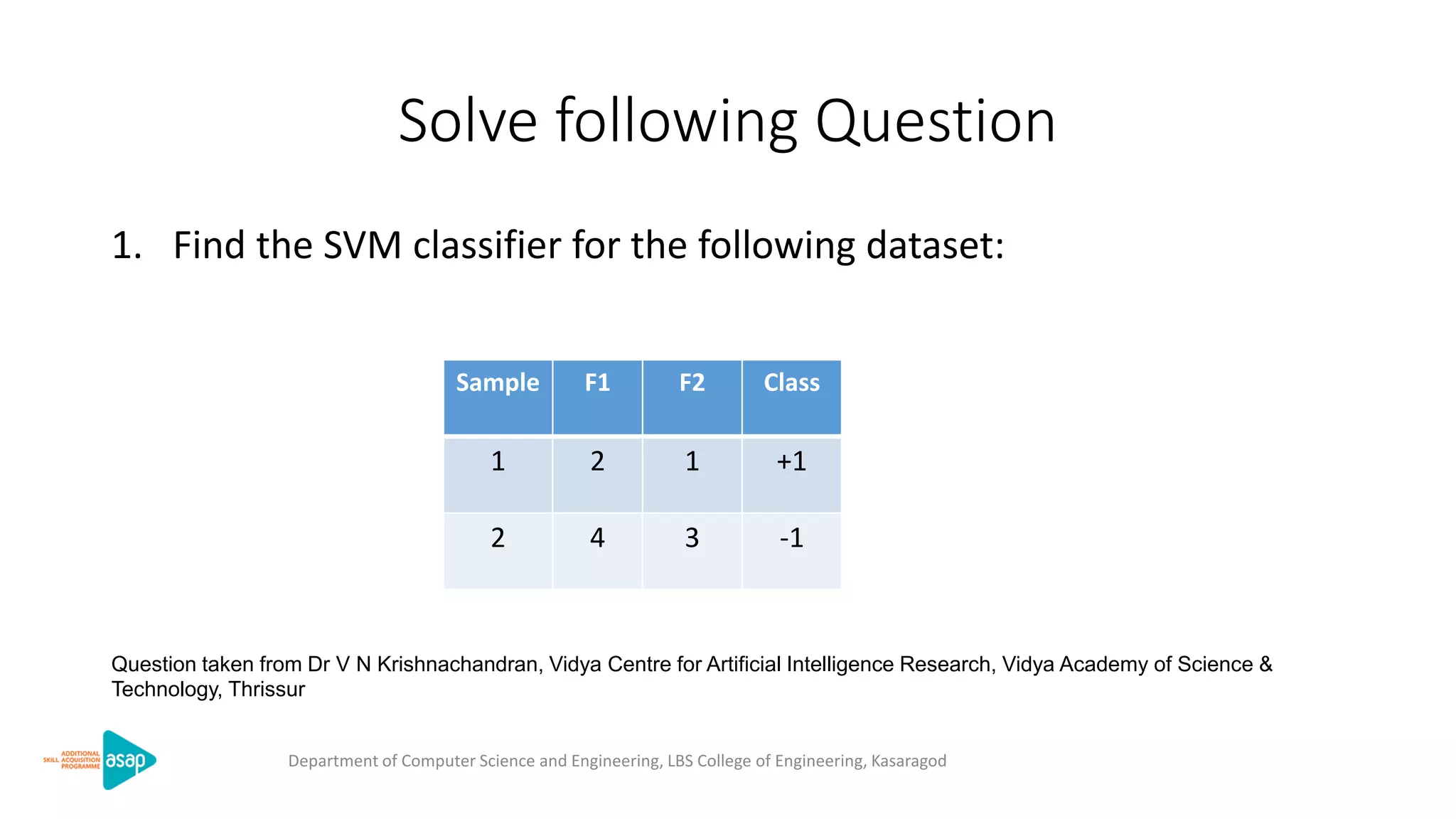
![13
Sample F1 F2 Class
1 2 1 +1
2 4 3 -1
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, LBS College of Engineering, Kasaragod
N = 2, 𝑥1 = (2,1), 𝑥2 = 4,3 ,𝑦1 = +1, 𝑦2 = −1
(𝛼1+𝛼2) −
1
2
[𝛼1 𝛼1 𝑦1 𝑦1(𝑥1. 𝑥1) + 𝛼1 𝛼2 𝑦1 𝑦2(𝑥1. 𝑥2) + 𝛼2 𝛼1 𝑦2 𝑦1(𝑥2. 𝑥1) + 𝛼2 𝛼2 𝑦2 𝑦2(𝑥2. 𝑥2) ]
(𝛼1+𝛼2) −
1
2
[𝛼1
2(+1)(+1)(2x2 + 1x1) + 𝛼1 𝛼2(+1)(-1)(2x4 + 1x3) + 𝛼2 𝛼1(-1) (+1)(4x2 + 3x1) +
𝛼2
2(-1)(-1)(4x4 + 3x3) ]
α1y1 + α2y2 =0 α1− α2 = 0
Find vector 𝛼 which maximizes 𝛼𝑖 −
1
2
𝛼𝑖 𝛼𝑗 𝑦𝑖 𝑦𝑗 (𝑥𝑖. 𝑥𝑗)
Subject to 𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 = 0
α =(𝛼1, 𝛼2)
(𝛼1+𝛼2) −
1
2
[5𝛼1
2 -22𝛼1 𝛼2 + 25𝛼2
2 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/svm-200515172618/75/Support-Vector-Machines-13-2048.jpg)
![14
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, LBS College of Engineering, Kasaragod
Find values of 𝛼1 and 𝛼2which maximizes ∅(α) = (𝛼1+𝛼2) −
1
2
[5𝛼1
2 -22𝛼1 𝛼2 + 25𝛼2
2 ]
Subject to conditions α1− α2 = 0, 𝛼1 > 0, 𝛼2 > 0
Substituting 2 in 1, ∅(α) = (𝛼1+𝛼1) −
1
2
[5𝛼1
2 -22𝛼1 𝛼1 + 25𝛼1
2 ]
2
1
= (2𝛼1) −
1
2
[8𝛼1
2 ]
2−8𝛼1 = 0For ∅(α) to be maximum
𝑑∅
𝑑𝛼1
= 0 𝛼1 = ¼ 𝛼2 = ¼
Second derivative is –ve so this is maximum
Sample F1 F2 Class
1 2 1 +1
2 4 3 -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/svm-200515172618/75/Support-Vector-Machines-14-2048.jpg)
![15
Compute 𝑤 and b
𝑏 =
1
2
(𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑖:𝑦 𝑖=+1(𝑤. 𝑥𝑖) + 𝑚𝑎𝑥𝑖:𝑦 𝑖=−1(𝑤. 𝑥𝑖))𝑤 = 𝛼𝑖 𝑦𝑖 𝑥𝑖
𝑤 = 𝛼1 𝑦1 𝑥1 + 𝛼2 𝑦2 𝑥2
=
1
4
+1 2,1 +
1
4
(−1)(4,3)
=
1
4
[ 2,1 + −4, −3 ] =
1
4
[ −2, −2 ] = −
1
2
, −
1
2
𝑏 =
1
2
( (𝑤. 𝑥1) + (𝑤. 𝑥2))
=
1
2
( −
1
2
× 2 −
1
2
× 1 + (−
1
2
× 4 −
1
2
× 3))
Sample F1 F2 Class
1 2 1 +1
2 4 3 -1=
1
2
( −
3
2
+ (−
7
2
)) =
1
2
−
10
2
= −
5
2
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, LBS College of Engineering, Kasaragod](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/svm-200515172618/75/Support-Vector-Machines-15-2048.jpg)
![16
SVM Classifier Function: f( 𝑥) =(𝑤. 𝑥) - b
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, LBS College of Engineering, Kasaragod
= −
1
2
, −
1
2
. (𝑥1, 𝑥2) +
5
2
= −
1
2
𝑥1 −
1
2
𝑥2 +
5
2
= −
1
2
[𝑥1 + 𝑥2−5]
Equation of maximal margin line
f( 𝑥) = 0 𝑥1 + 𝑥2 = 5
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
1
2
3
4
5
6
Sampl
e
F1 F2 Class
1 2 1 +1
2 4 3 -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/svm-200515172618/75/Support-Vector-Machines-16-2048.jpg)
