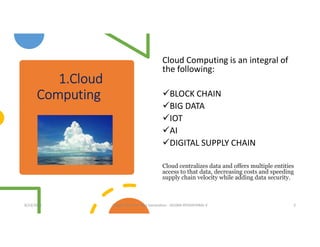
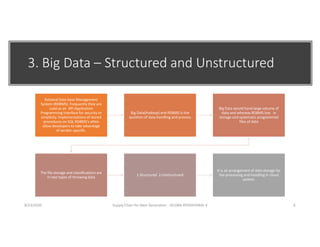
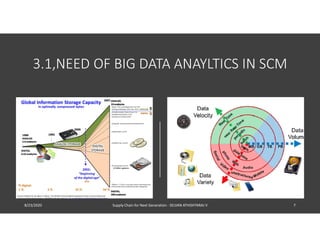
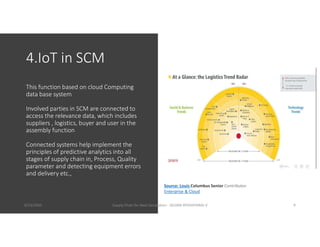
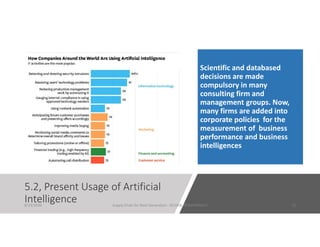
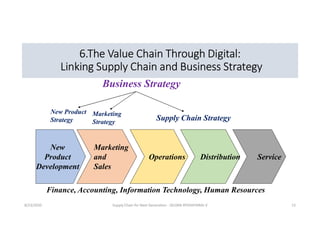
The document discusses emerging technologies that will transform next generation supply chains, including cloud computing, blockchain, big data, IoT, AI/ML, and digital supply chains. It describes how these technologies will integrate to provide benefits such as more accurate forecasting and inventory control, simplified logistics and order fulfillment, enhanced remote management capabilities, faster production times, improved training, and tighter quality control. Specifically, cloud computing will centralize data access, blockchain can securely track transactions, big data analytics enables predictive insights, IoT connects all parties, and AI/ML automates decision making. Together these technologies pave the way for fully digital, customized, and data-driven supply chains.