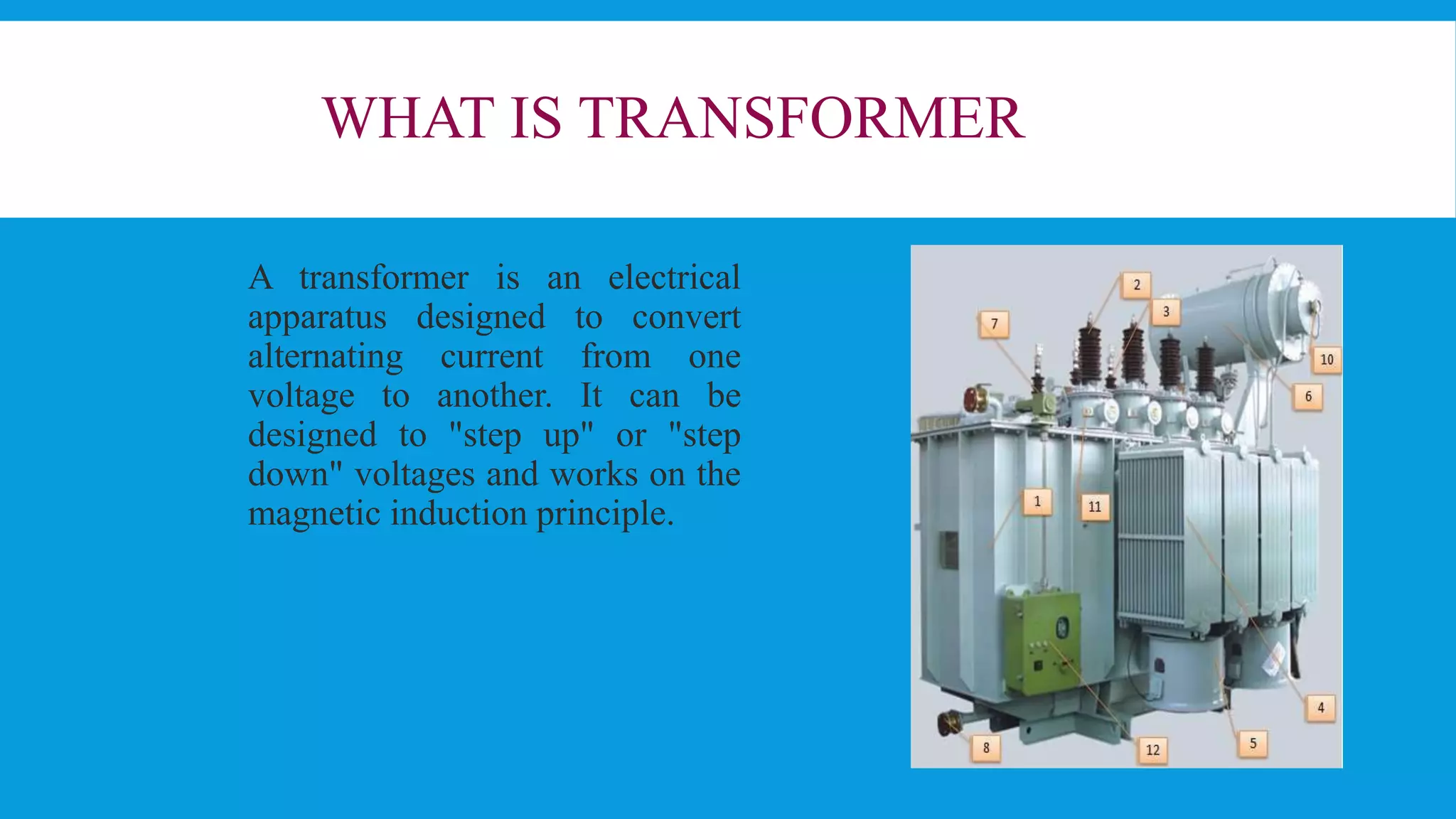
The document is a presentation on a summer training at a 33/11 kV substation. It discusses key components of a substation including transformers, buses, circuit breakers, isolators, relays, insulators, and current/potential transformers. A substation transforms voltage from high to low and distributes power. Single line diagrams show electrical connections simplified to single lines per phase. The bus connects equipment and maintains equal voltage across phases. Transformers step down voltage from 33 kV to 11 kV for distribution. Protective devices like circuit breakers, isolators, and relays isolate or interrupt faults.


















![Summer_Tranning_satihs[1].pptx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/summertranningsatihs1-221218101756-30b4a4a4/75/Summer_Tranning_satihs-1-pptx-20-2048.jpg)