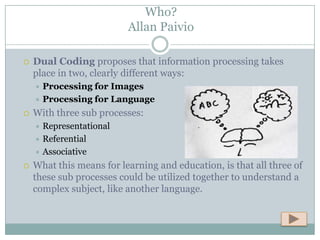
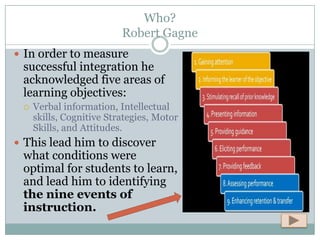
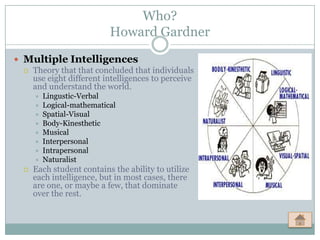
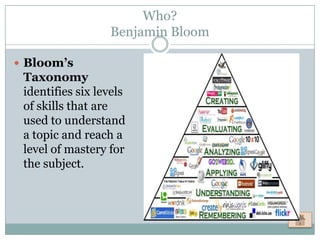
Cognitive Learning Theory focuses on thinking and mental processes as behaviors that lead to learning. It examines learning as an intricate process involving thoughts, ideas, realizations, and acquired information rather than just reactions. Approaches discussed in the document include Dual Coding Theory, Gagne's nine events of instruction, Gardner's Theory of Multiple Intelligences, and Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning. The document also provides examples of how teachers can apply concepts from Cognitive Learning Theory, such as Multiple Intelligences, in their classrooms to better understand students' strengths and customize instruction.