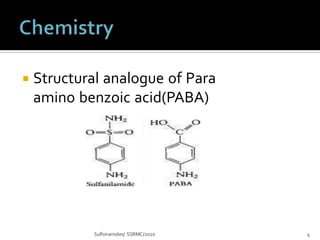
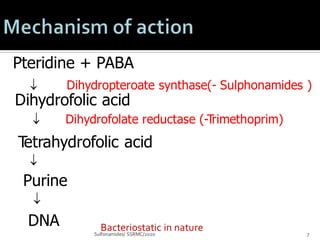
Sulfonamides and cotrimoxazole are antibacterial drugs that work by inhibiting folic acid synthesis. Sulfonamides are classified based on half-life as short, intermediate, or long acting. Cotrimoxazole is a combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim that has synergistic antibacterial effects. These drugs are used to treat infections like toxoplasmosis, UTIs, nocardiosis, and pneumocystis pneumonia. Common adverse effects include nausea, crystalluria, rashes, and hemolytic anemia in G6PD deficiency.