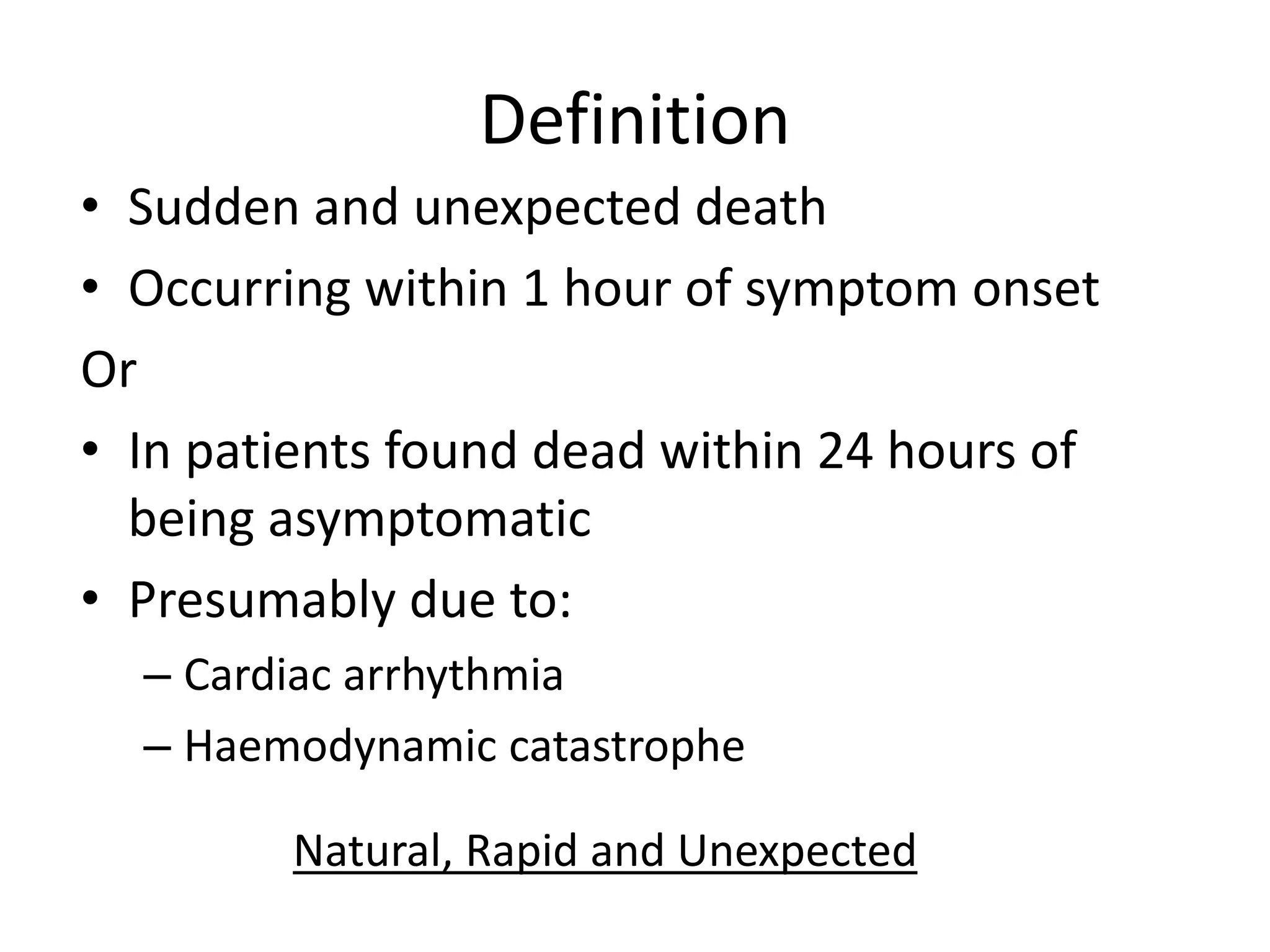
This document discusses sudden cardiac death (SCD), defined as unexpected death from cardiac causes within one hour of symptom onset or within 24 hours of being asymptomatic. The main causes of SCD are cardiac arrhythmias and hemodynamic catastrophes due to structural heart disease, ischemic heart disease, or inherited arrhythmia syndromes. Risk factors for SCD include age over 35, male sex, left ventricular dysfunction, ventricular arrhythmias, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, and family history of cardiac disease or sudden death. Mechanisms of SCD include abnormal automaticity, triggered activity due to early or late afterdepolarizations, and reentry phenomena involving scar tissue or functional conduction blocks. High-risk patients should undergo evaluation including