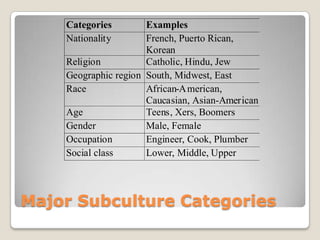
A subculture is a group that differentiates itself from the larger culture and has beliefs or interests that vary from the dominant culture. Subcultures are often identified through symbolic uses of style including fashion, mannerisms, and slang. Examples of subcultures include hipsters from the 1940s and fans devoted to minor details of their interest. Race, religion, geography, age, gender, occupation and social class are common categories used to define subcultures. Within the US, major racial subcultures are Caucasian, African American and Asian American groups.