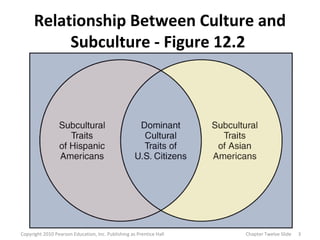
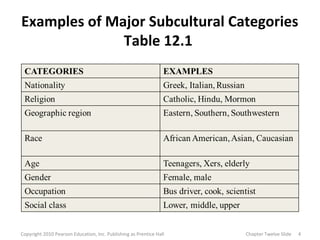
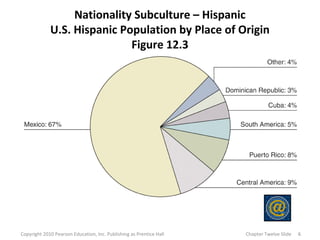
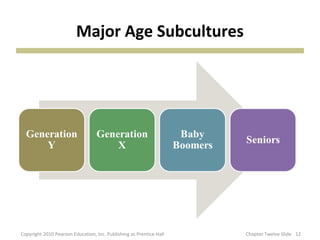
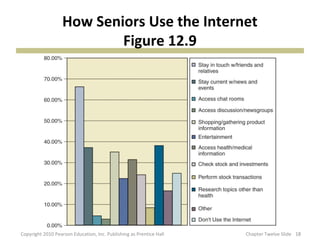
This document discusses various subcultures and how they relate to consumer behavior. It defines subculture as a distinct group within a larger society and explores examples like nationality (discussing Hispanics), religious, regional, racial, age-based (generations, older consumers), gender-based and working women subcultures. Each subculture exhibits trends in consumer preferences, brand loyalty, media usage and spending habits. The document stresses the importance for marketers to understand how multiple, overlapping subcultural identities influence consumer behavior.