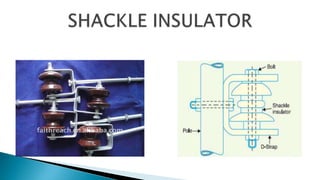
This document discusses conductors and insulators used in electrical machines. It provides details on common conductors like copper, aluminum, and silver. It also describes different types of insulators used for power transmission, including pin insulators, post insulators, suspension insulators, strain insulators, and shackle insulators. Properties of various materials that make them suitable as conductors or insulators are explained. The document concludes with a summary of the key points covered.