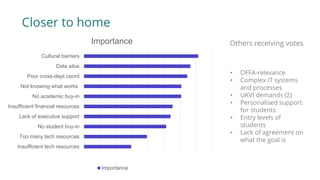
1) The document discusses how converging factors like changing enrollment patterns, student expectations, and perceptions of value are driving the need for increased student engagement. It also notes that retention is important for institutional sustainability.
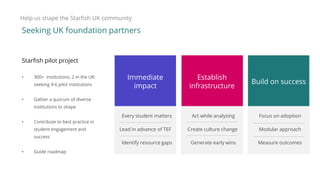
2) Findings from the Gates Foundation emphasize the importance of collaboration between academic and professional services, measuring effectiveness of programs, focusing on student ownership of success, and establishing the right culture for student success initiatives.
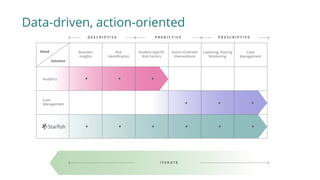
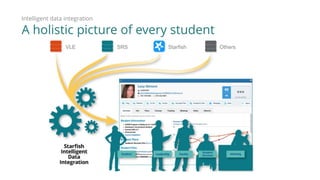
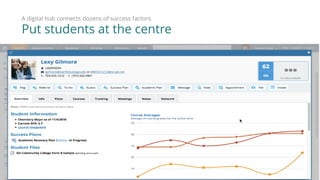
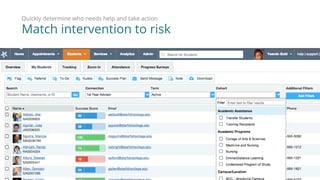
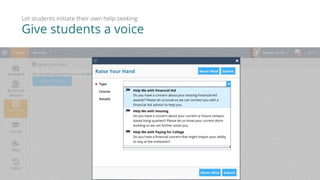
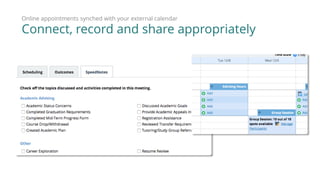
3) The Starfish Student Success Partnership uses a holistic, data-driven approach to identify at-risk students and match them to targeted interventions through an integrated digital hub. It aims to put students at the center, connect them to resources, and remove obstacles to support.