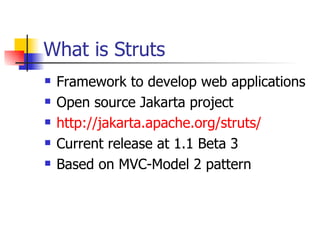
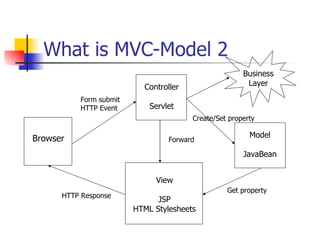
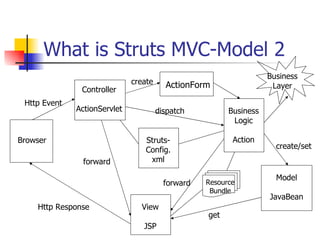
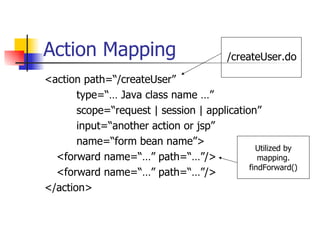
The document provides an overview of the Struts framework, which is an open source MVC framework for developing web applications in Java. It describes the key components of Struts including the ActionServlet, Actions, ActionForms, the struts-config.xml file, and JSP views. The Struts framework uses the MVC pattern to separate the user interface from business logic and support the building of reusable components.
![Struts Overview Shakeel Mahate [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strutsshakeel-1227968837045073-9/75/Struts-Overview-1-2048.jpg)