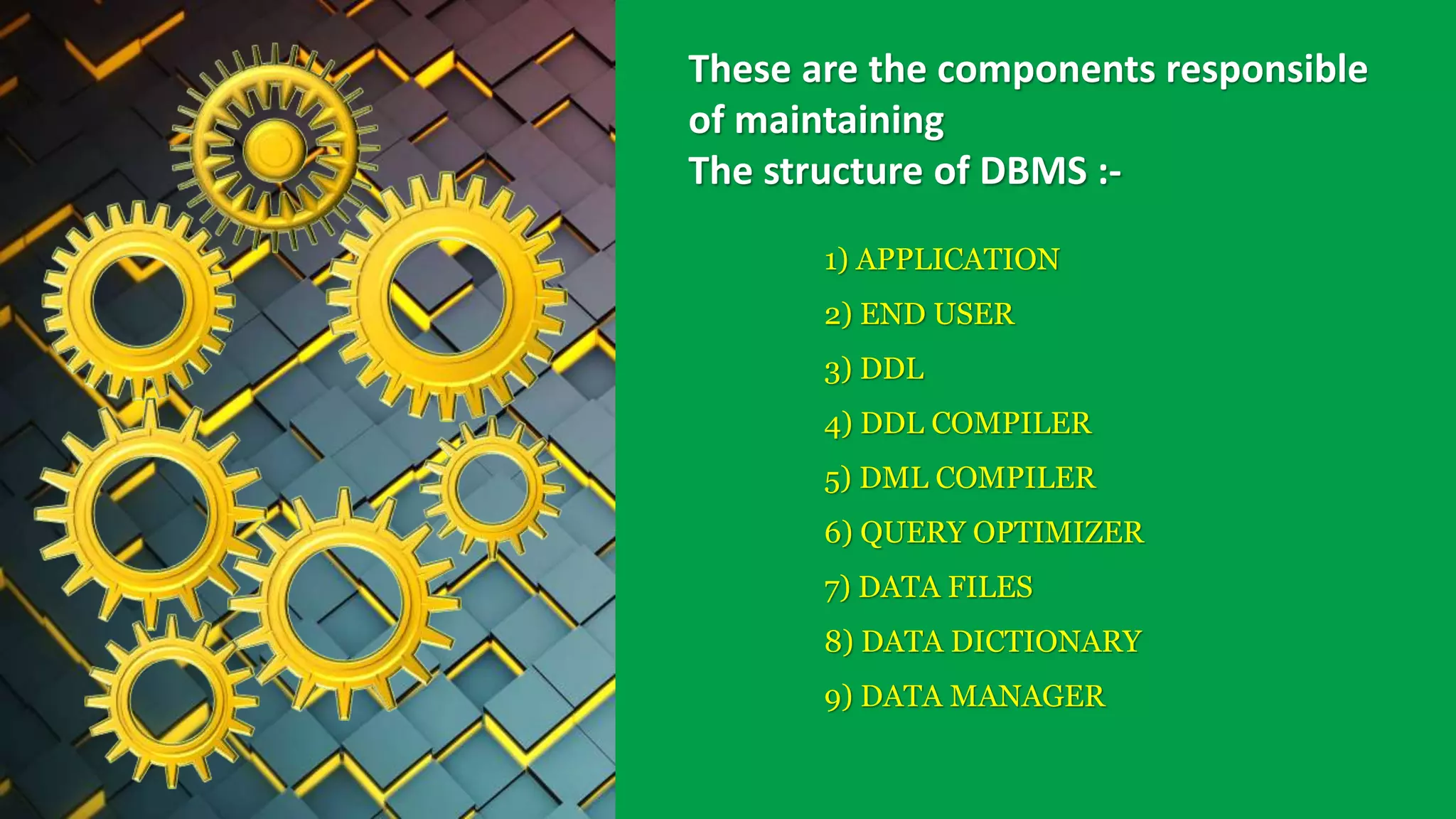
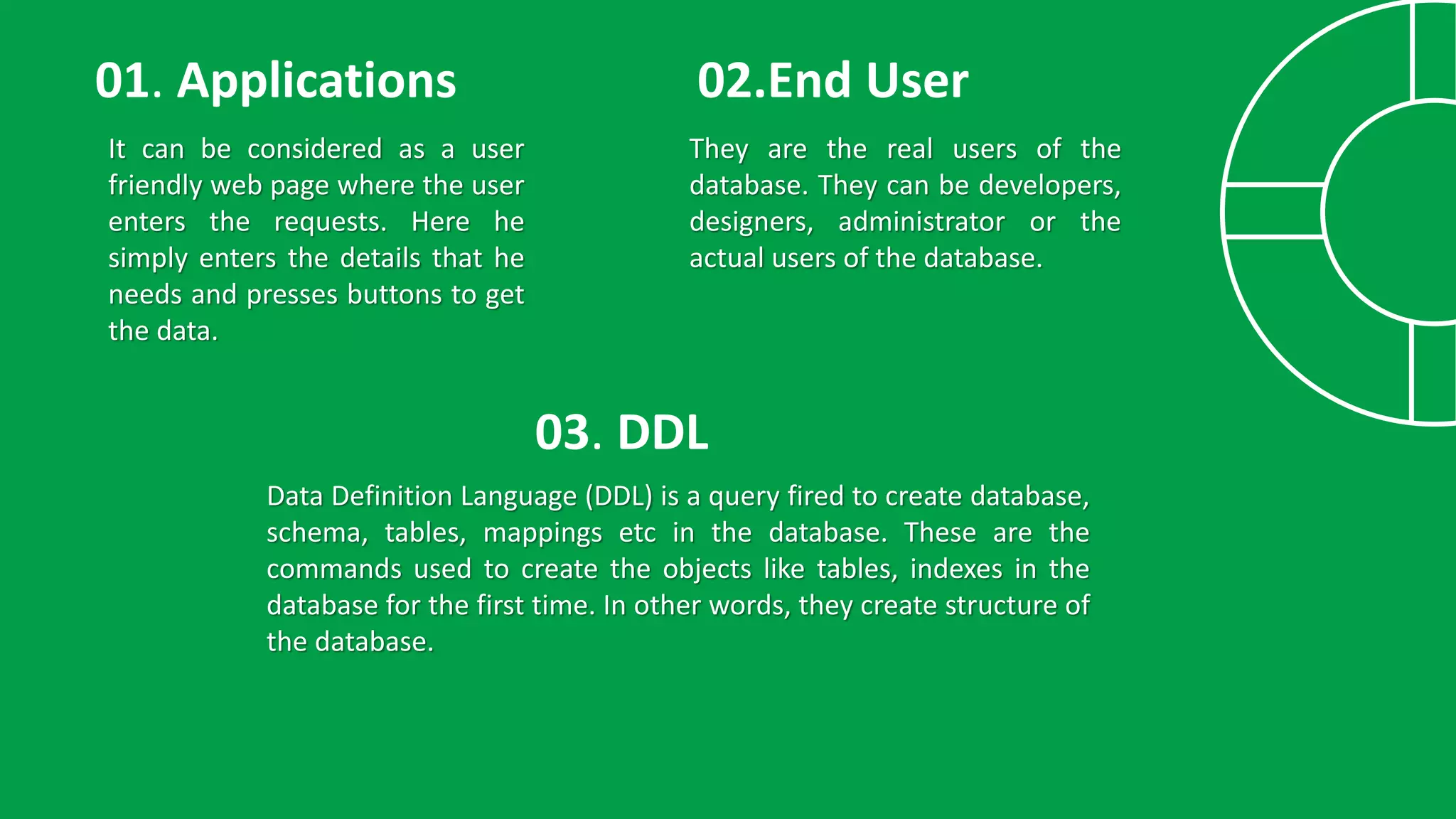
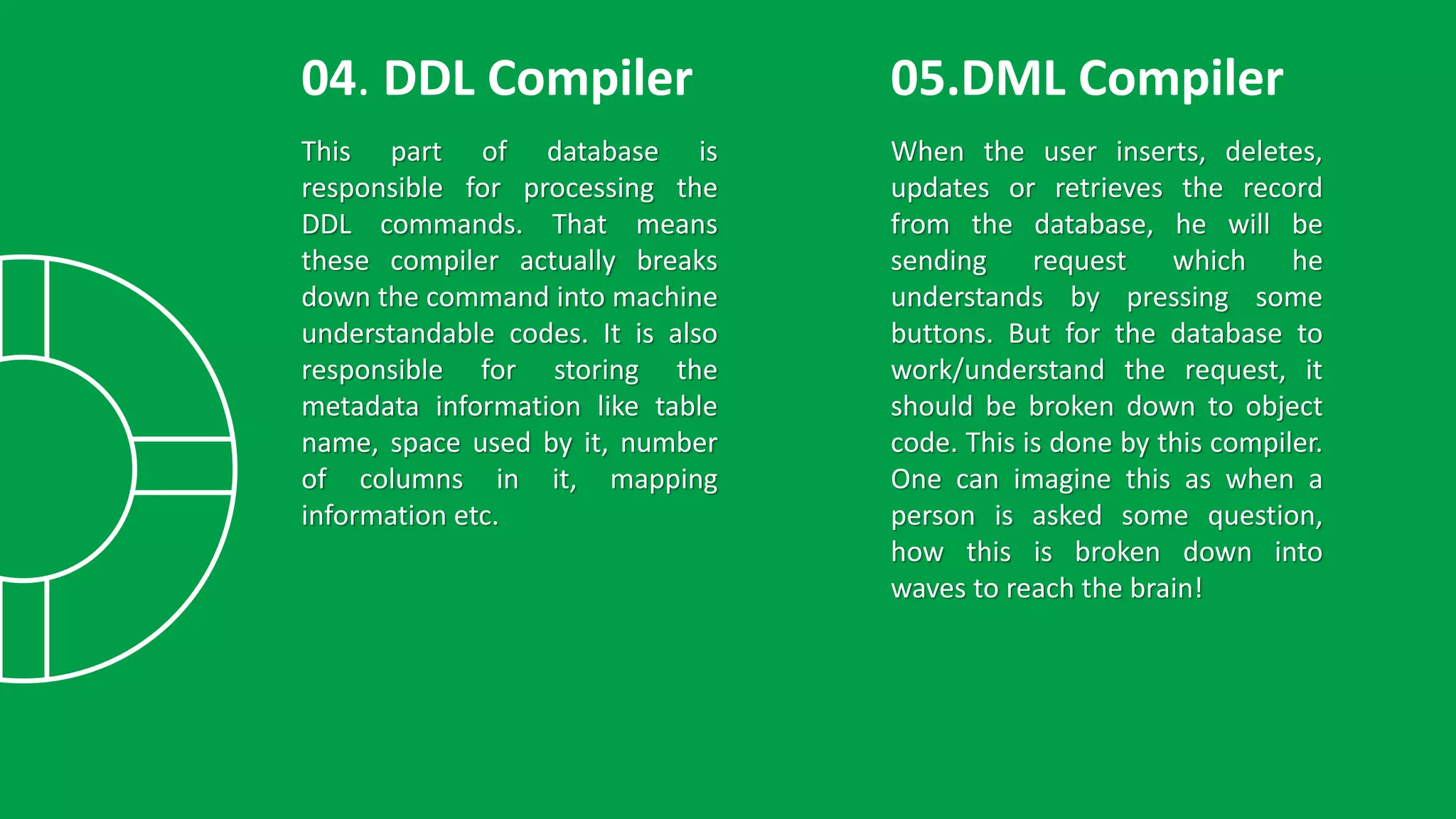
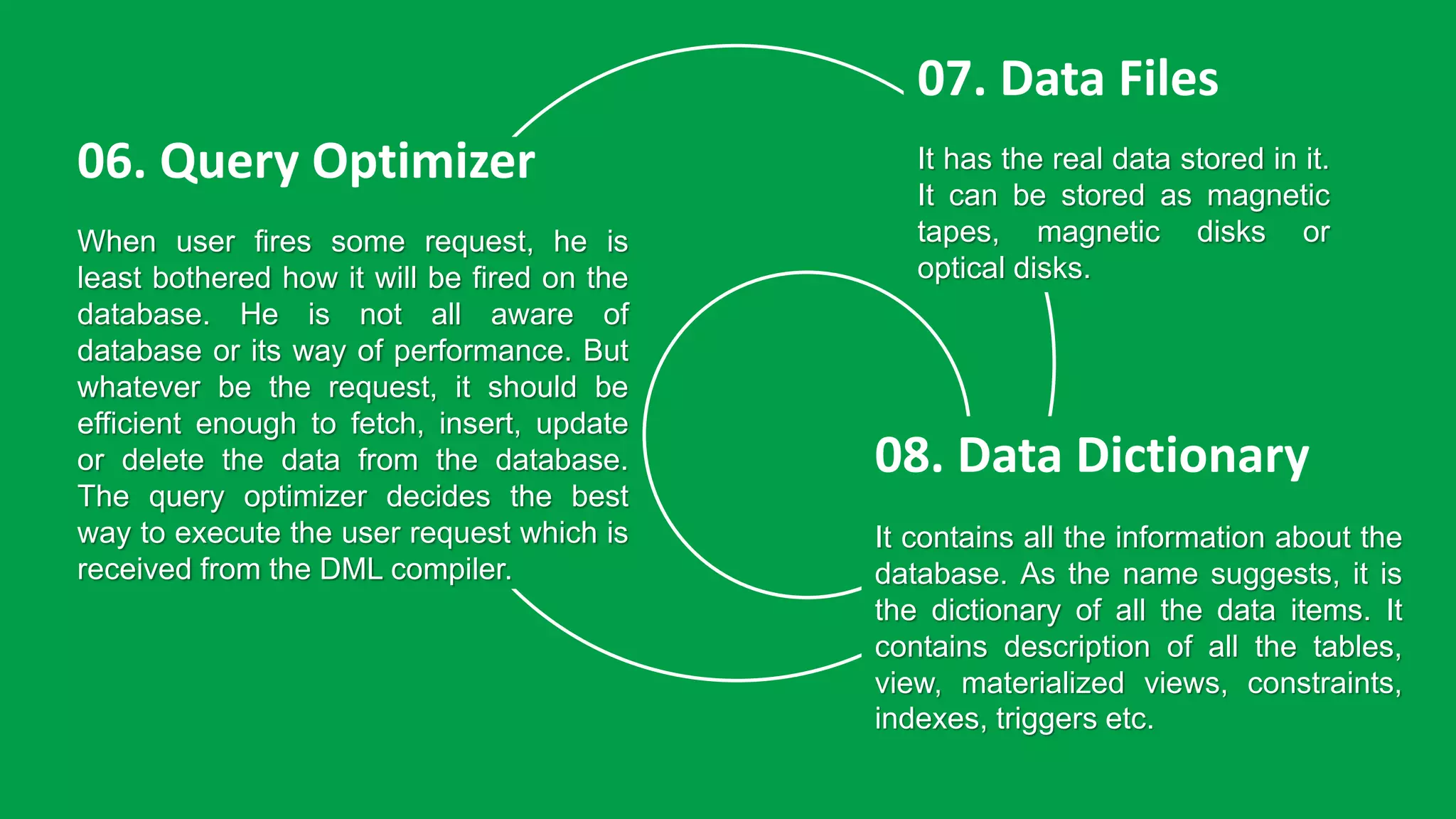
The presentation discusses the structure of a Database Management System (DBMS), highlighting its essential components such as application interfaces, users, and various compilers responsible for processing database commands. Key elements like the Data Definition Language (DDL) compiler, Data Manipulation Language (DML) compiler, query optimizer, data files, and data dictionary are explained, detailing their roles in managing data and ensuring efficient database operations. The stored data manager is emphasized for its critical functions in maintaining database integrity, handling concurrency, and providing backup solutions.