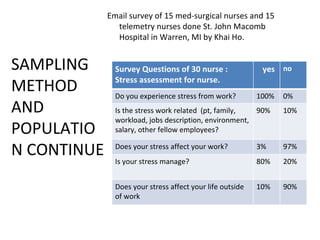
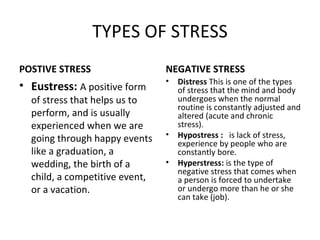
This poster presentation summarizes research on stress among hospital nurses and methods for reducing stress. It finds that nurses experience high levels of work-related stress due to factors like workload, staffing shortages, and interpersonal relationships. Prolonged stress can negatively impact nurses' health, work performance, and personal lives. The presentation then outlines a six-step approach to stress management, which involves identifying sources of stress, evaluating their impacts, designing appropriate coping strategies, implementing strategies, and evaluating their effectiveness in reducing stress. It provides examples of coping mechanisms for nurses to use at work and in their personal lives.