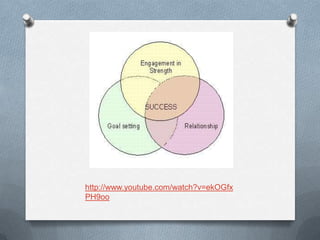
This document provides an overview of a seminar on character strengths. It defines character strengths as positive traits reflected in thoughts, feelings and behaviors. It outlines the main theorists in positive psychology, such as Seligman and Peterson. It discusses the history of positive psychology and lists the 24 character strengths organized under 6 virtues. The document also discusses how to apply character strengths in areas like education, sports, and politics and provides learning outcomes and suggested readings.





































![Examples
O Name: Tiger Woods
O Sport: Golf
O Turned Pro: 8
O Known For: Formerly
the World no.1 he is the
highest-paid
professional athlete in
the world, having
earned an estimated
US$90.5 million from
winnings and
endorsements in
2010.[6][7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strengthspresentation-120206093023-phpapp01/85/Strengths-presentation-38-320.jpg)