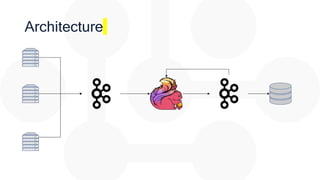
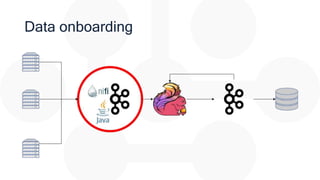
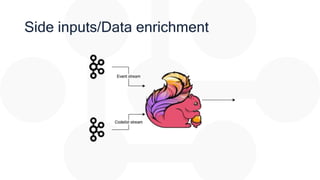
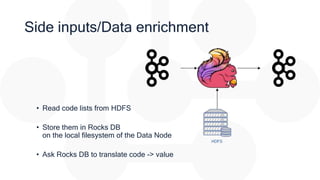
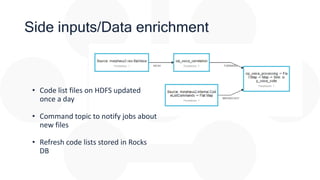
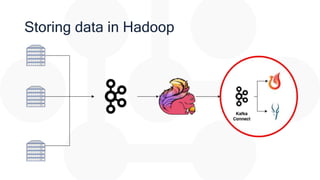
The document discusses the integration of Apache Flink for real-time stream processing in mobile networks, emphasizing its relevance for mobile network operators. It covers topics such as data sources, architecture, stream processing challenges, use cases in telecommunications, and the deployment of Flink in Hadoop environments. The document also explores various functionalities of Flink and associated technologies like Apache Kafka, HBase, and data enrichment techniques.














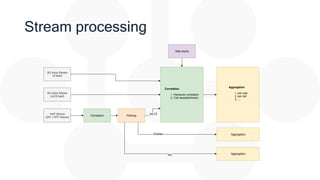

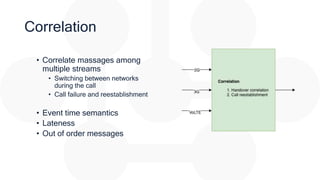
![Correlation
override def processElement(
value: SipVoice,
ctx: KeyedProcessFunction[String, SipVoice,
SipVoices]#Context,
out: Collector[SipVoices]): Unit = {
val startTime = parseTime(value.startTime)
val (key, values) =
sipVoiceState
.keys
.asScala
.find(s => math.abs(s - startTime) <= waitingTime)
.map(k => (k, value :: sipVoiceState.get(k)))
.getOrElse {
val triggerTimeStamp =
ctx.timerService().currentProcessingTime() + delayPeriod
ctx
.timerService
.registerProcessingTimeTimer(triggerTimeStamp)
sipVoiceTimers
.put(triggerTimeStamp, startTime)
(startTime, List(value))
}
sipVoiceState.put(key, values)
}
override def onTimer(
timestamp: Long,
ctx: KeyedProcessFunction[String, SipVoice,
SipVoices]#OnTimerContext,
out: Collector[SipVoices]): Unit = {
if (sipVoiceTimers.contains(timestamp)) {
val sipVoiceKey = sipVoiceTimers.get(timestamp)
val correlationId = UUID.randomUUID().toString
val correlatedSipVoices =
sipVoiceState
.get(sipVoiceKey)
.map(_.toCorrelated(correlationId))
.sortBy(_.startTime)
out.collect(SipVoices(correlatedSipVoices))
correlatedSipVoice.inc()
inStateSipVoice.dec(correlatedSipVoices.size)
sipVoiceTimers.remove(timestamp)
sipVoiceState.remove(sipVoiceKey)
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streamprocessingonmobilenetworksv04published-181108081225/85/Stream-processing-on-mobile-networks-26-320.jpg)