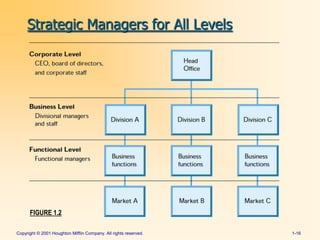
The document summarizes key aspects of strategic management and the strategic management process. It discusses how strategic management helps firms succeed by choosing strategies to attain superior performance. The strategic management process involves defining a mission and goals, analyzing external opportunities/threats and internal strengths/weaknesses, selecting strategies, and implementing and adjusting strategies over time based on feedback. It also discusses various levels of strategies, such as business, functional, global, and corporate strategies.