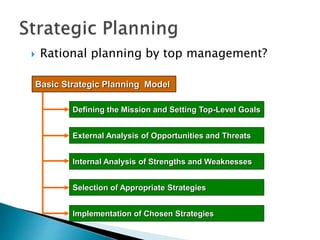
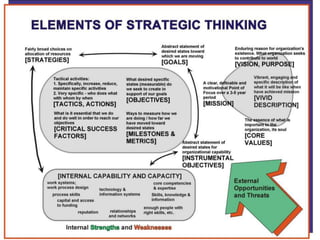
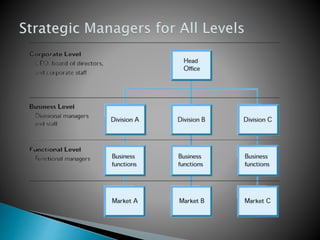
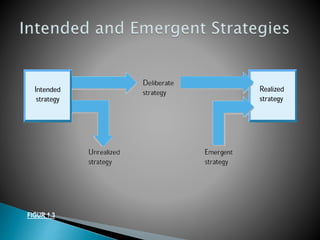
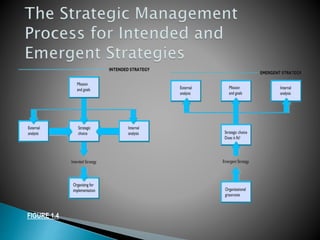
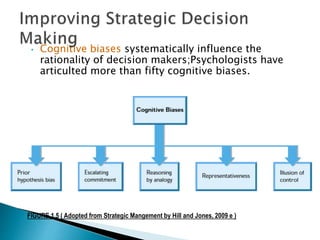
This document discusses strategic management and the strategic planning process. It defines strategy as actions managers take to increase organizational performance and gain competitive advantage. The strategic planning process involves analyzing the external environment, assessing internal strengths and weaknesses, selecting strategies, and implementing and adjusting strategies. The document outlines various strategic approaches organizations can take, such as cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. It emphasizes that strategic planning requires adapting to a changing environment.