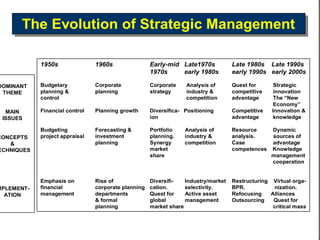
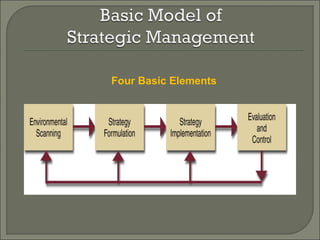
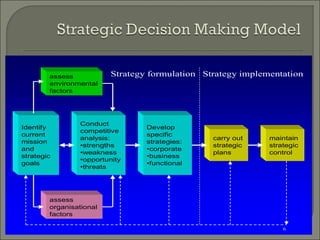
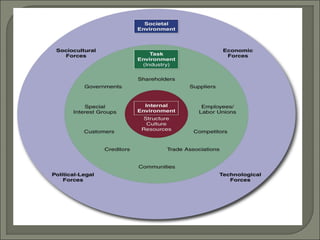
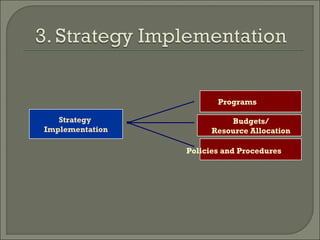
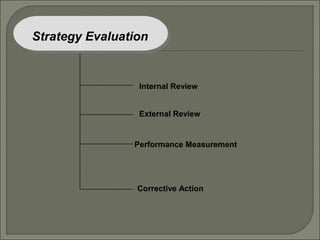
This document discusses the evolution of strategic management from the 1950s to the present. It outlines the dominant themes, main issues, concepts and techniques, and implementation approaches during different decades. Some key elements discussed include conducting environmental scans, competitive analysis, developing corporate and business level strategies, and implementing strategic plans. The strategic management process involves strategy formulation, implementation, evaluation, and making corrections.