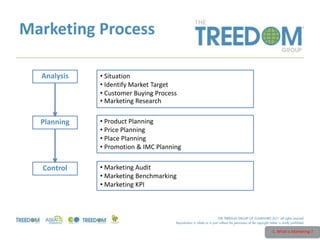
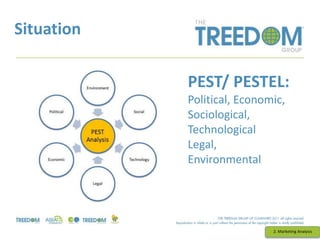
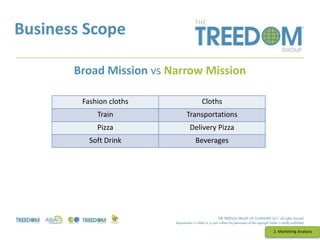
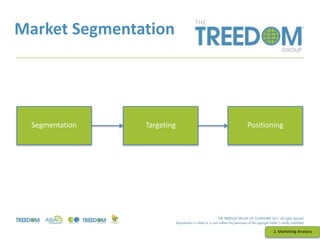
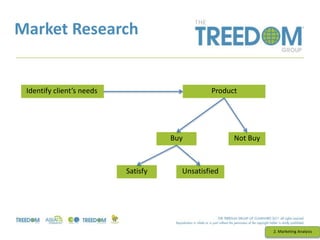
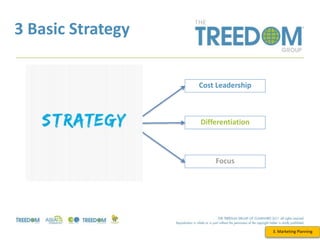
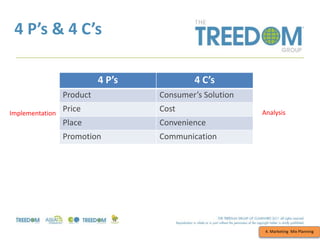
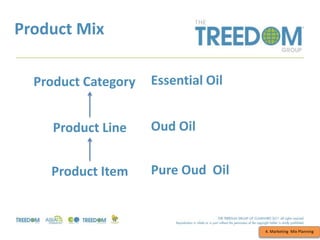
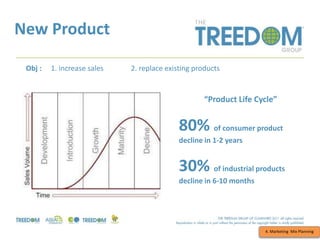
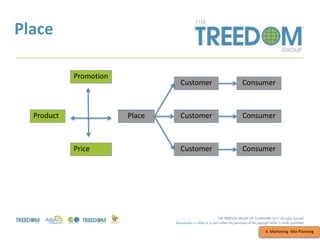
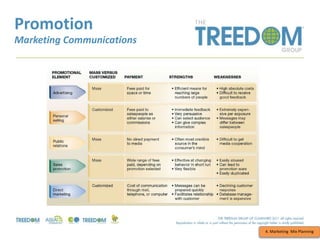
This document provides an overview of strategic marketing planning. It begins with defining key marketing terms and concepts. It then covers analyzing the marketing situation and identifying target markets through research. The bulk of the document outlines developing a marketing plan, including determining strategy and tactics. It discusses the marketing mix of product, price, place, and promotion. Finally, it briefly mentions controlling the marketing plan through audits, benchmarks, and key performance indicators.