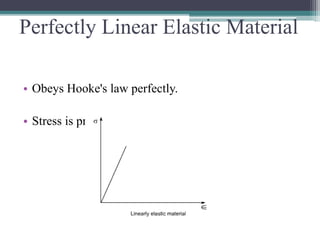
This document discusses strain diagrams and the different types of materials. It defines strain as the ratio of change in dimension of a body to its original dimension when subjected to an external force. There are four main types of strain: tensile, compressive, volumetric, and shear. The document then describes seven types of materials: rigid, perfectly linear elastic, rigid-perfectly plastic, rigid with strain hardening, elastic perfectly plastic, elasto-plastic with strain hardening, and visco-elastic. Visco-elastic materials can be modeled using Maxwell, Kelvin-Voigt, or linear standard body models.