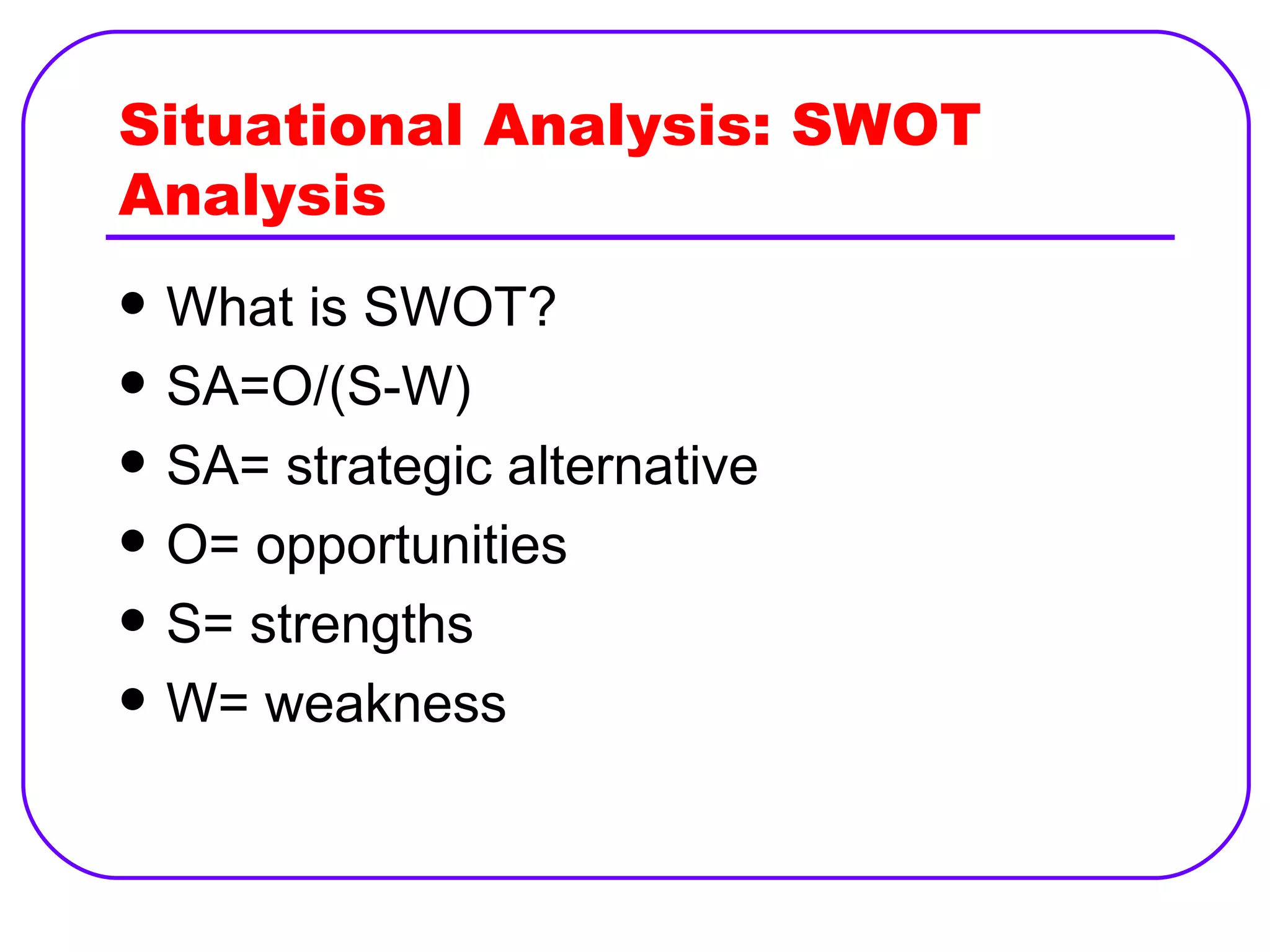
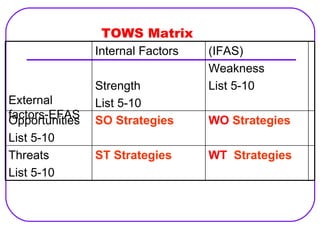
The document discusses various strategic analysis frameworks including SWOT analysis, TOWS matrix, and Porter's generic competitive strategies. SWOT analysis involves identifying internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. The TOWS matrix builds on SWOT by matching strengths/weaknesses with opportunities/threats to generate alternative strategies. Porter's strategies are cost leadership, differentiation, and focus on a narrow or broad target. The document also covers Porter's requirements for successful implementation of the generic strategies and market location tactics for offensive and defensive positioning.