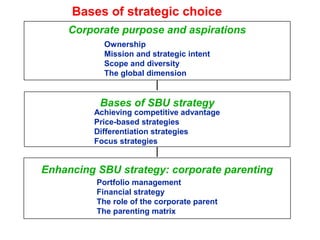
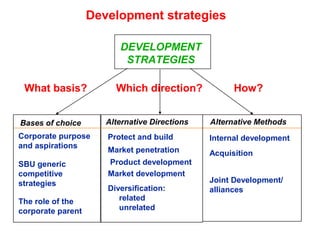
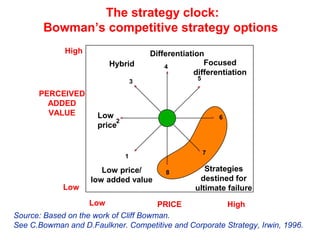
The document discusses strategic choices for businesses. It explains that strategic choices depend on factors like ownership, mission, scope, and competitive advantages. Businesses can pursue price-based strategies, differentiation strategies, or focus strategies. The document also contains a "strategy clock" that graphically shows the options and tradeoffs between low price/value and perceived value. Key questions for strategic choice include considering the environment, stakeholders, available resources, and sustaining the chosen strategies.