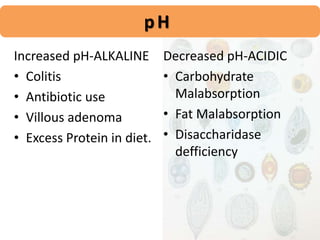
This document provides information about stool examination, including its definition, composition, collection, macroscopic and microscopic examination, color, odor, normalcy parameters, and chemical examination. It defines stool as the waste residue of the human digestive tract expelled during defecation. It describes the various components of stool including undigested food, intestinal secretions, bacteria, and epithelial cells. Methods for collection and examination of stool are outlined, along with normal ranges and clinical significance of various findings.