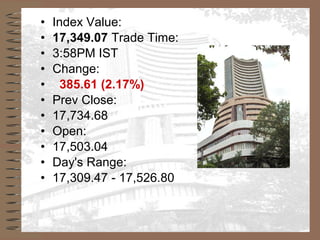
The document provides information on stock exchanges in India, including the major exchanges like the Bombay Stock Exchange and National Stock Exchange. It discusses the key players in stock exchanges like brokers, jobbers, and investors. It also covers topics like speculation, causes of price fluctuations, the role of SEBI in regulating exchanges, and how companies are rated. The largest stock exchange is the Bombay Stock Exchange, located in Mumbai, which accounts for over two-thirds of trading in India.