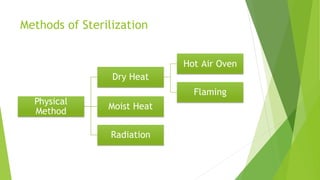
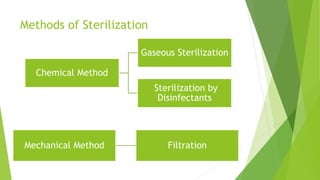
The document outlines aseptic techniques essential for preventing contamination in pharmaceutical preparations and testing. It defines various sterilization processes, including dry heat and moist heat sterilization, alongside their methods, advantages, and disadvantages. Additionally, it details sources of contamination, terms related to sterilization, and the design and operation of sterilization equipment like hot air ovens and autoclaves.