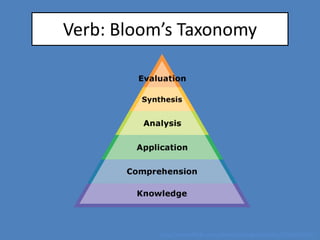
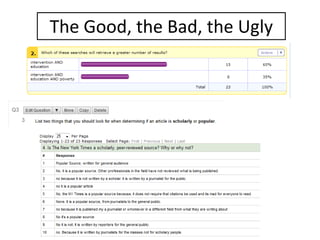
The document discusses quick assessment techniques that can be used in one-shot library instruction sessions. It recommends drafting learning outcomes using Bloom's Taxonomy and composing assessment questions based on the outcomes. The document reviews tools for quick assessment, such as polls, quizzes, and minute papers, and provides best practices for question drafting. The goal of assessment is to identify instructional gaps, determine how to spend class time effectively, and provide evidence of the impact of the instruction.