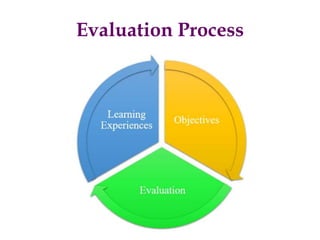
The document discusses various topics related to evaluation processes and test construction, including:
- The purposes of tests such as assigning grades, measuring progress, and assessing teaching effectiveness.
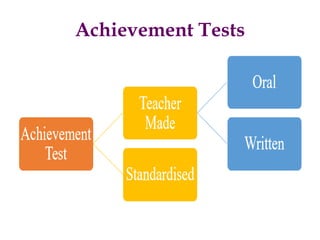
- Steps in test construction such as developing a table of specifications and determining test format.
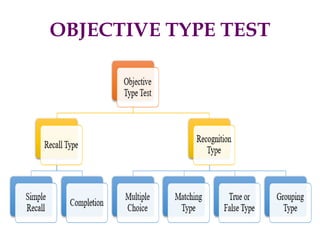
- Types of test questions like multiple choice, short answer, and essay questions. Guidelines for writing different types of questions are provided.
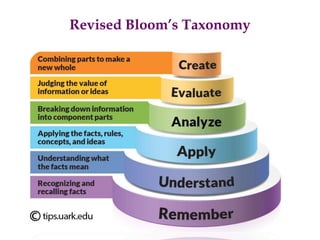
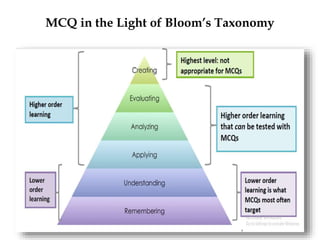
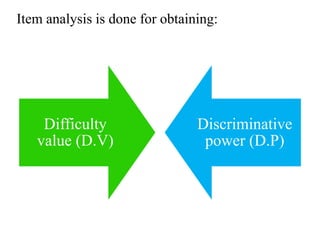
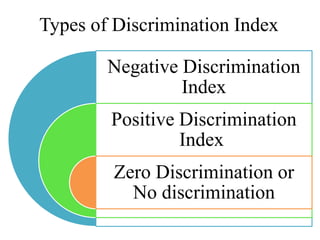
- Item analysis which is used to select appropriate test items based on difficulty value and discrimination power. Formulas for calculating difficulty value and discrimination index are outlined.
- Advantages and disadvantages of different question types are compared. Best practices for writing multiple choice questions, short answer questions, and essay questions are discussed














































![References
• www.u.arizona.edu/~jag/POL602/Designing-Managing-MCQs.pdf
• Dewey, R. A. (1998, January 20). Writing multiple choice items
which require comprehension. Retrieved November 3, 2003 from
• http://www.psywww.com/selfquiz/aboutq.html.
• Carneson J, Delpierre G and Masters, K (1996). Designing and
managing multiple choice questions. Retrieved from Centre for
Educational Technology, University of Capetown Web site:
http://web.uct.ac.za/projects/cbe/mcqman/mcqchp3.html.
• Green, K. (n.d.). Sample multiple choice questions that test higher
order thinking and application [PDF document]. Retrieved from
Washington State University Office of Assessment of Teaching and
Learning Web site:
http://oai.wsu.edu/large_classes/Sample%20multiple%
20choice%20questions%20for%20higher%20order%20thinking_atl.
pdf.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/msu23-10-2019-200314094628/85/Sreedevi-P-S-66-320.jpg)
