Static binding is resolved at compile time based on the reference variable type. Dynamic binding is resolved at runtime based on the actual object type. The document provides examples of static and dynamic binding using method overriding. It also defines abstract classes and interfaces. Abstract classes can contain abstract and non-abstract methods while interfaces contain only abstract methods. The key difference between abstract classes and interfaces is that abstract classes support inheritance of implementation while interfaces support multiple inheritance of signature only.

![}
ClassTT
{
Publicstaticvoidmain(Stringarr[])
{
A a= newC();//methodcall isstaticallybindedsoitwill call atcompile time itself andprintClassA
a.A1(); //method
B.A1()//use of classname toaccessthe staticmethod
}
}
Dynamic Binding: dynamic binding also known as late binding it
means method implementation that actually determined at run time and
not at compile time.
ClassA
{
Publicdoit()
{
S.O.P(“Iamin A”);
}
}
ClassB extendsA
{
Publicdoit()
{
S.O.P(“Iamin B”);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticbinding-220203072324/85/Static-binding-2-320.jpg)
![}
ClassC extendsB
{
Publicdoit()
{
S.O.P(“Iamin C”);
}
}
ClassTest
{
Publicstaticvoidmain(Stringarr[])
{
A x= newB();
x.doit();//itwill print Iamin B
}}
Anotherexampleof dynamicbindinggivenas
classA1
{
voidwho()
{
System.out.println("i aminAAA");
}
}
classB1 extendsA1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticbinding-220203072324/85/Static-binding-3-320.jpg)
![{
voidwho()
{
System.out.println("i amoinBBB");
}
}
class C1 extendsB1
{
voidwho()
{
System.out.println("i amincc");
}
}
classDynamicbinding
{
publicstaticvoidmain(Stringarr[])
{
A1 a=newB1();
a.who();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticbinding-220203072324/85/Static-binding-4-320.jpg)

![{
S.O.P(“thisisacall for me”);
}
Public staticvoidmain(Stringarr[])
{
B b= newB();
b.callMe();
}
}
Note:
1. Abstractclass isnot interface.
2. An abstractclass musthave an abstract method
3. Abstractclass can have constructor,membervariable andnormal methods.
4. Abstractclassescan neverbe instantiated.
5. When you extend abstract class with abstract method you must define the
abstract method in child class. or make child class abstract.
Abstract is an important feature of OOPs.it means hiding complexity. Abstract
class used to provide abstraction.
Example: we are casting instance of car type under Vehicle .now vehicle
reference can be used to provide implementation but it will hide the actual
implementation process.
abstract class vehicle
{
public abstract void engine();
}
public class Car extends Vehicle
{
Public void engine()
{
System.out.println(“Car engine”);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticbinding-220203072324/85/Static-binding-6-320.jpg)
![//here you can write any other code
}
public static void main(String arr[])
{
Vehicle v=new Car();
v.engine();
}
}
Output: car Engine
Abstract methods are usually declared where two or more subclasses are expected to do
similar things in different ways through different implementation.
These subclasses extend the same abstract class and provide different implementation for
abstract method.
INTERFACE:
Interfaceis collection of abstractmethods and static final data members.
Interfacecannotbe instantiated but their reference variablecan be created.
Syntax:
interface identifier
{
Static final data members;
Implicit abstractmethod();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticbinding-220203072324/85/Static-binding-7-320.jpg)

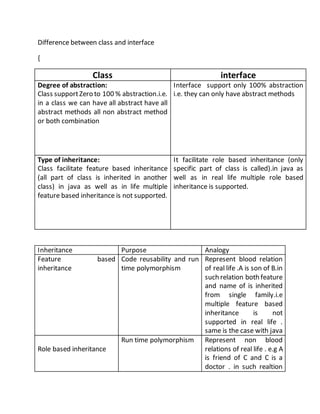





![}
}
class Tomato implements Fruit, Vegetable {
boolean peel = false;
boolean root= false;
public Tomato() {}
public boolean hasAPeel()
//must havethis method,
// becauseFruit declared it
{
return peel;
}
public boolean isARoot()
//must have this method,
// because Vegetable declared it
{
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticbinding-220203072324/85/Static-binding-16-320.jpg)

![// (whattype.doesThisHaveAPeelOrIsThisRoot
// (tomatoFruit));
//can not treat tomatoFruitas a Vegetable
// withoutcasting it to a Vegetable or Tomato
}
}
Example: write a programto calculate area of class rectangle and class
triangle through interface .
class Rectangle
{
public float compute(float x, float y)
{
return(x* y);
}
}
class Triangle
{
public float compute(float x,float y)
{
return(x * y/2);
}
}
class InterfaceArea
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle();
Triangle tri = new Triangle();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticbinding-220203072324/85/Static-binding-18-320.jpg)

![return x+y;
}
public double Add(doublex , double y, double z)
{
return x+y+z;
}
}
class Subtractionimplements Subb
{
public int sub(intx,int y)
{
return x-y;
}
public float sub(floatx,float y)
{
return x-y;
}
public double sub(doublex , double y)
{
return x-y;
}
}
class Math
{
public static void main(String arr[])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticbinding-220203072324/85/Static-binding-20-320.jpg)
