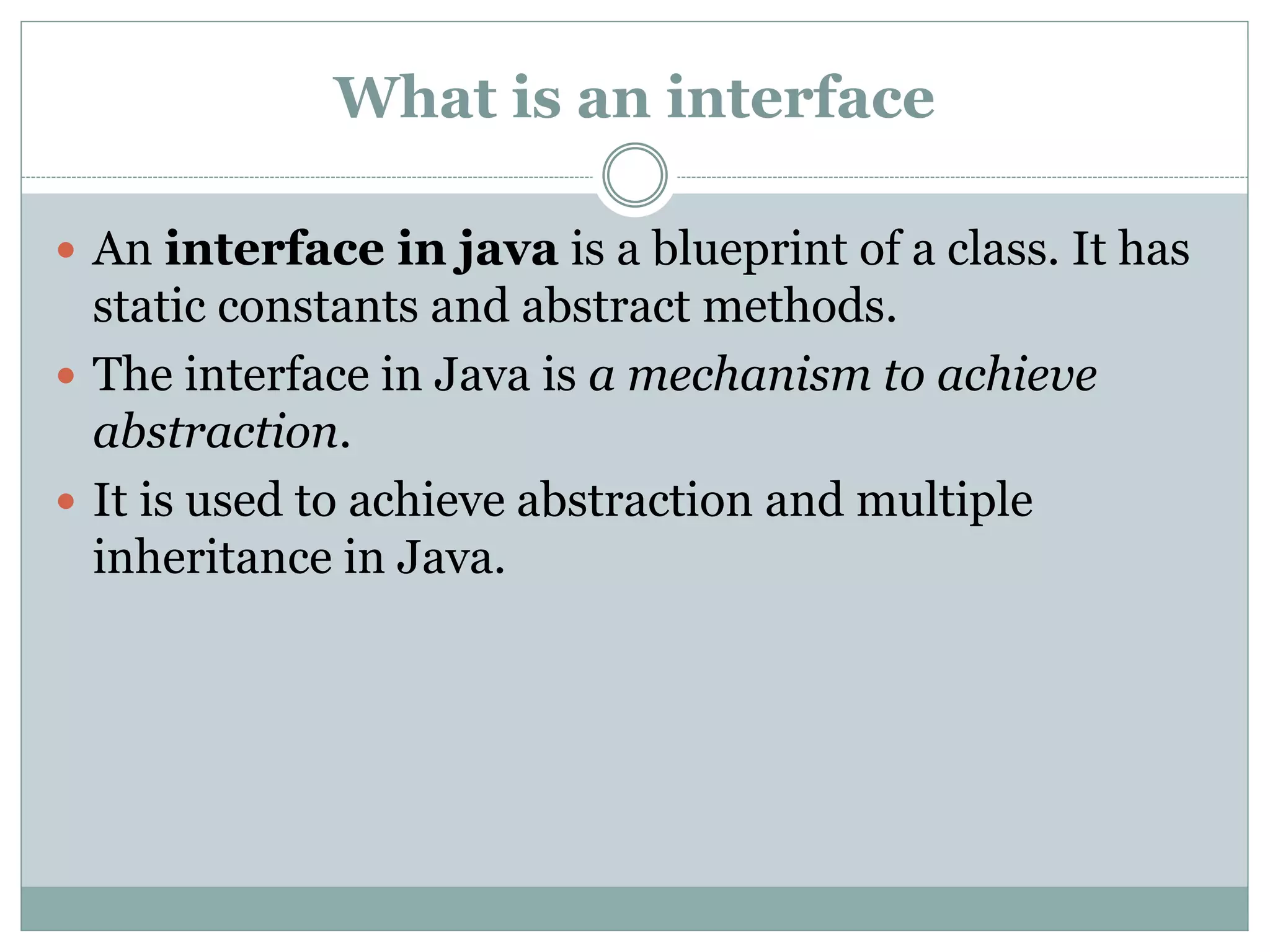
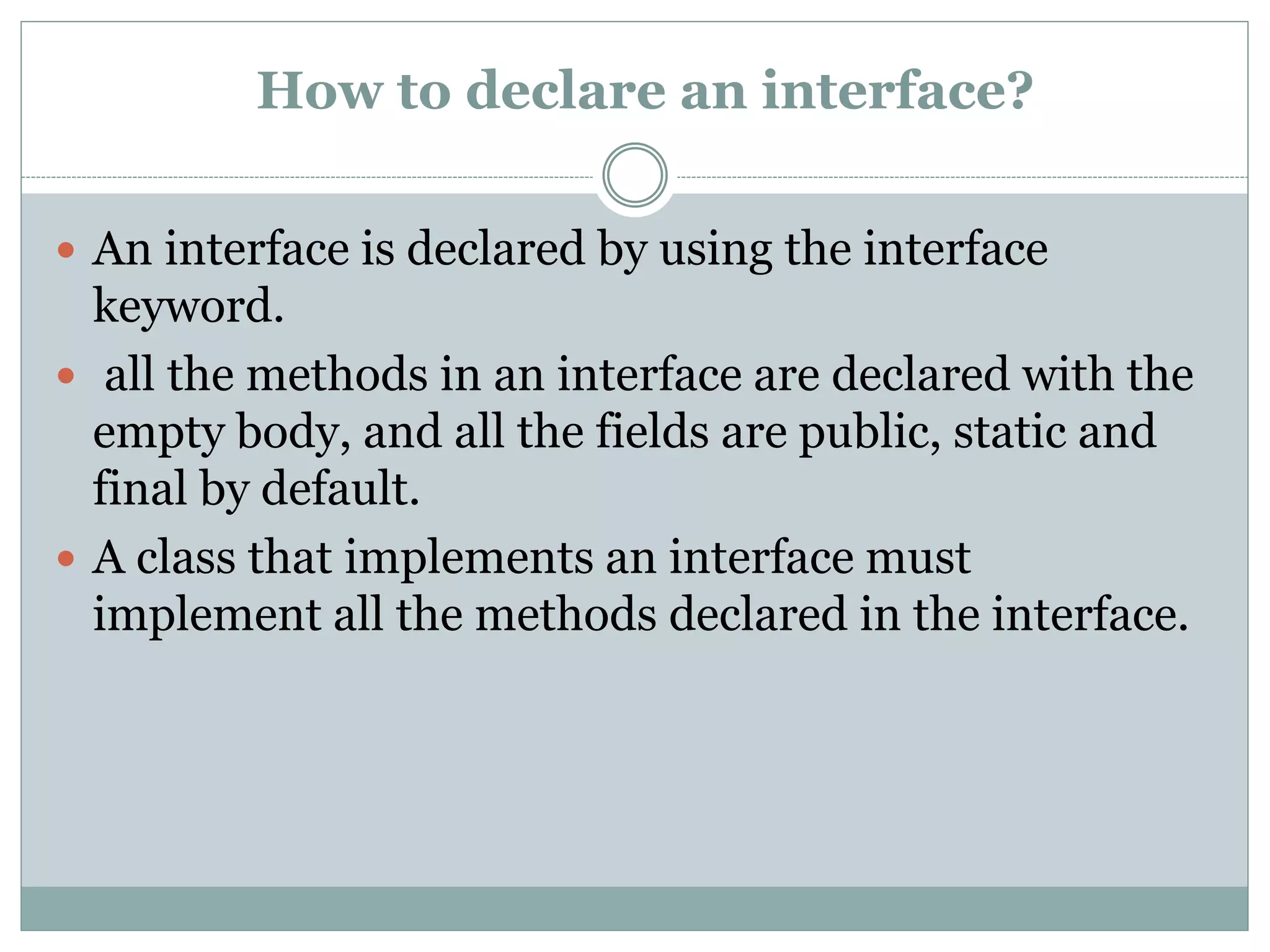
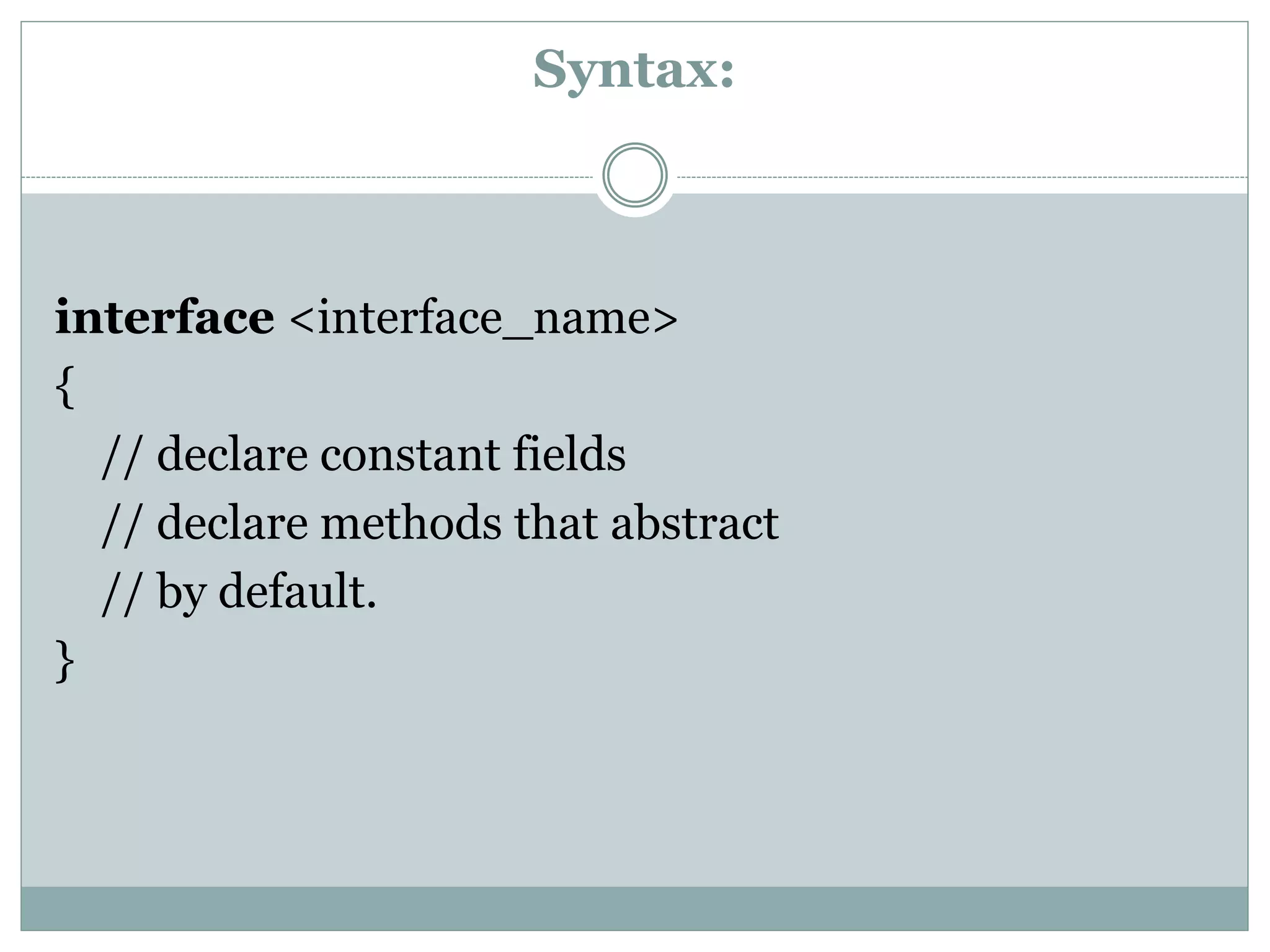
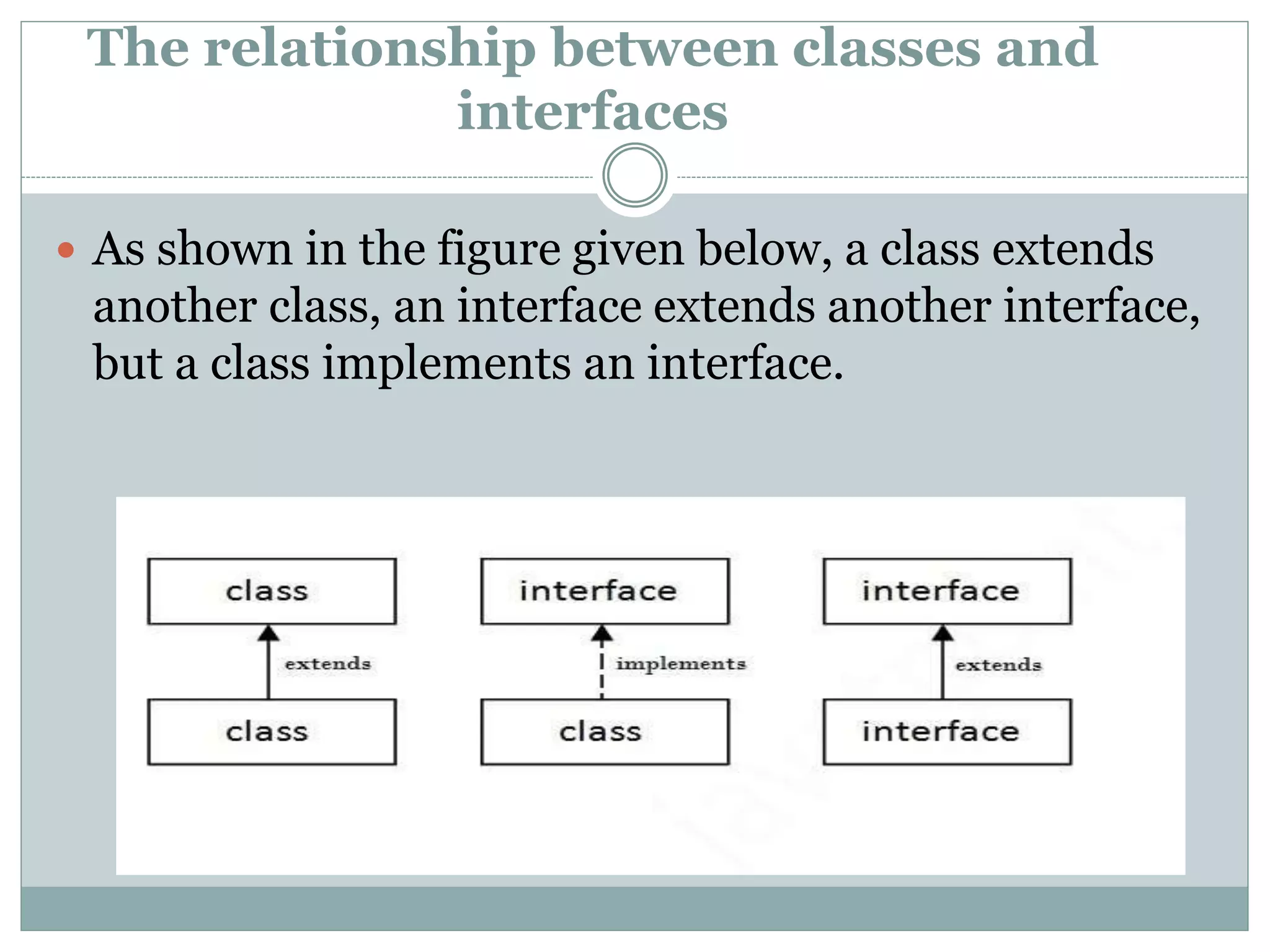
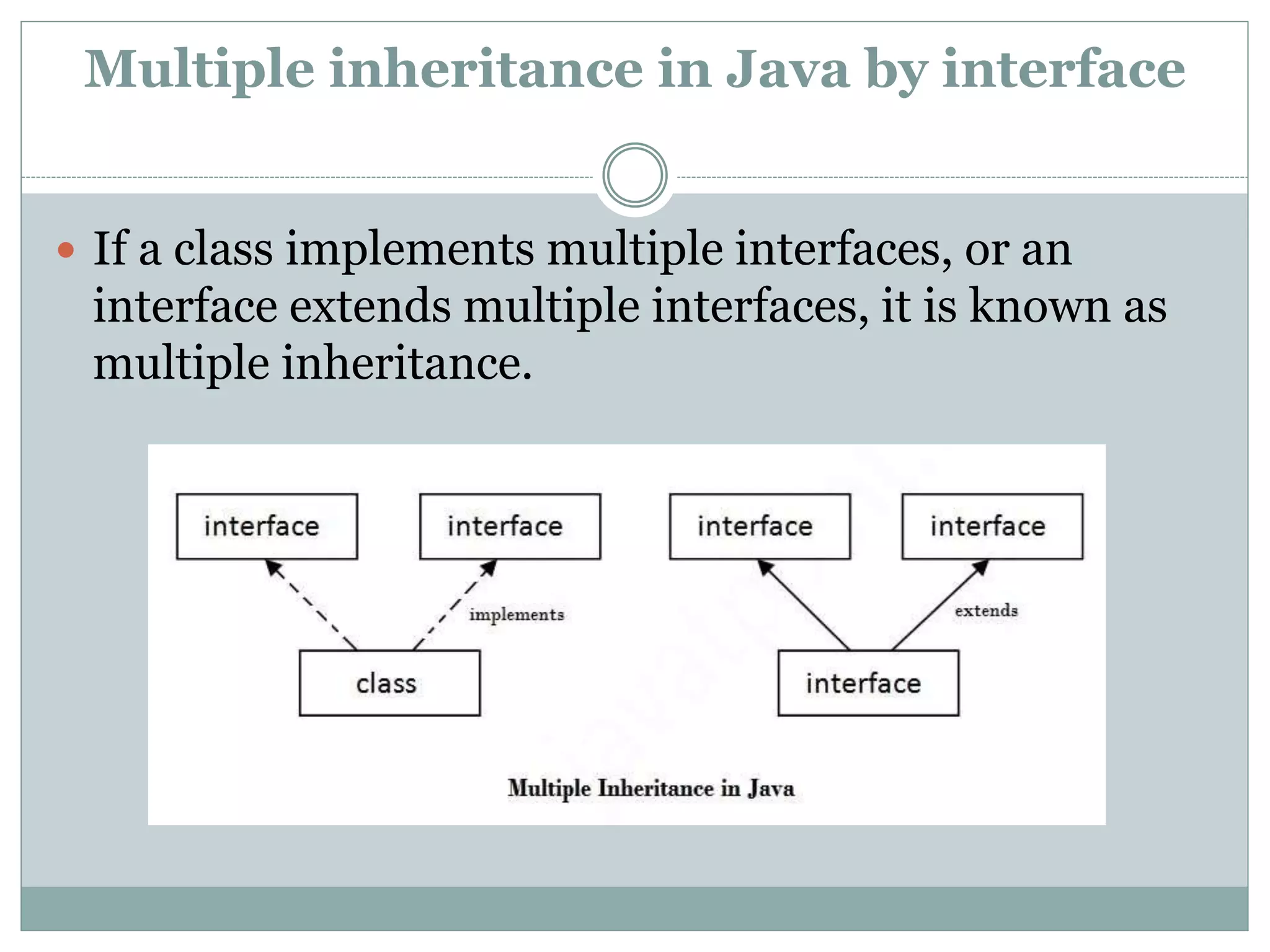
An interface in Java is a blueprint for classes that enables abstraction and multiple inheritance through abstract methods and static constants. It allows classes to implement multiple interfaces, circumventing the ambiguity associated with multiple inheritance in classes. Interfaces are declared using the 'interface' keyword, and any class implementing an interface must define all its methods.



![Java Interface Example
//Interface declaration: by first user
interface Drawable
{
void draw();
}
//Implementation: by second user
class Rectangle implements Drawable
{
public void draw()
{
System.out.println("drawing
rectangle");
}
}
class Circle implements Drawable
{
public void draw()
{
System.out.println("drawing circle");
}
}
//Using interface: by third user
public class TestInterface1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Drawable d=new Circle();//In real
scenario, object is provided by
method e.g. getDrawable()
Drawable r=new Rectangle();
d.draw();
r.draw();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfaceinjava-190405210634/75/Interface-in-java-multiple-inheritance-in-java-interface-implementation-9-2048.jpg)
![Multiple inheritance using interface
interface Printable
{
void print();
}
interface Showable
{
void show();
}
public class A7 implements
Printable,Showable
{
public void print()
{
System.out.println("Hello");
}
public void show()
{
System.out.println("Welcome");
}
public static void main(String
args[])
{
A7 obj = new A7();
obj.print();
obj.show();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfaceinjava-190405210634/75/Interface-in-java-multiple-inheritance-in-java-interface-implementation-11-2048.jpg)