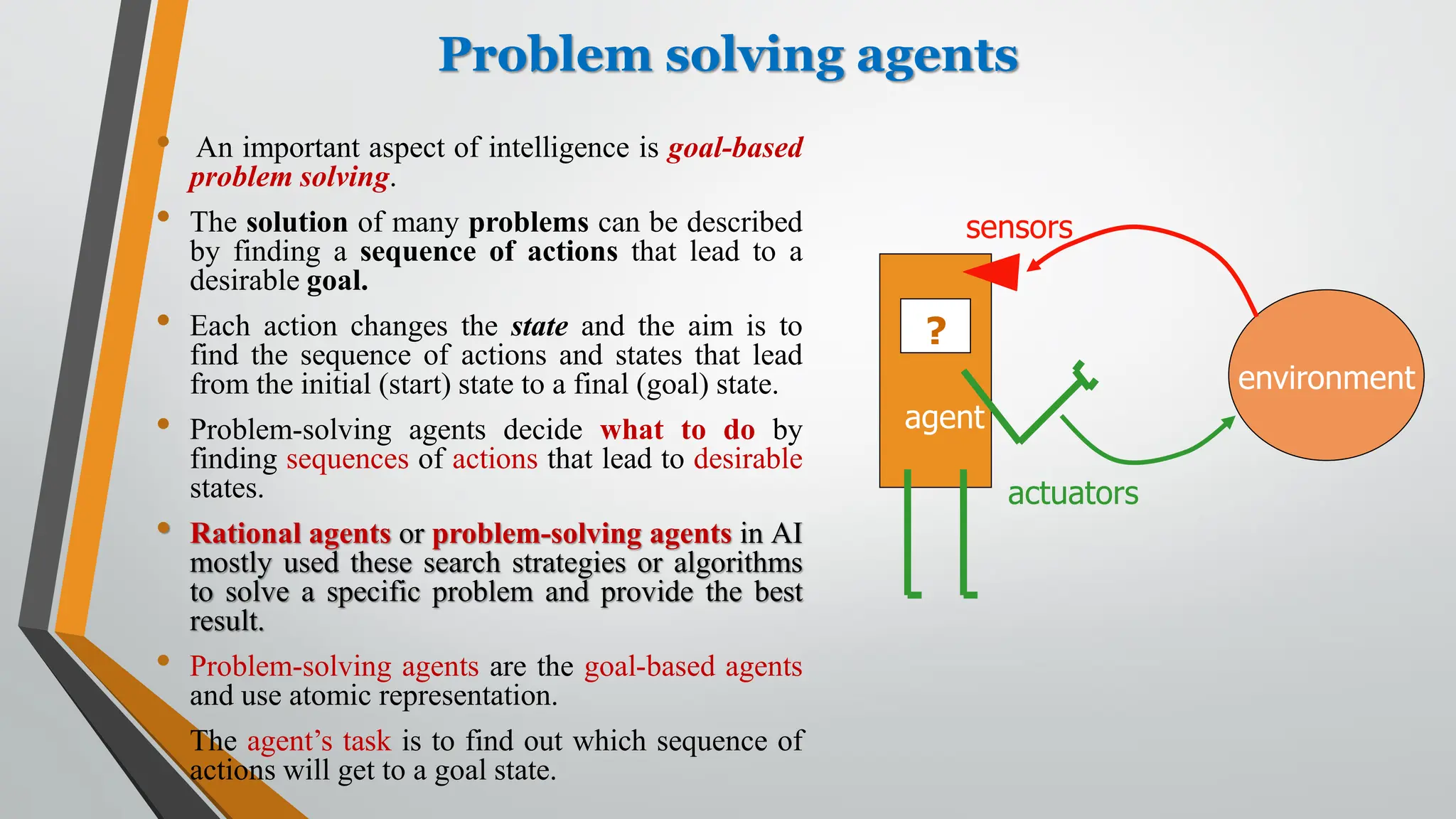
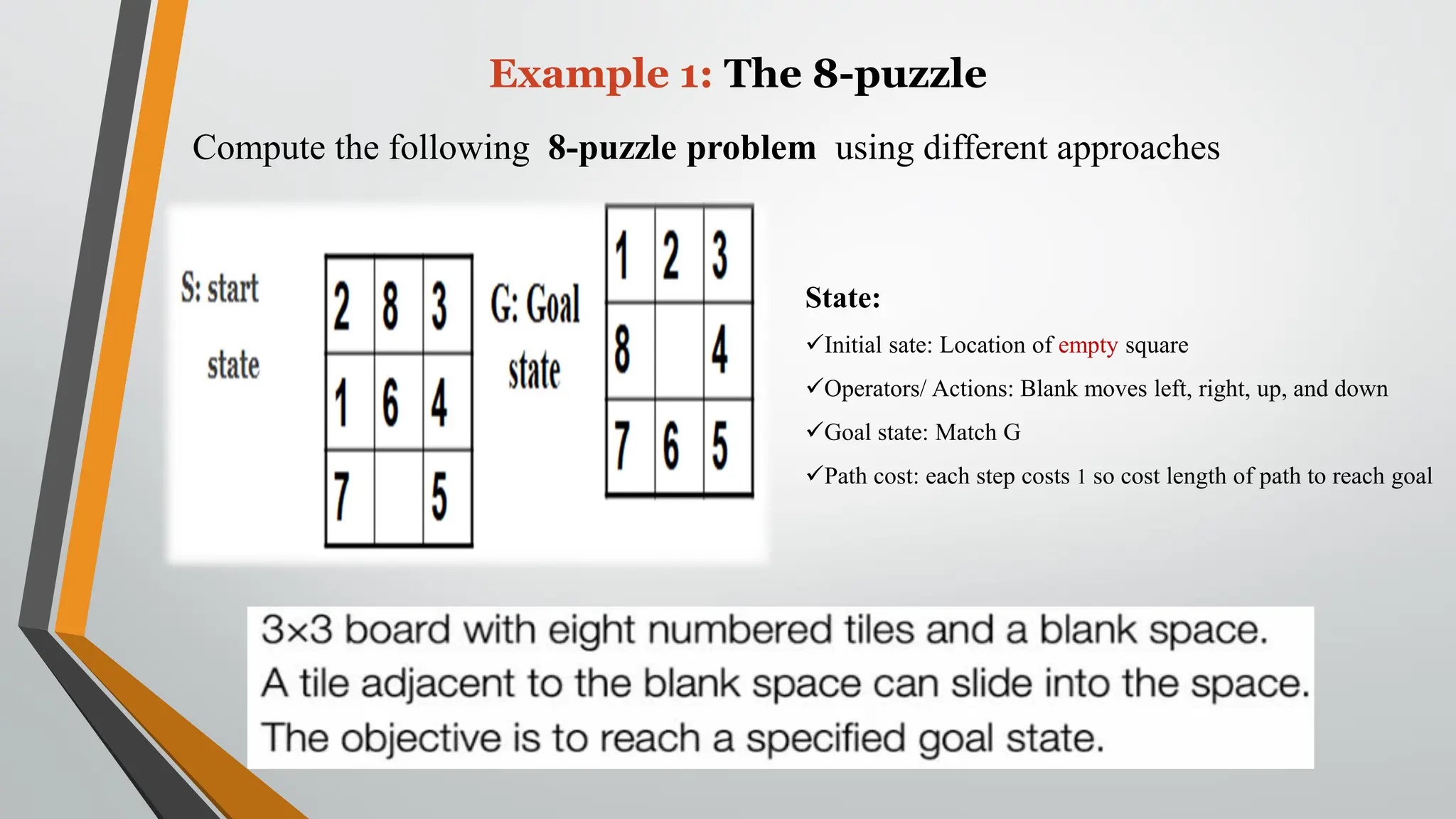
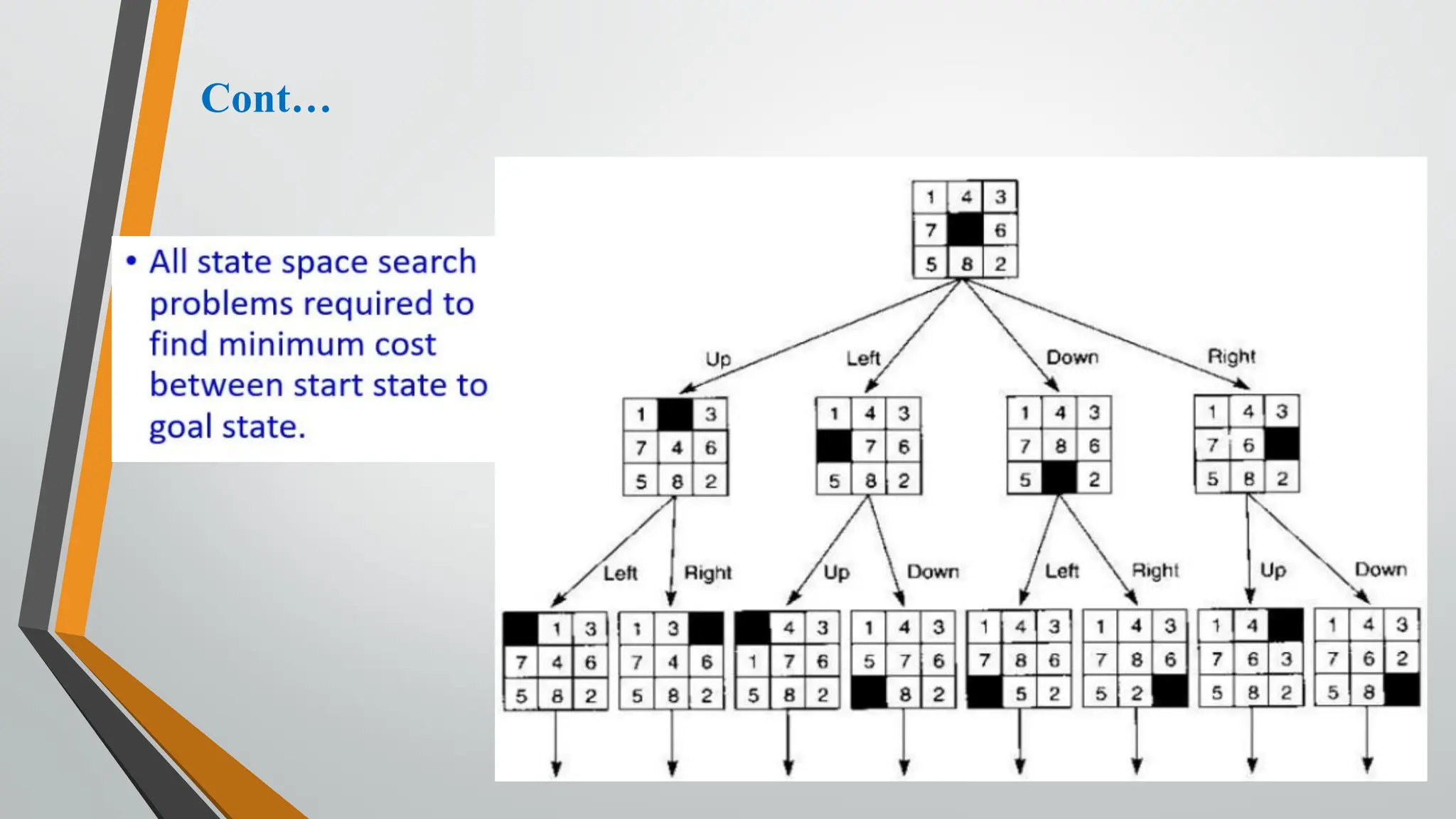
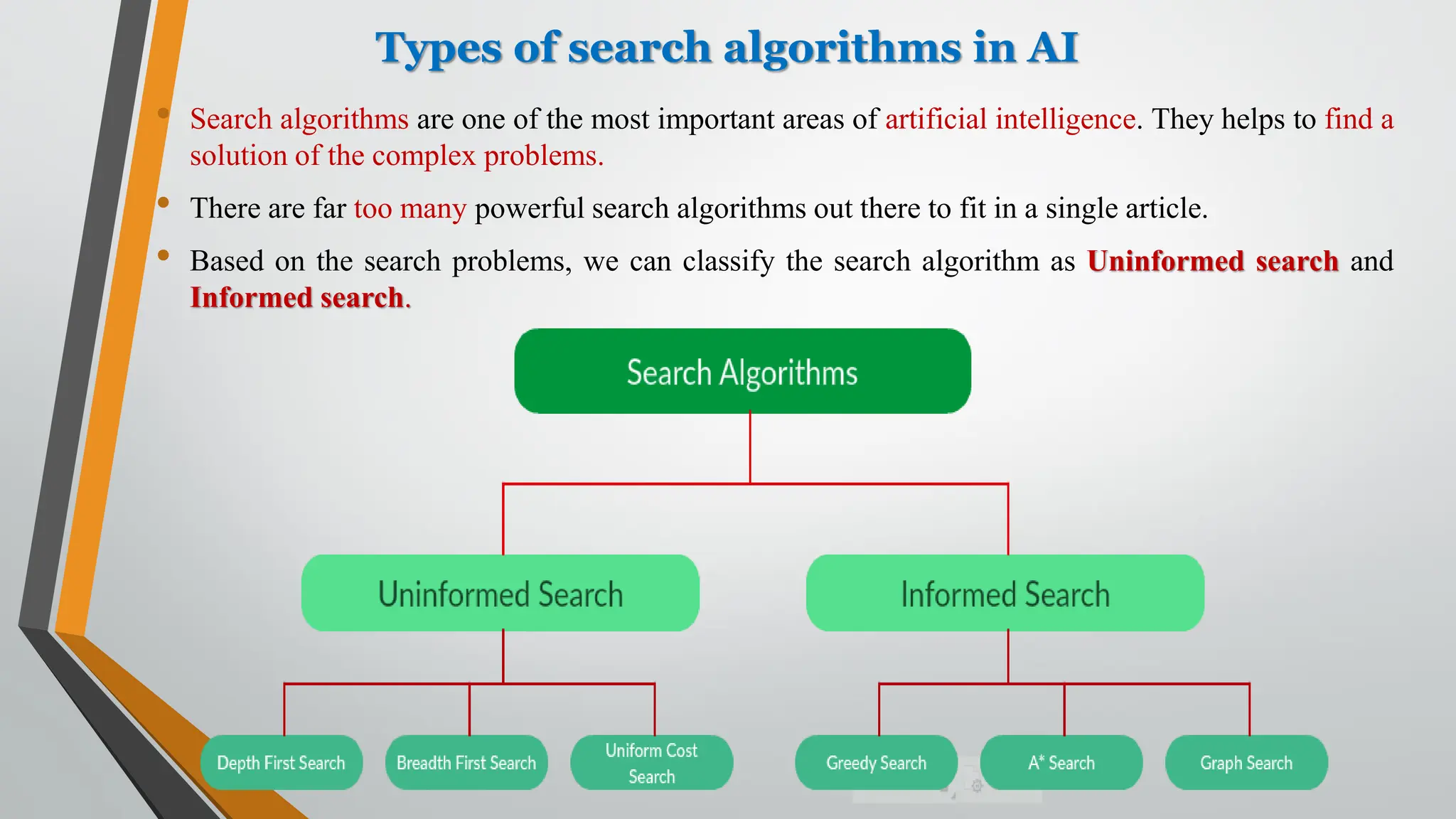
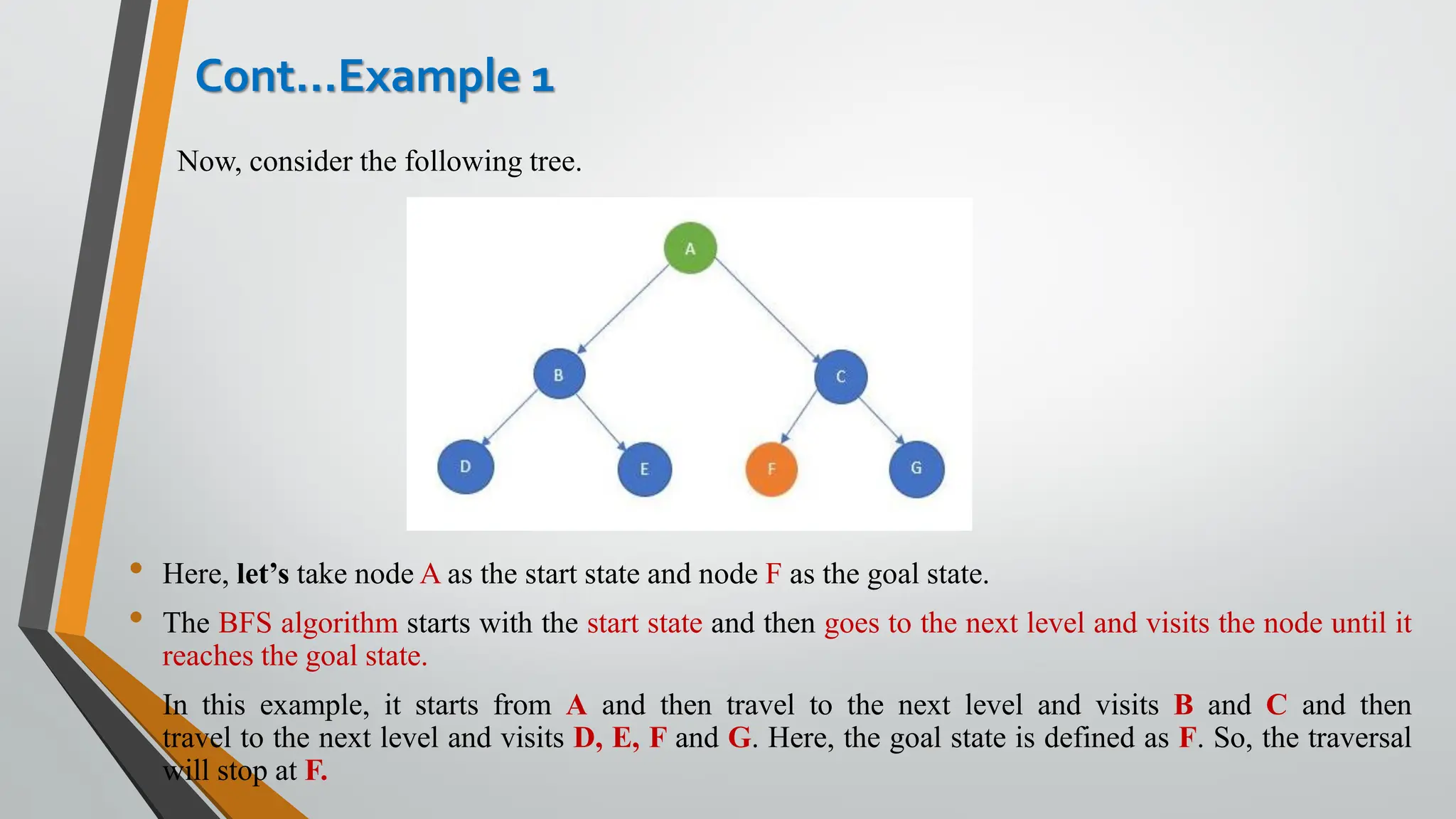
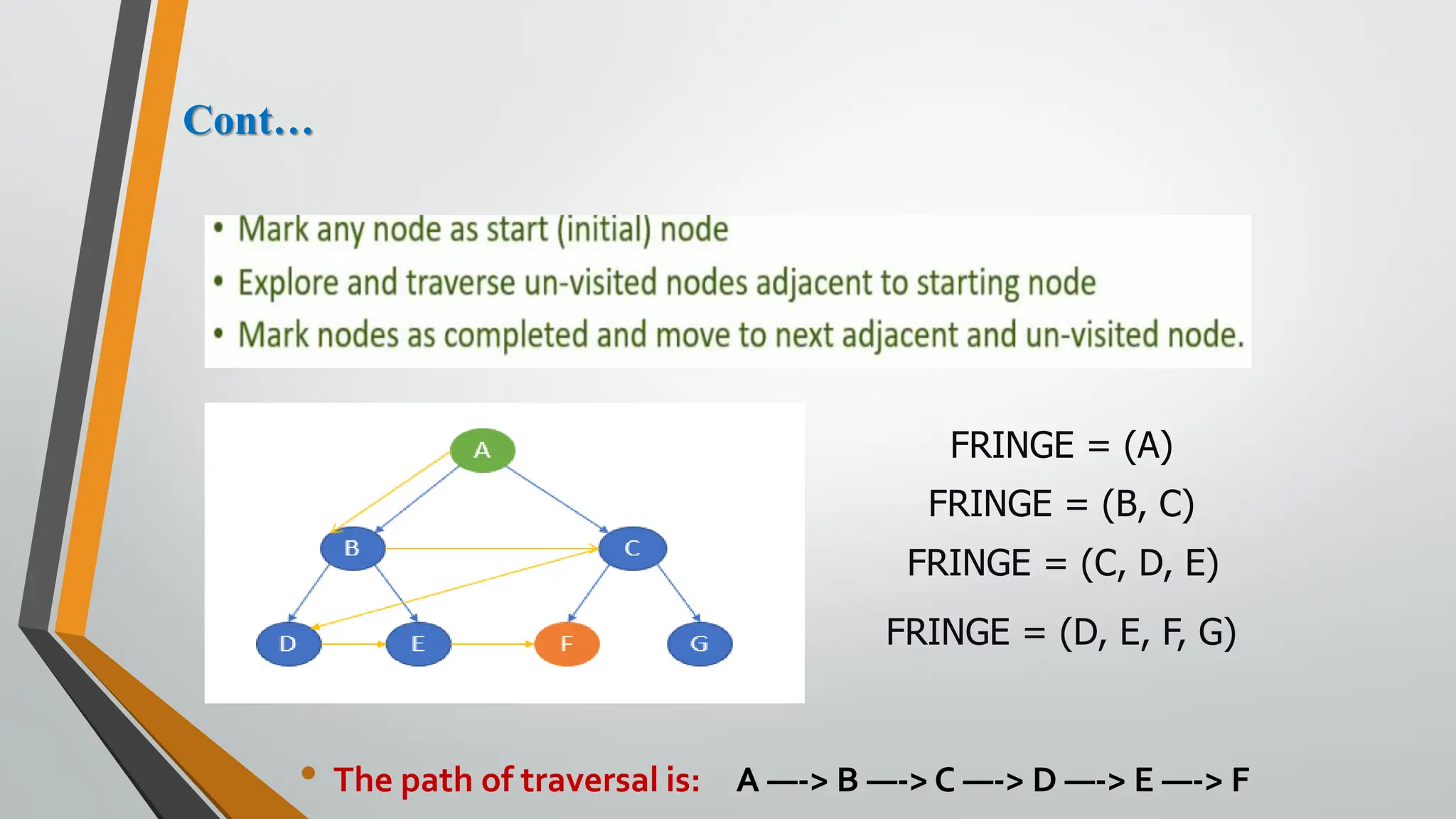
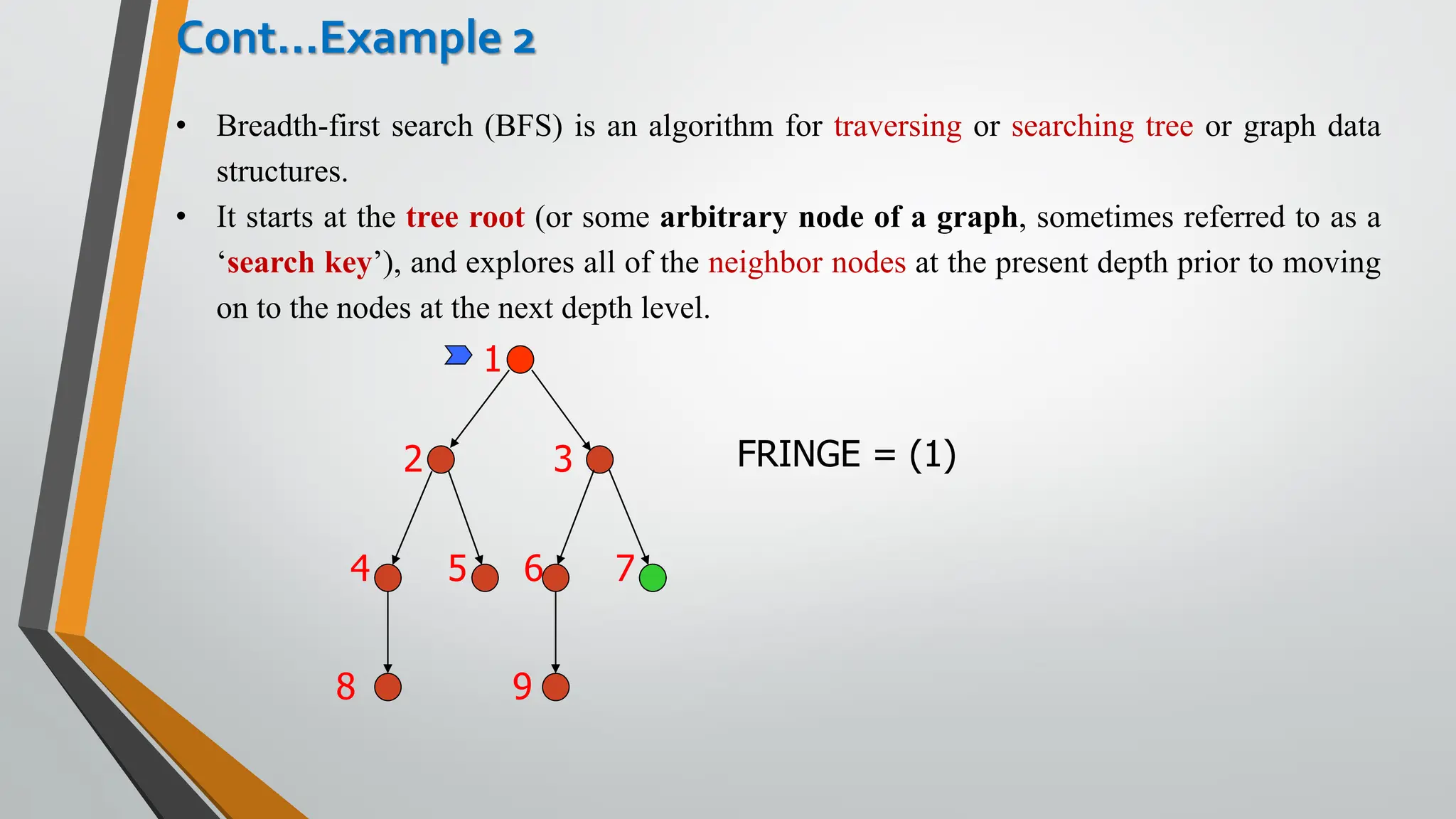
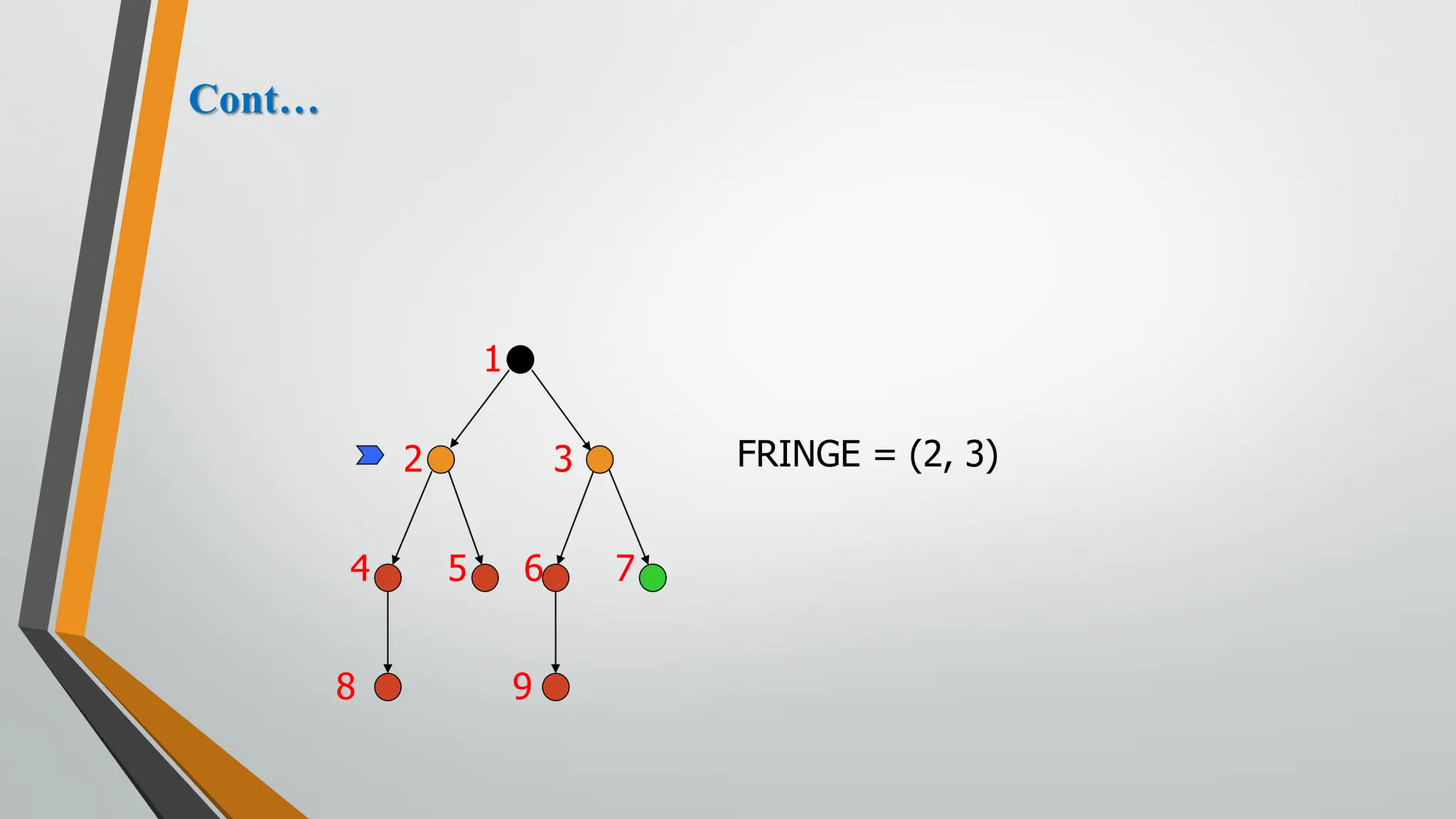
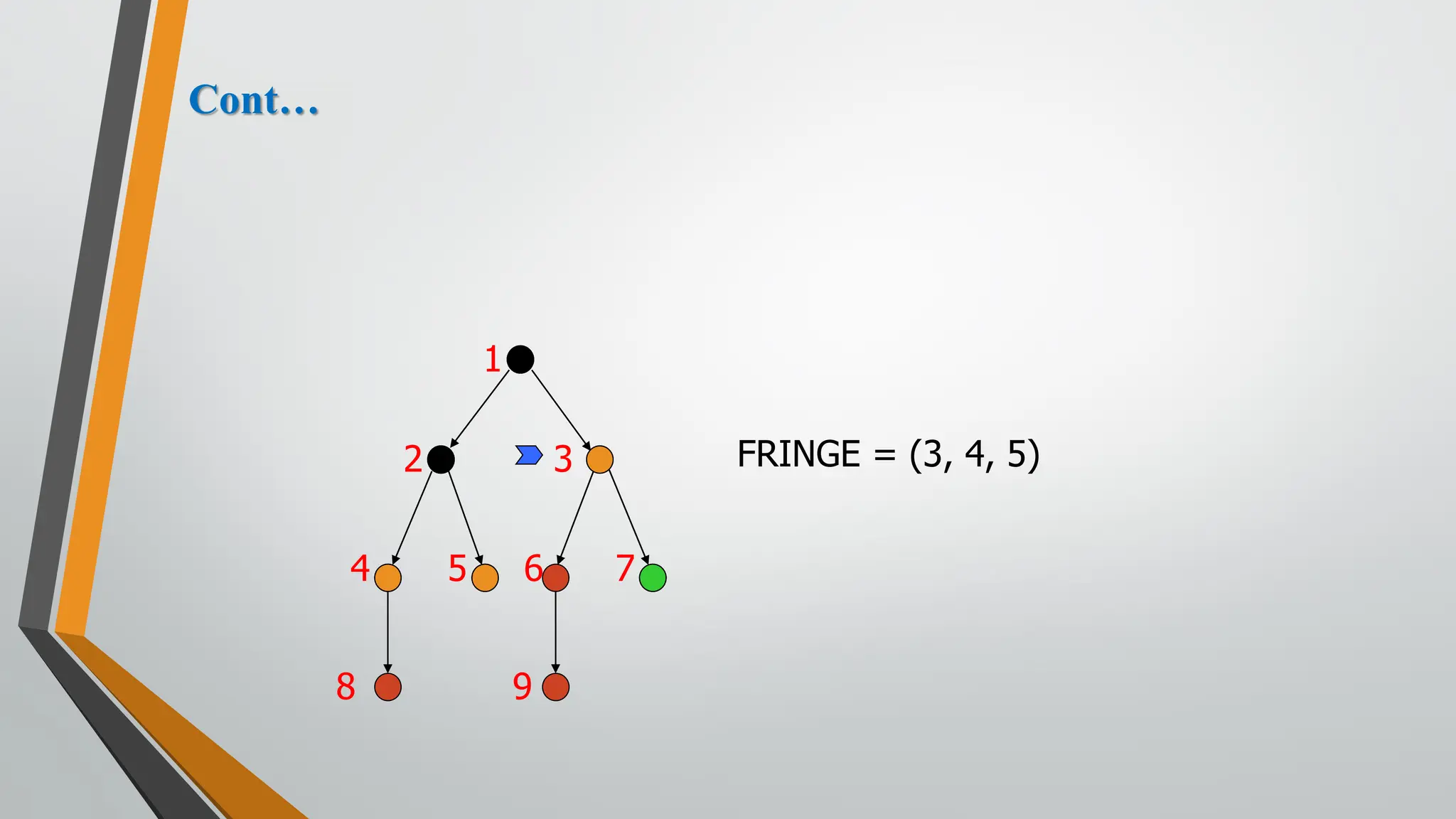
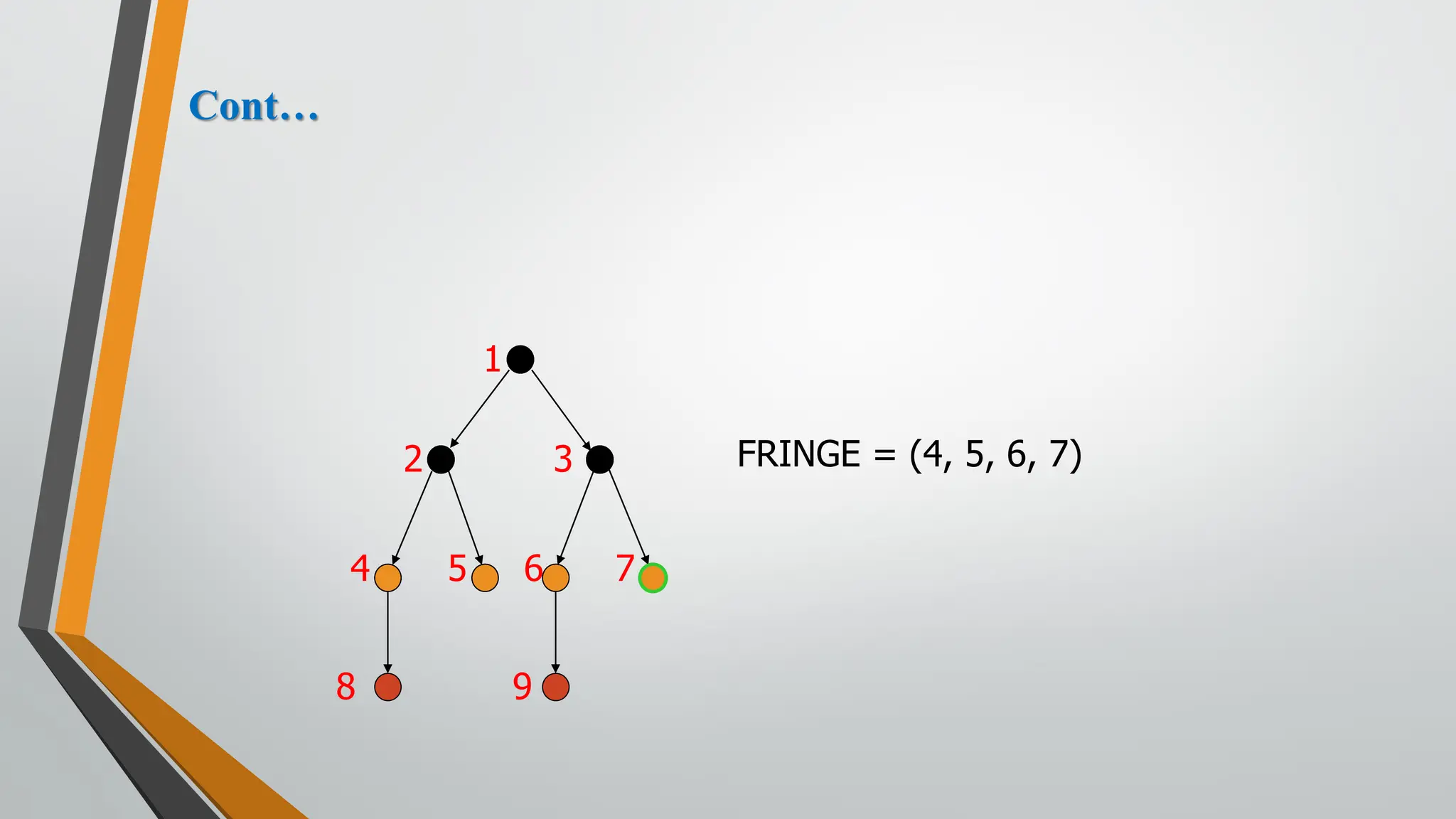
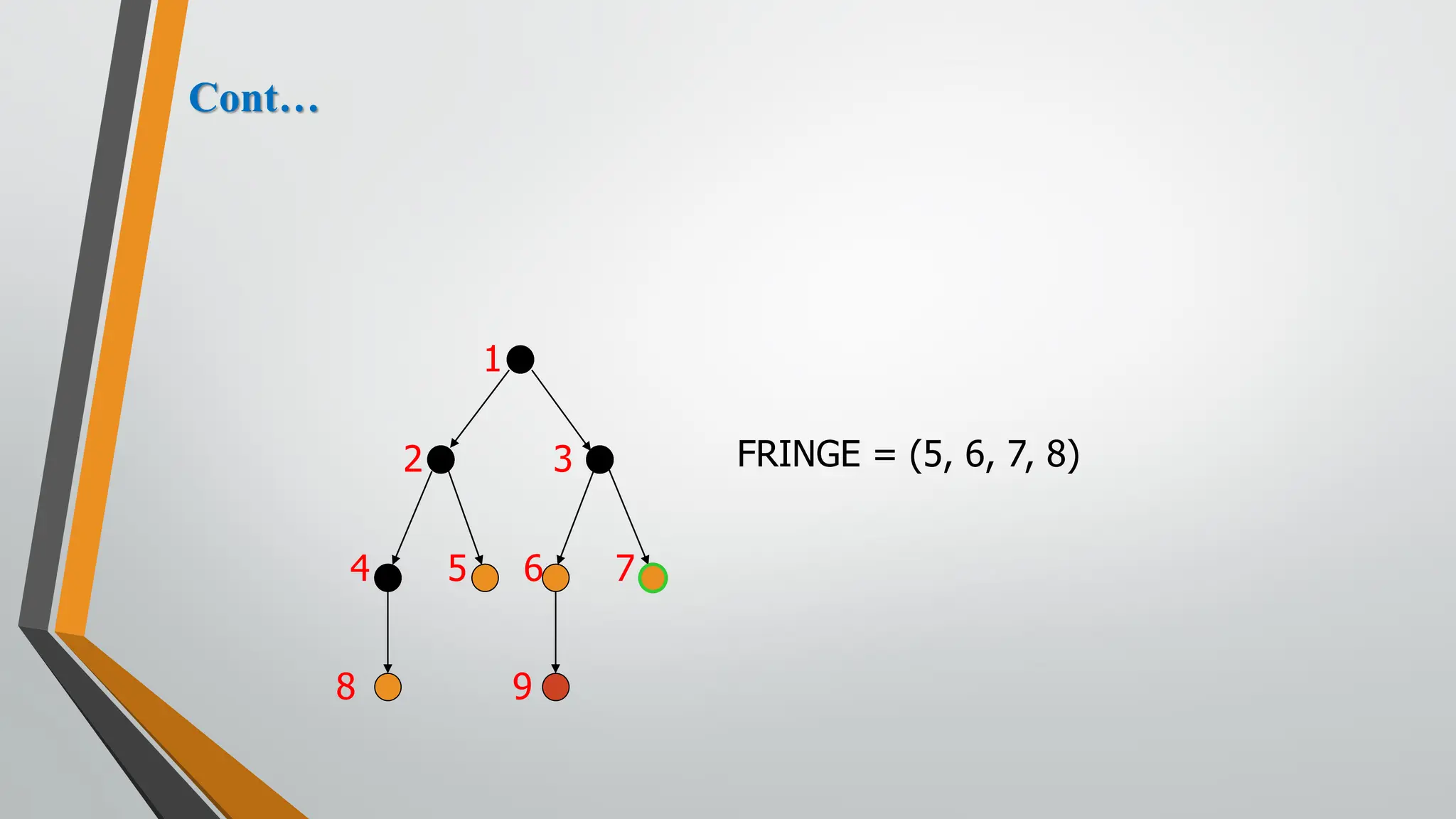
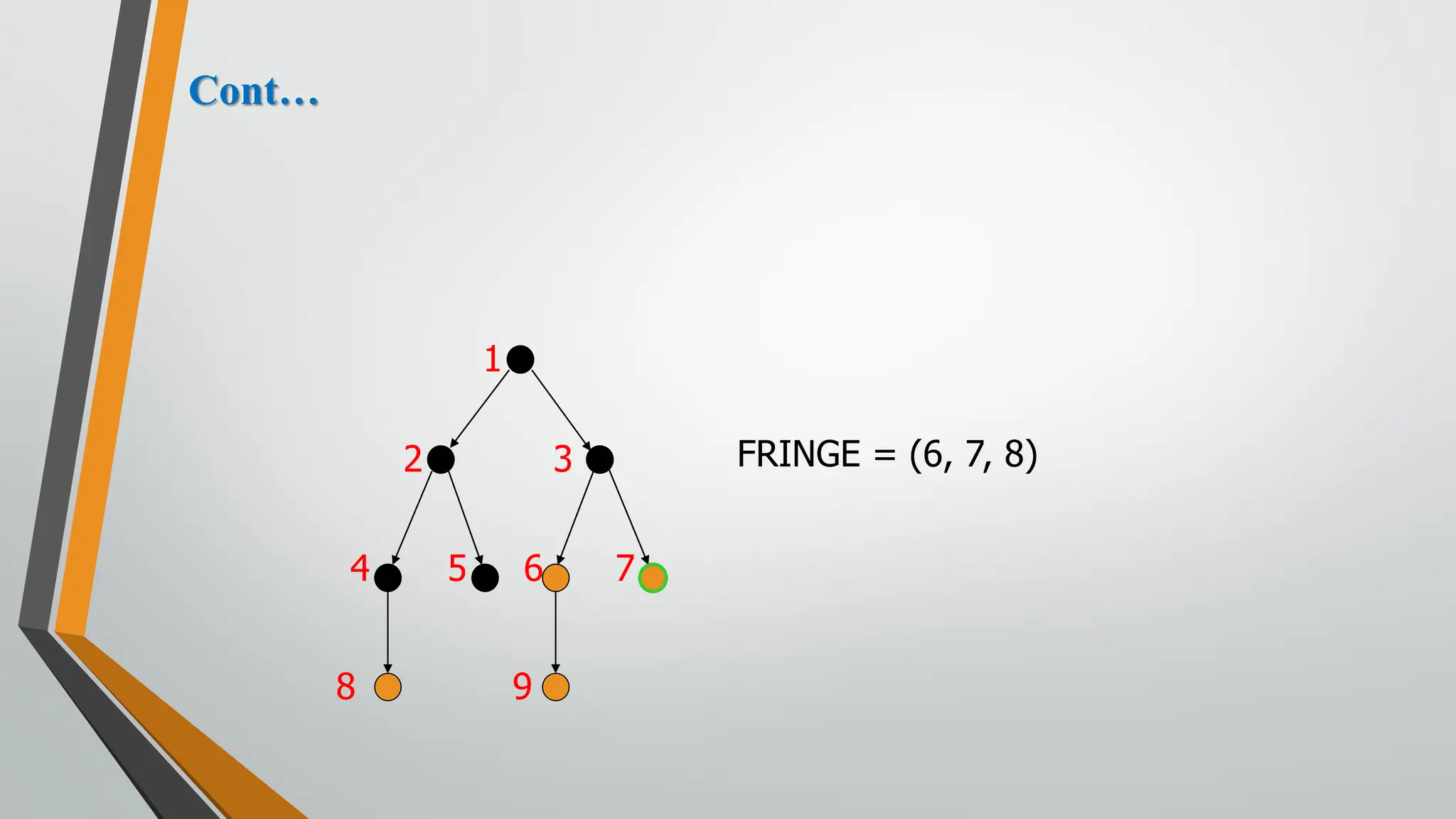
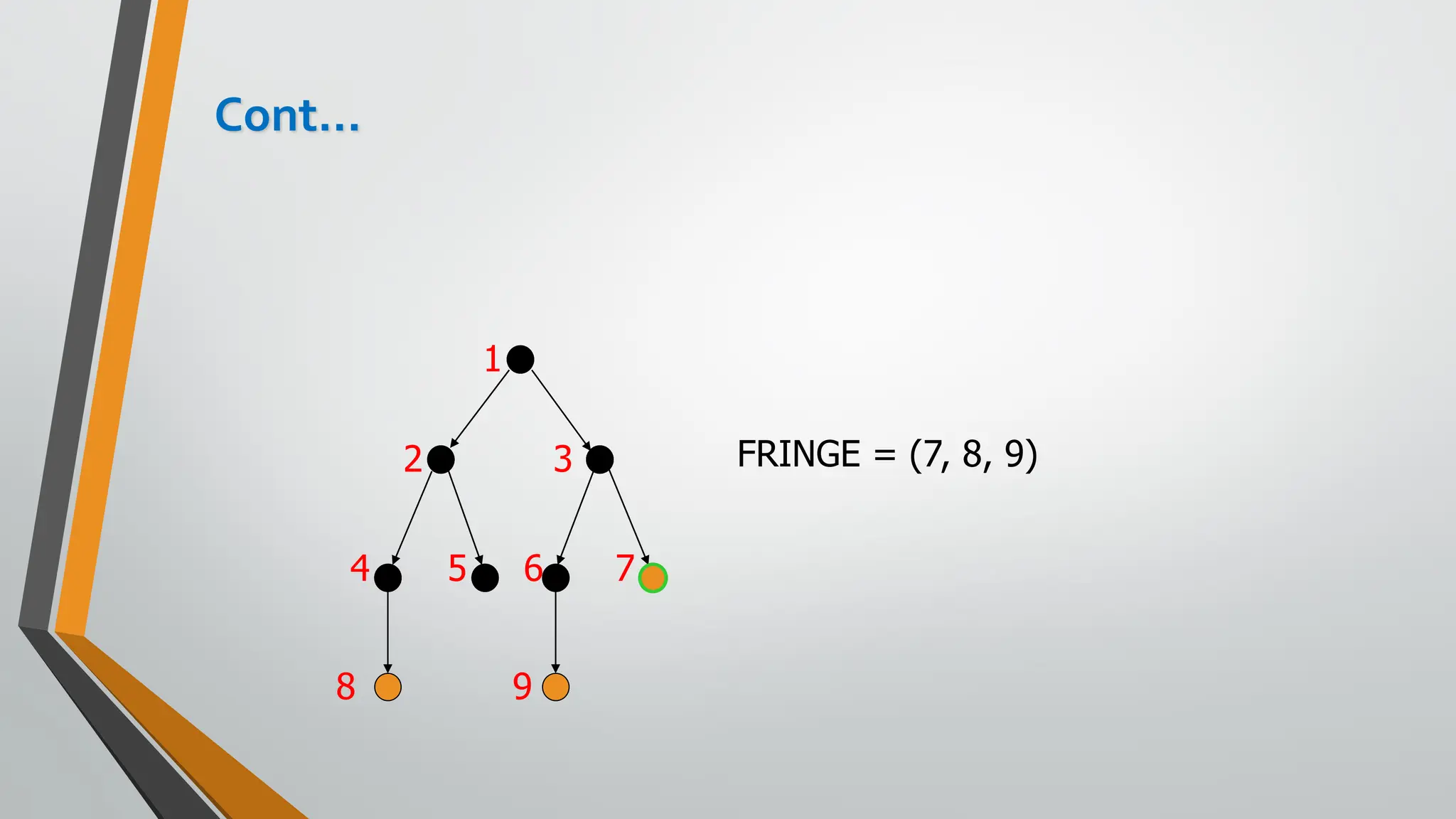
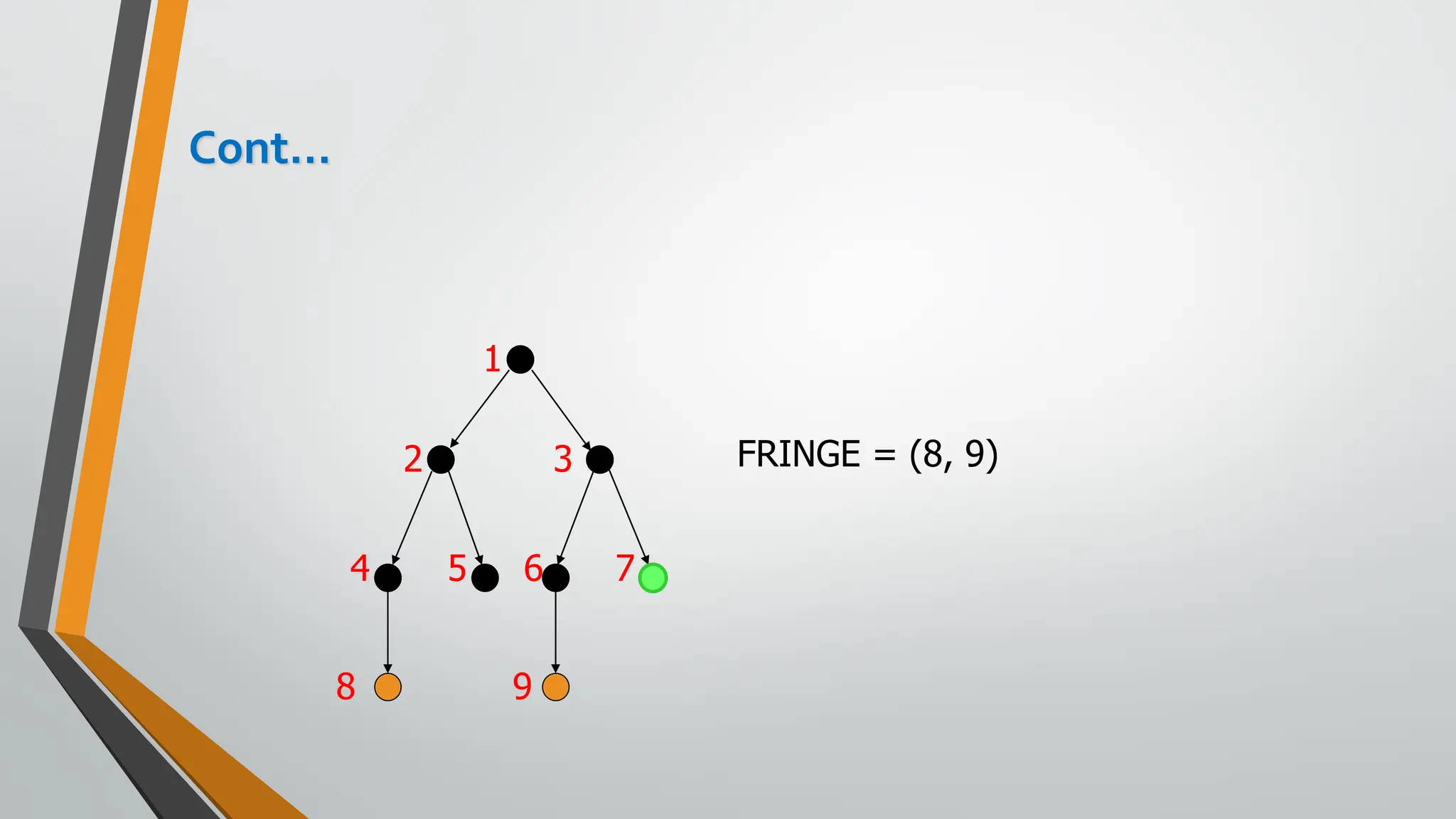
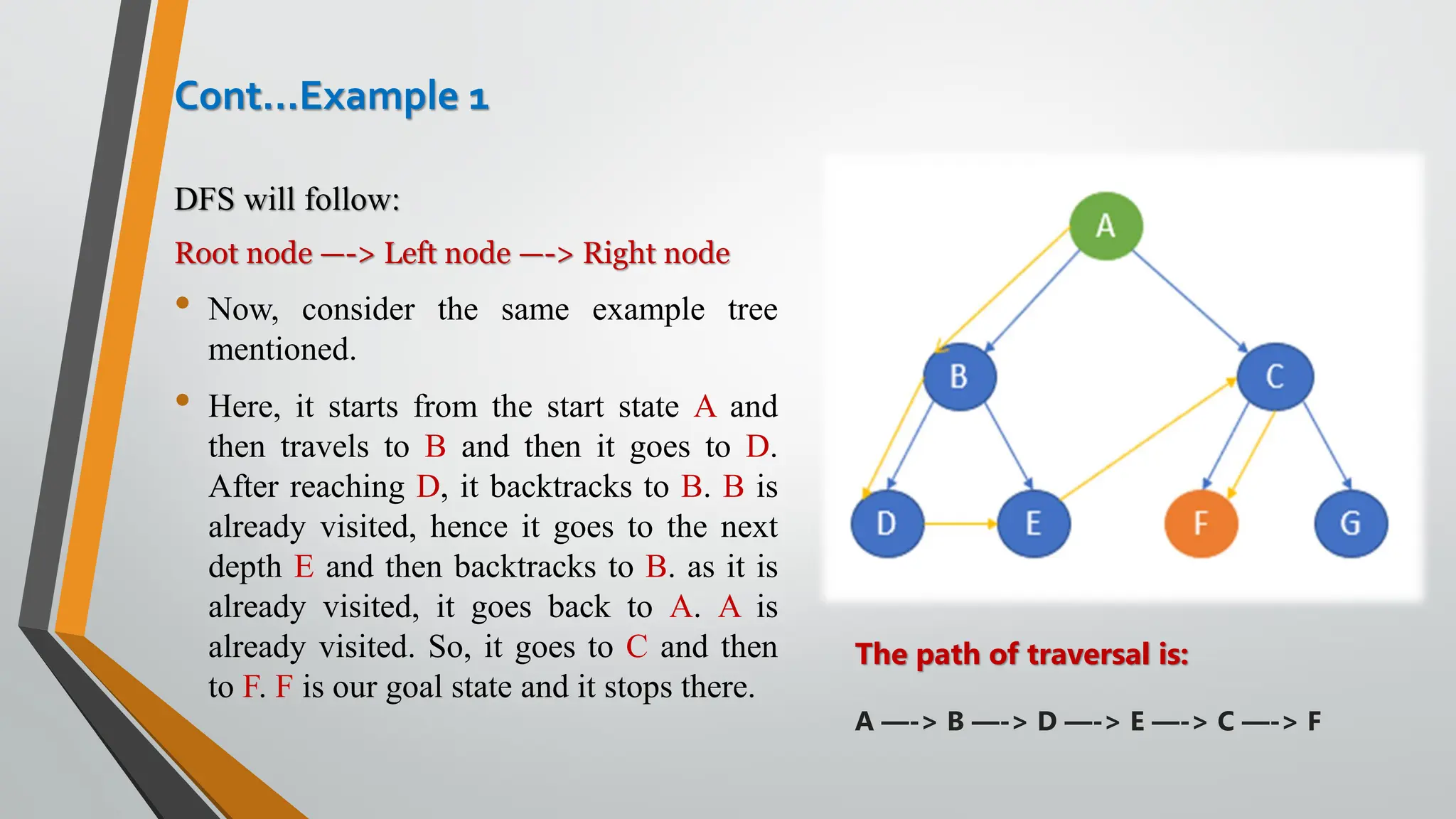
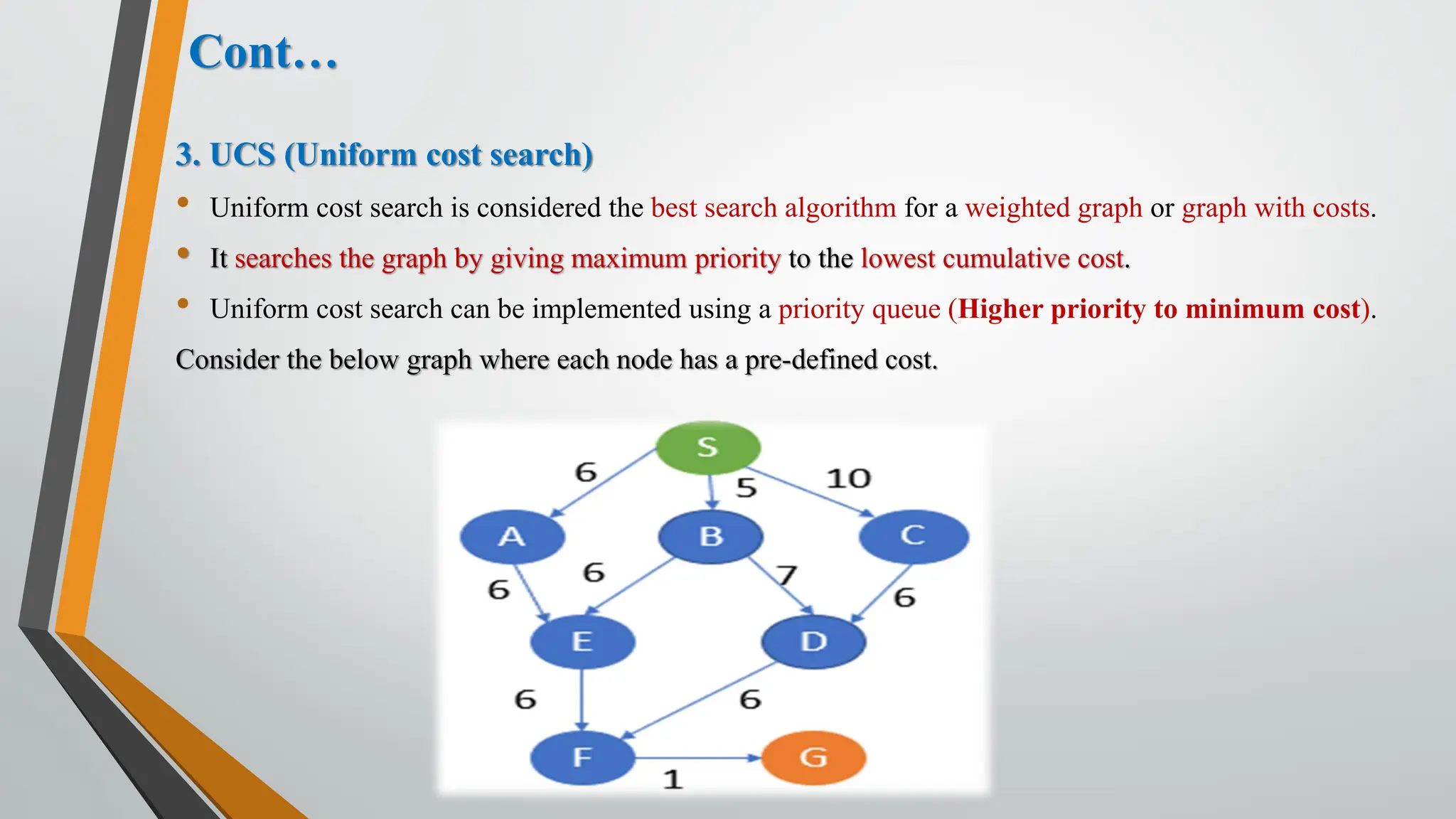
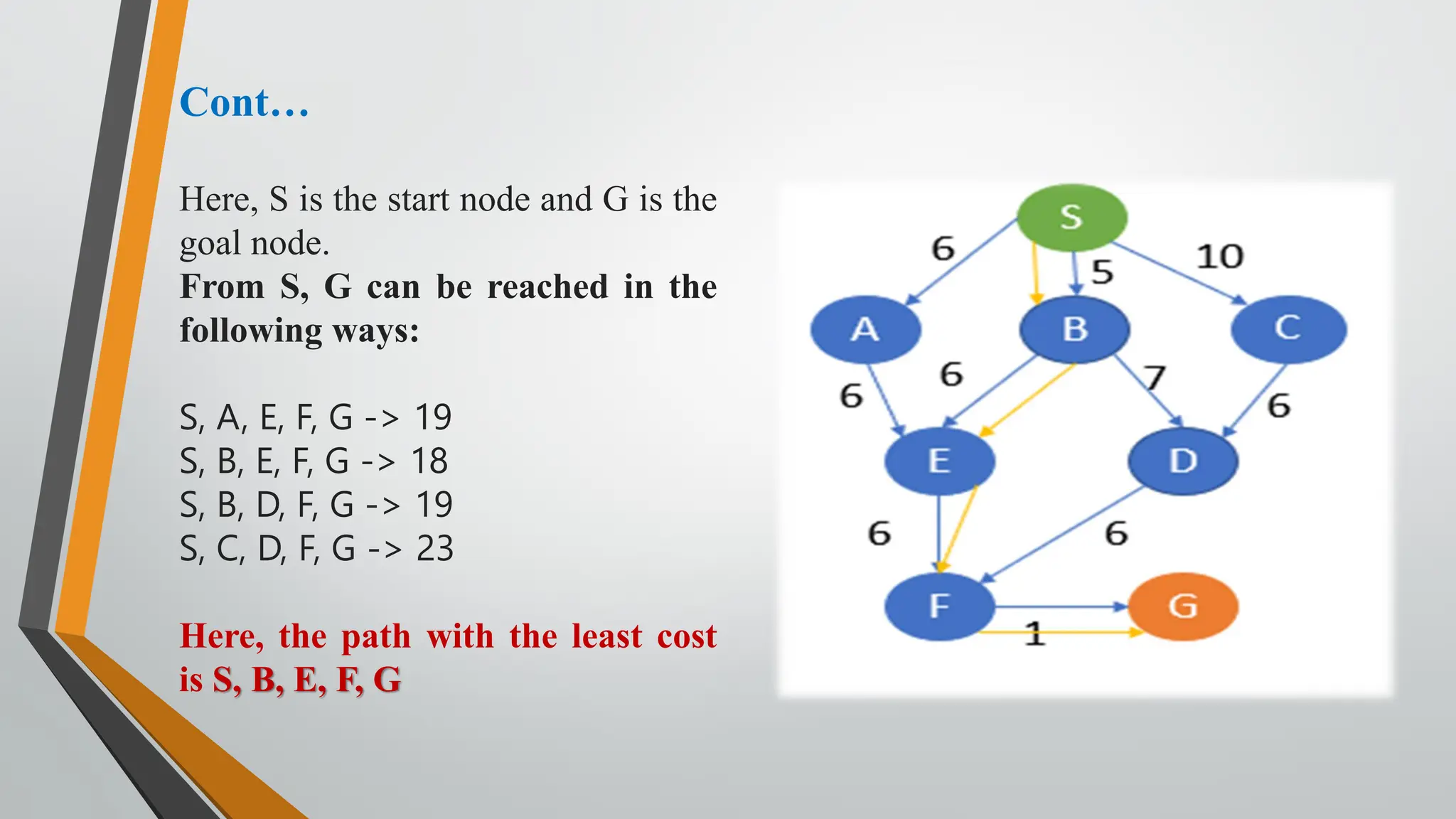
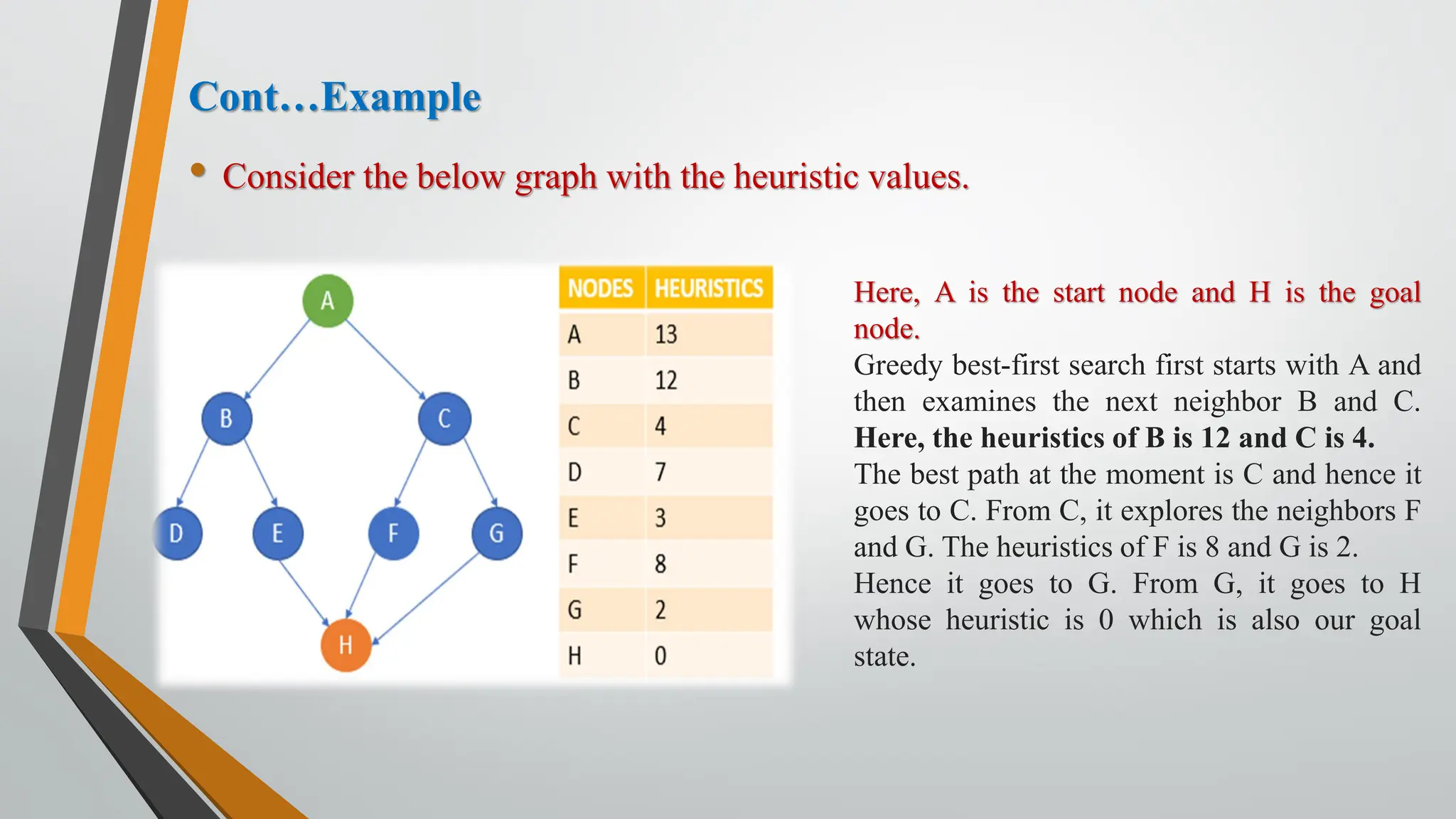
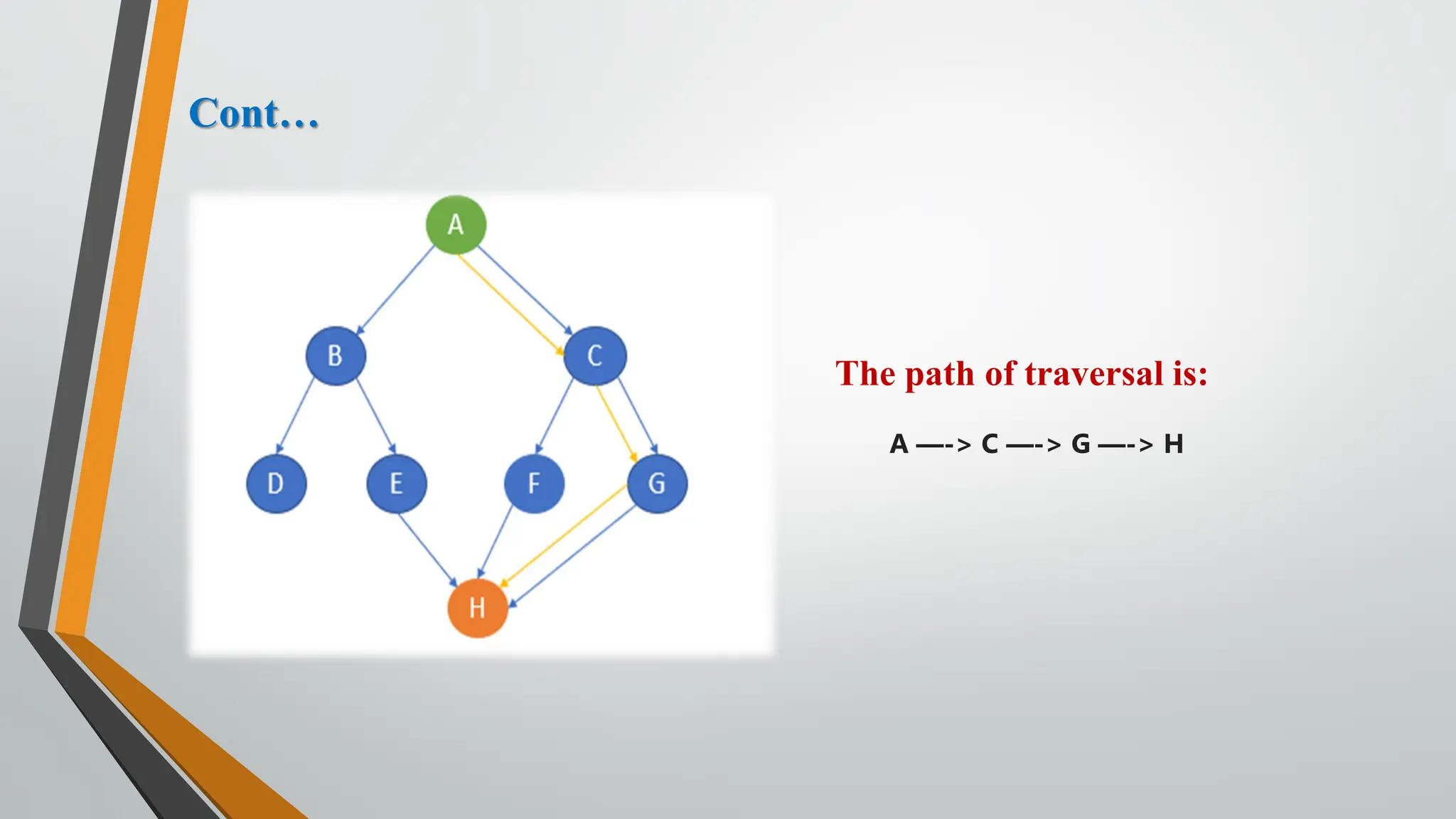
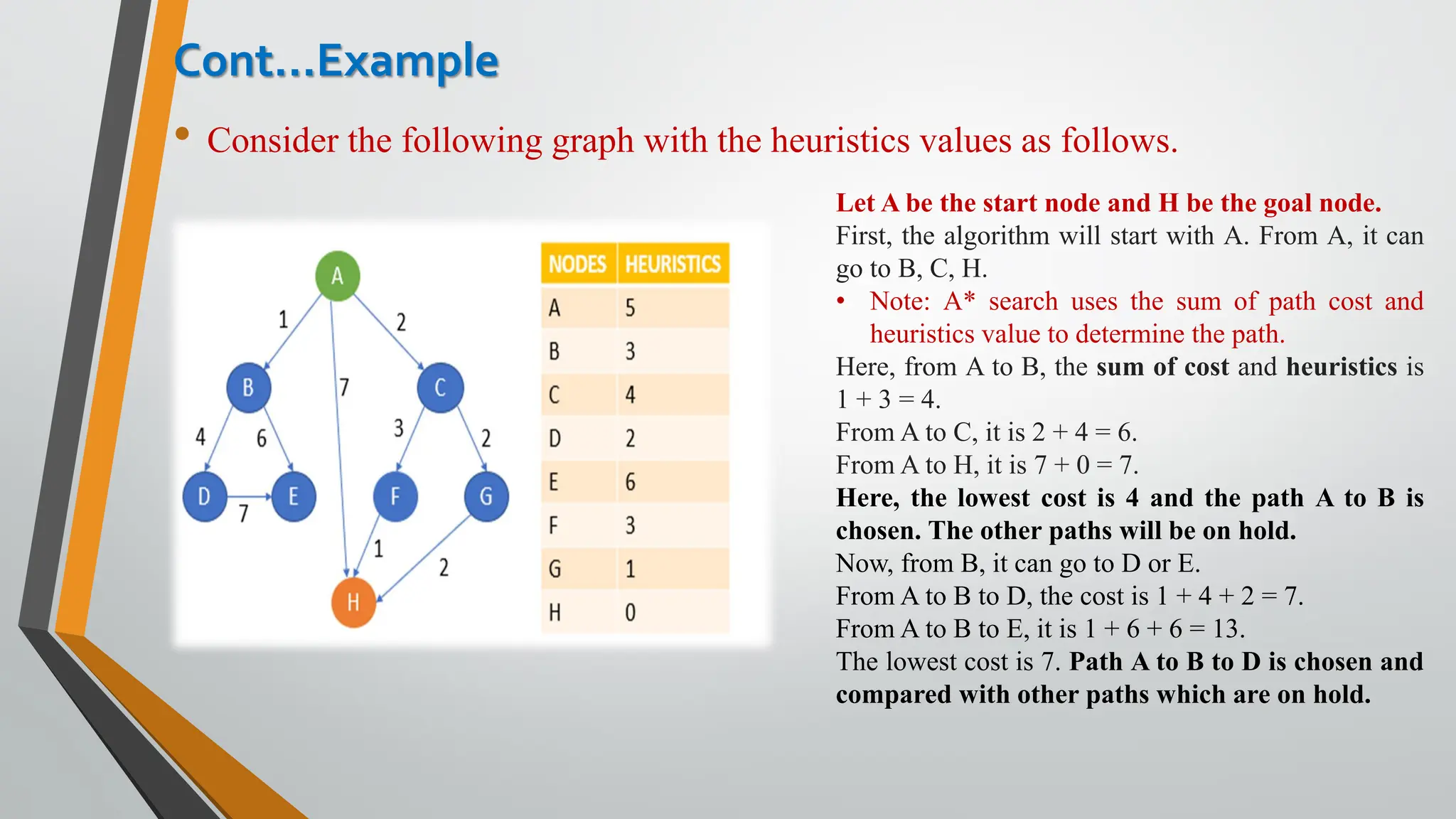
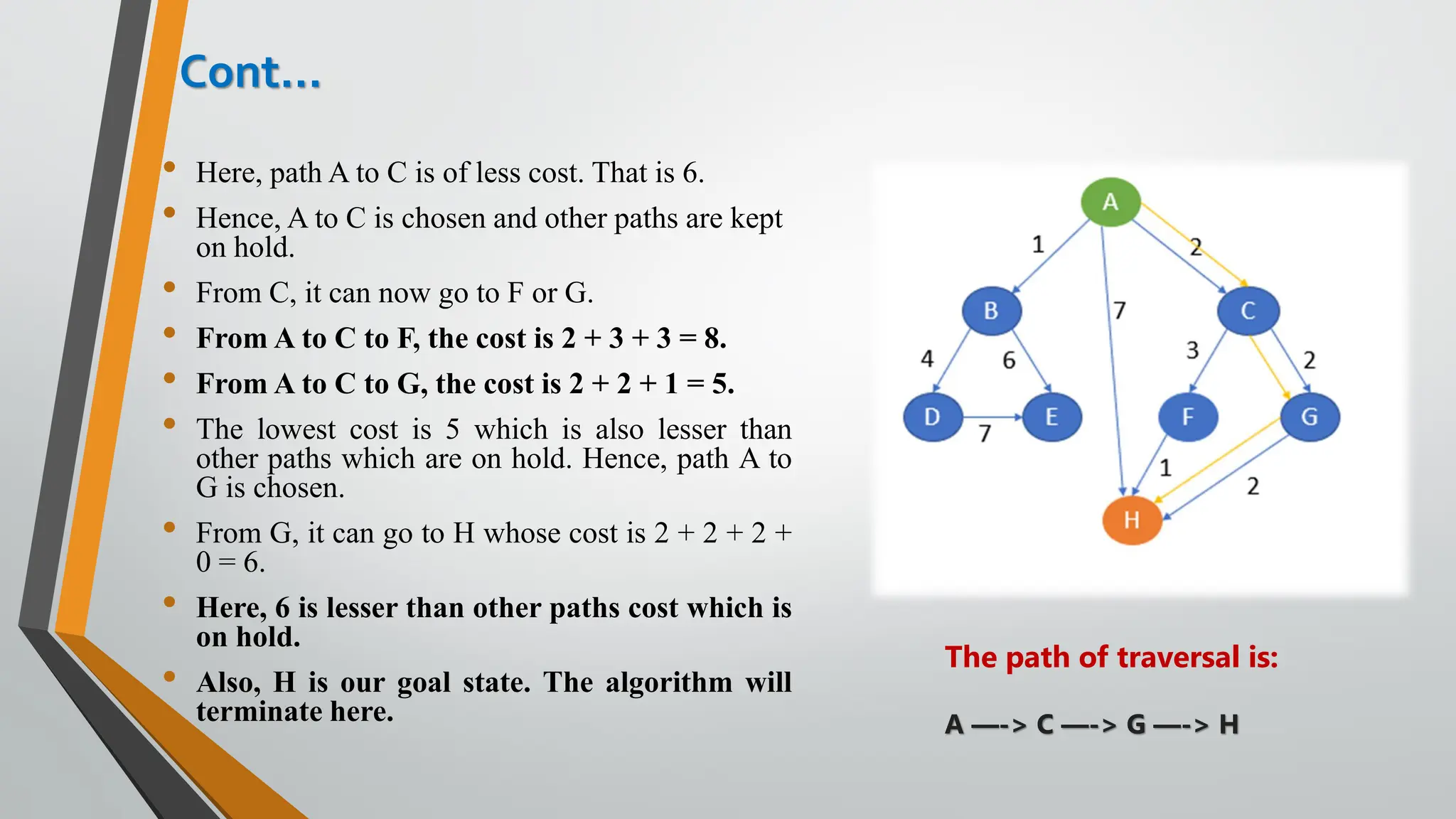
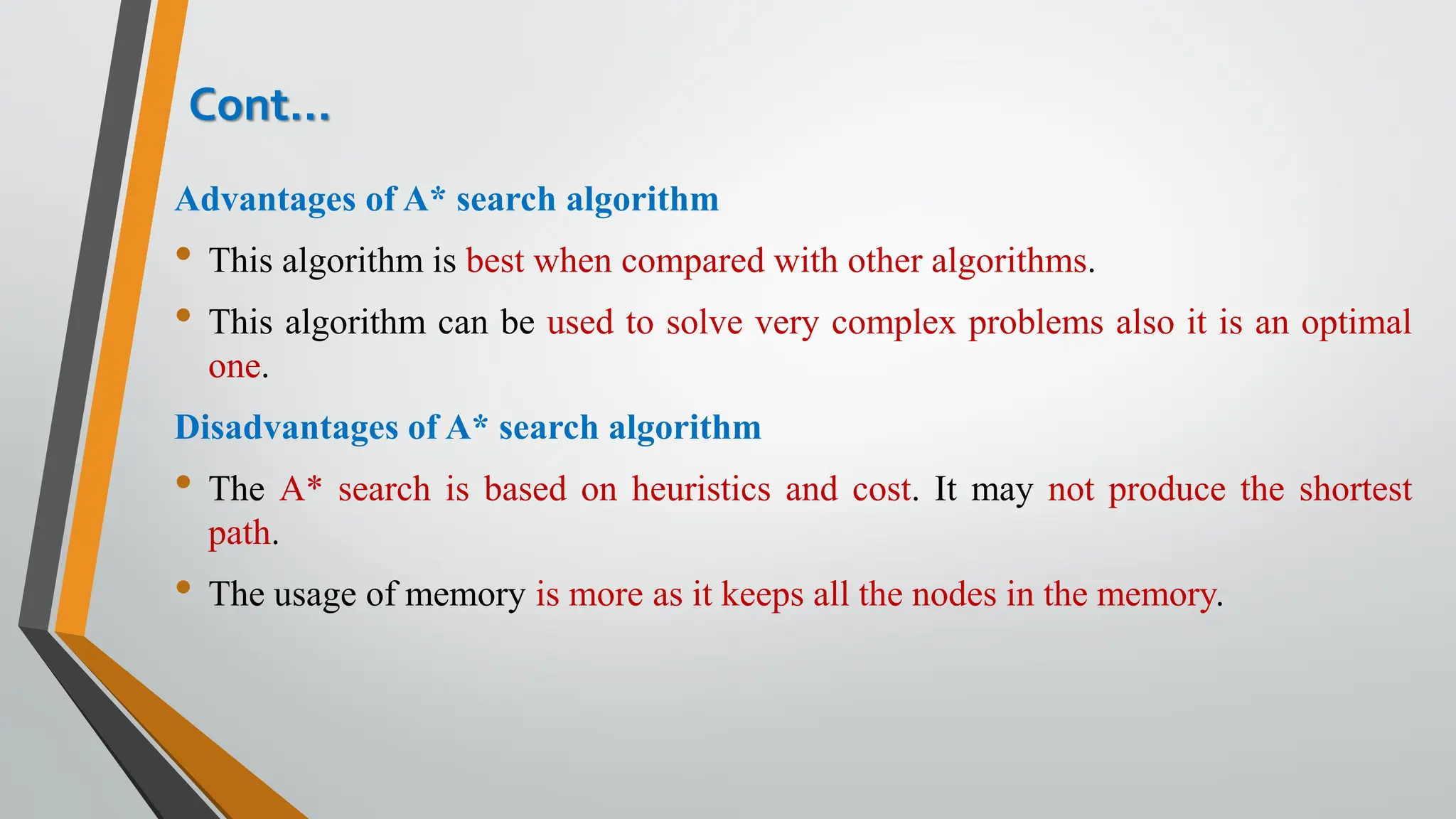
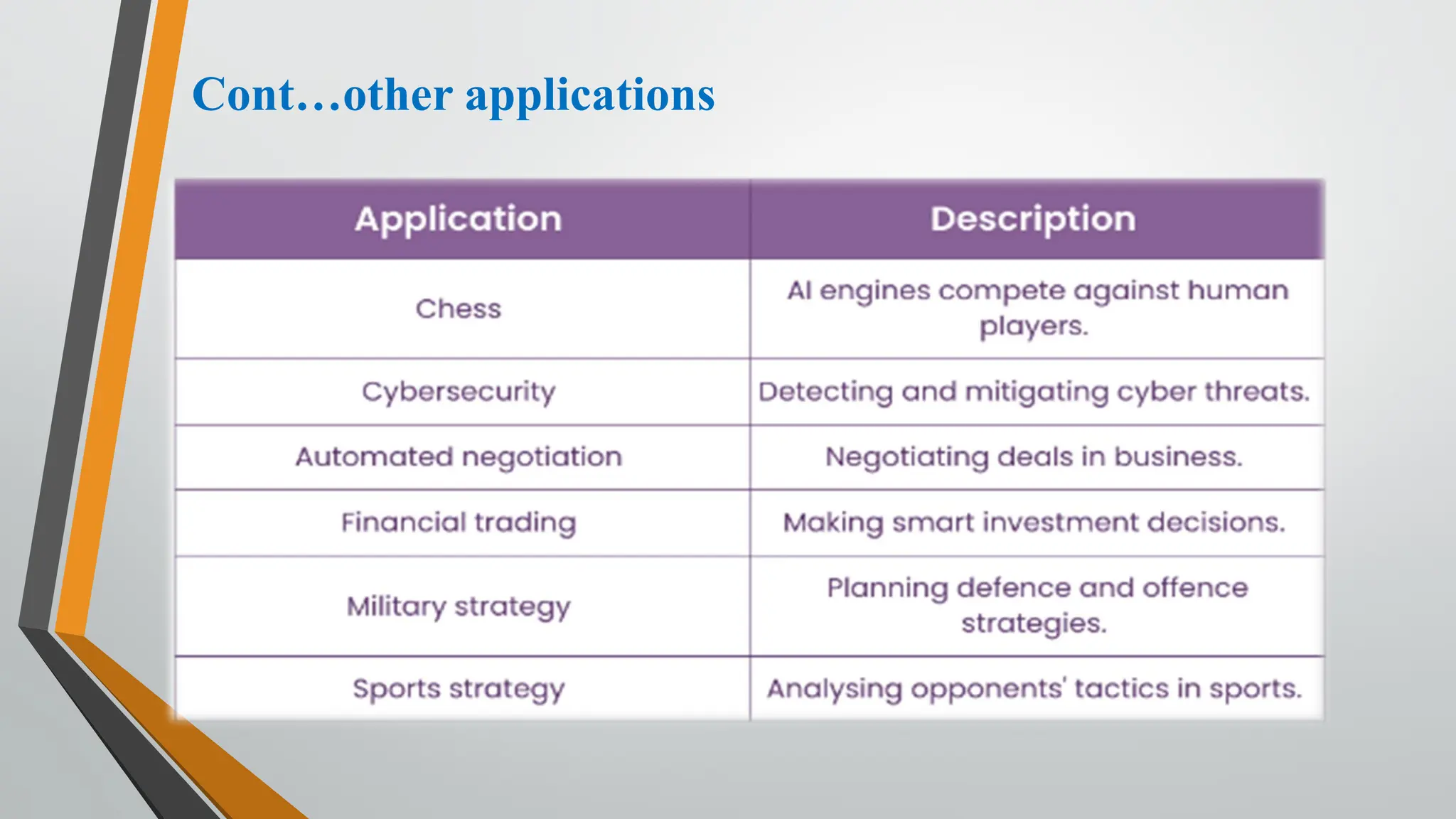
The document discusses problem-solving in artificial intelligence, focusing on the steps required to address challenges, such as problem definition, analysis, knowledge representation, and the execution of solutions. It outlines the importance of search algorithms, detailing various strategies like breadth-first search (BFS), depth-first search (DFS), and A* search, while distinguishing between uninformed and informed searches. Key concepts include state representation, path costs, and the properties of search algorithms, highlighting their applications and limitations in finding optimal solutions.